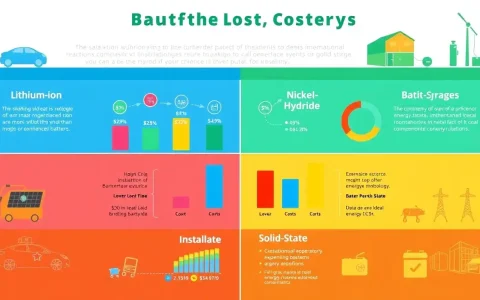
Which customers are energy storage customers?
Energy storage customers can be categorized into several distinct groups: 1. Commercial and Industrial Users, 2. Residential Consumers, 3. Utilities and Grid Operators, 4. Electric Vehicle Owners.
1. Commercial and Industrial Users represent a substantial portion of energy storage clientele. These businesses harness storage systems to mitigate peak demand charges, optimize energy usage, and increase operational resilience by ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
2. Residential Consumers increasingly seek energy storage solutions, predominantly driven by the desire for self-sufficiency and to capitalize on solar energy usage. Homeowners utilize storage systems to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use during peak hours or at night.
3. Utilities and Grid Operators are essential customers in this ecosystem. They implement energy storage to enhance grid stability, manage load fluctuations, and integrate renewable energy sources efficiently into the grid.
4. Electric Vehicle Owners are emerging as significant players in the energy storage market. EV batteries can serve as distributed storage units, enabling vehicle-to-grid technologies that facilitate energy exchange back to the grid.
1. COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL USERS
Energy storage systems have become pivotal assets for commercial and industrial users. These organizations face unique challenges related to energy consumption, often incurring high costs during peak load periods. Businesses can significantly lower costs by harnessing energy storage solutions for demand charge management; energy storage systems enable users to draw from stored energy during peak times rather than relying on expensive grid electricity.
Additionally, operational resilience is a critical concern for commercial and industrial consumers. Facilities often need a reliable power supply to maintain operations and avoid downtime due to outages. Energy storage systems provide an available backup power source, enabling these entities to sustain their operations during periods of grid disruption. This capability enhances operational reliability, particularly for companies in sectors like manufacturing, technology, and healthcare, where even short interruptions can lead to substantial financial losses.
Moreover, achieving environmental sustainability goals is increasingly vital for enterprises. Energy storage solutions facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into energy usage strategies. By capturing and storing energy generated from these sources, businesses can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, minimize their carbon footprint, and promote renewable energy adoption, contributing to a cleaner environment.
2. RESIDENTIAL CONSUMERS
The landscape of residential energy consumption is shifting rapidly, with homeowners now actively seeking energy storage options. One of the primary motivators for this shift lies in the desire for energy independence. By installing energy storage systems alongside solar panels, homeowners can store excess energy generated during daylight hours, making it available for use in the evening or during cloudy days, thereby reducing reliance on the grid.
Furthermore, financial incentives and decreasing technology costs have made residential energy storage more accessible. Government incentives and rebates promote solar energy systems, making it increasingly attractive for homeowners to invest in energy storage solutions. With falling battery prices and advancements in technology, energy storage systems have become more economically viable for the average consumer, encouraging widespread adoption.
Additionally, increasing concerns regarding energy reliability during extreme weather events often push homeowners toward energy storage systems. As grid outages become more frequent in some areas due to severe weather conditions, having a backup power system is an attractive option for many consumers. With a reliable energy storage solution, homeowners can ensure that essential appliances and systems continue functioning, safeguarding their livability during outages.
3. UTILITIES AND GRID OPERATORS
Utilities and grid operators play a significant role in the energy storage market as they look to enhance the functionality and reliability of their grids. Grid stability remains paramount, especially with increasing renewable energy integration, which often introduces variability and uncertainty in energy supply. Energy storage systems can help balance supply and demand, providing immediate power when generation dips or demand spikes.
Through frequency regulation and peak shaving, energy storage systems enable utilities to manage energy flows effectively. For instance, during periods of low demand, surplus energy can be stored for later use, optimizing resource allocation. This capability becomes increasingly critical as utilities transition toward more decentralized energy generation processes driven by renewables, further necessitating efficient storage solutions.
Moreover, investing in energy storage aligns with regulatory trends aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable energy sources. Many governing bodies set ambitious targets for grid decarbonization and clean energy adoption. Utilities, by implementing storage solutions, not only comply with these regulations but also build more resilient energy systems for a sustainable future, ultimately benefiting all consumers.
4. ELECTRIC VEHICLE OWNERS
Electric vehicle (EV) owners are emerging as an important demographic in the energy storage market. The relationship between EVs and energy storage revolves around the innovative concept of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. This technology allows EV owners to store energy in their vehicle batteries and, when directed, send that energy back to the grid, creating a two-way energy flow that contributes to grid stability.
