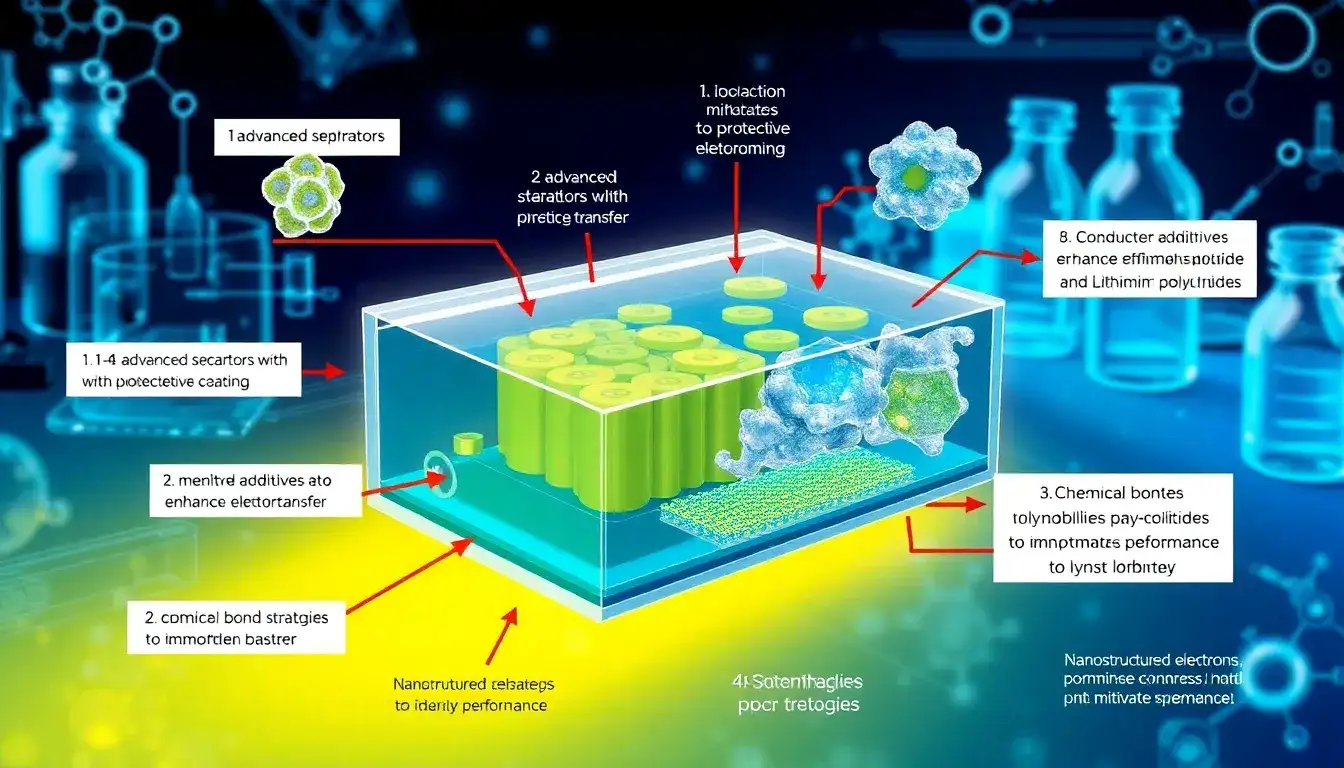
Strategies proposed to mitigate polysulfide shuttling in lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries focus on preventing the dissolution, migration, and unwanted reactions of soluble lithium polysulfides (LiPSs), which degrade battery performance and cycle life. Key approaches include:
1. Functional Protective Layers on Anode and Cathode
- A conductive, flexible polymer composite layer applied on the lithium anode, such as one containing polyaniline and functionalized graphite, can effectively reduce polysulfide dissolution and shuttle effect by capturing polysulfides and reducing lithium ion dissolution. This layer also prevents overcharge caused by polysulfide migration.
- Composite coatings like V2O5 combined with polypyrrole (PPy) have been shown to block the bidirectional movement of polysulfides, enhancing battery stability.
2. Use of Solid-State Electrolytes
- Solid-state electrolytes physically block polysulfide diffusion through the electrolyte, mitigating the shuttle effect while also enhancing safety by eliminating flammable liquid electrolytes.
3. Functional Separators and Cathode Engineering
- Designing separators with functional groups or coatings that trap or repel polysulfides to block their migration from the cathode to the anode.
- Incorporating materials in the sulfur cathode that strongly bind polysulfides, such as porous carbons, metal oxides, or conductive polymers, to reduce polysulfide dissolution into the electrolyte.
4. Electrolyte Additives
- Introducing specially designed electrolyte additives that interact favorably with sulfur species to form a stable interface at the cathode-electrolyte boundary. These additives control reactions to suppress polysulfide solubility and improve lithium ion transport, enhancing cycling performance.
Summary Table of Strategies
| Strategy | Mechanism | Example Materials/Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer composite anode layers | Captures polysulfides, reduces lithium ion loss | Polyaniline + functionalized graphite |
| Solid-state electrolytes | Physical barrier to polysulfide diffusion | Ceramic or polymer-based solid electrolytes |
| Functional separators | Block polysulfide shuttle via selective adsorption or repulsion | Coated membranes with metal oxides or conductive polymers |
| Sulfur cathode modification | Binding polysulfides to reduce dissolution | Porous carbons, metal oxides, conductive polymers |
| Electrolyte additives | Stabilizes cathode interface, controls polysulfide chemistry | Novel additives compatible with sulfur cathode |
These strategies collectively aim to suppress the polysulfide shuttle by capturing or immobilizing polysulfides, physically blocking their migration, or chemically stabilizing the electrolyte interface, thereby enhancing the lifespan and performance of Li-S batteries.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-strategies-are-being-proposed-to-mitigate-polysulfide-shuttling-in-lithium-sulfur-batteries/