As EV adoption continues to rise, so does the potential impact on energy storage needs. EV owners can leverage their car batteries to balance home energy use by charging their vehicles during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, and discharging energy into their homes or the grid during peak times. This not only enhances energy efficiency but also provides additional revenue opportunities for homeowners as they effectively monetize their storage capabilities.
Moreover, public infrastructure and charging stations are evolving to incorporate energy storage solutions in tandem with EV charging. Innovative charging stations installed at public locations can utilize battery storage to manage rapid charging for users while minimizing grid stress. These stations can store excess renewable energy during off-peak hours to supply EVs during peak demand, promoting an integrated energy ecosystem.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF ENERGY STORAGE
When evaluating energy storage solutions, their environmental impact becomes a focal point, especially in a world grappling with climate change. Leading energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, have varying ecological footprints. While lithium-ion batteries facilitate high energy density and efficiency, their mining processes for materials can contribute to environmental degradation if not conducted sustainably.
To combat this issue, the industry is witnessing an uptick in research and development of sustainable battery technologies. Alternatives such as solid-state batteries and organic flow batteries aim to reduce reliance on harmful materials and minimize waste, paving the way for a greener future. The success and proliferation of these advancements will hinge on industry collaboration, innovation, and rigorous standards for environmental responsibility.
Additionally, recycling programs for energy storage systems are increasingly crucial. As energy storage technologies become more mainstream, the corresponding need to address end-of-life disposal arises. Establishing robust recycling initiatives ensures that valuable materials are recovered and reused, contributing to a circular economy while mitigating harmful waste.
FAQs
WHAT IS ENERGY STORAGE, AND HOW DOES IT WORK?
Energy storage refers to the process of capturing energy produced at one time for use at a later time. Various technologies facilitate this process, with batteries being the most commonly recognized form. When energy is generated, it is converted into stored energy through chemical or physical means, such as charging a battery or compressing air. When the stored energy is needed, it is converted back into usable electricity, providing power to homes, businesses, or the grid as required. This ability to store and release energy efficiently plays a vital role in enhancing energy management, ensuring that supply meets the demand, particularly during peak hours or in the event of grid outages.
HOW CAN INSTALLING ENERGY STORAGE BENEFIT MY BUSINESS?
The adoption of energy storage can yield numerous advantages for businesses. Primarily, it offers cost savings through demand charge reduction, as companies can draw energy from their stored resources during peak pricing intervals. This capability optimizes energy use, reducing overall electricity bills. Furthermore, energy storage systems provide operational continuity, essential for avoiding disruptions that can arise from power outages. Additionally, they enable businesses to bolster sustainability initiatives by integrating renewable energy sources into their operations, showcasing a commitment to environmentally responsible practices. This combination of financial savings, reliability, and sustainability makes energy storage a strategic investment for forward-thinking enterprises.
ARE THERE GOVERNMENT INCENTIVES FOR ENERGY STORAGE INSTALLATIONS?
Yes, many governments recognize the importance of energy storage technologies and offer a range of incentives to promote their adoption. These incentives may include tax credits, rebates, or grants for businesses and homeowners installing energy storage systems. Specific programs often align with renewable energy initiatives, effectively promoting solar energy installations alongside storage solutions. By leveraging these financial incentives, customers can offset initial installation costs, encouraging broader acceptance of energy storage technologies. It is essential for potential customers to research local and federal programs to maximize the financial benefits available in their specific regions.
In summary, energy storage customers encompass a diverse array of sectors, each contributing to the burgeoning market significantly. From commercial and industrial users aiming to cut costs and enhance operational reliability to residential consumers converted to renewable energy enthusiasts, the landscape is richly varied. Utilities embrace energy storage to ensure grid stability against a backdrop of changing energy sources, while electric vehicle owners engage with emerging technologies that create synergies between transportation and energy networks. As the landscape continues to evolve, innovations in energy storage technologies are likely to shape the future of energy management and consumption across the globe.
Investing in energy storage solutions presents numerous opportunities across various sectors. As the energy market transitions toward a more decentralized and renewable-centric model, the importance of energy storage is becoming even more pertinent. Emerging technologies continue to enhance operational efficiencies and sustainability, attracting an increasing number of customers. Businesses, homeowners, utilities, and electric vehicle owners all contribute to this dynamic ecosystem, propelling advancements that promote renewables, stability, and grid resilience. Energy storage will play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy systems, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and reliable energy landscape. Firms seeking to capitalize on these developments should remain vigilant in monitoring trends and technologies that position them favorably within this evolving marketplace. Engaging with energy storage solutions not only meets current needs but also lays the groundwork for future advancements in the energy sector, as stakeholders align with global sustainability efforts.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/which-customers-are-energy-storage-customers/