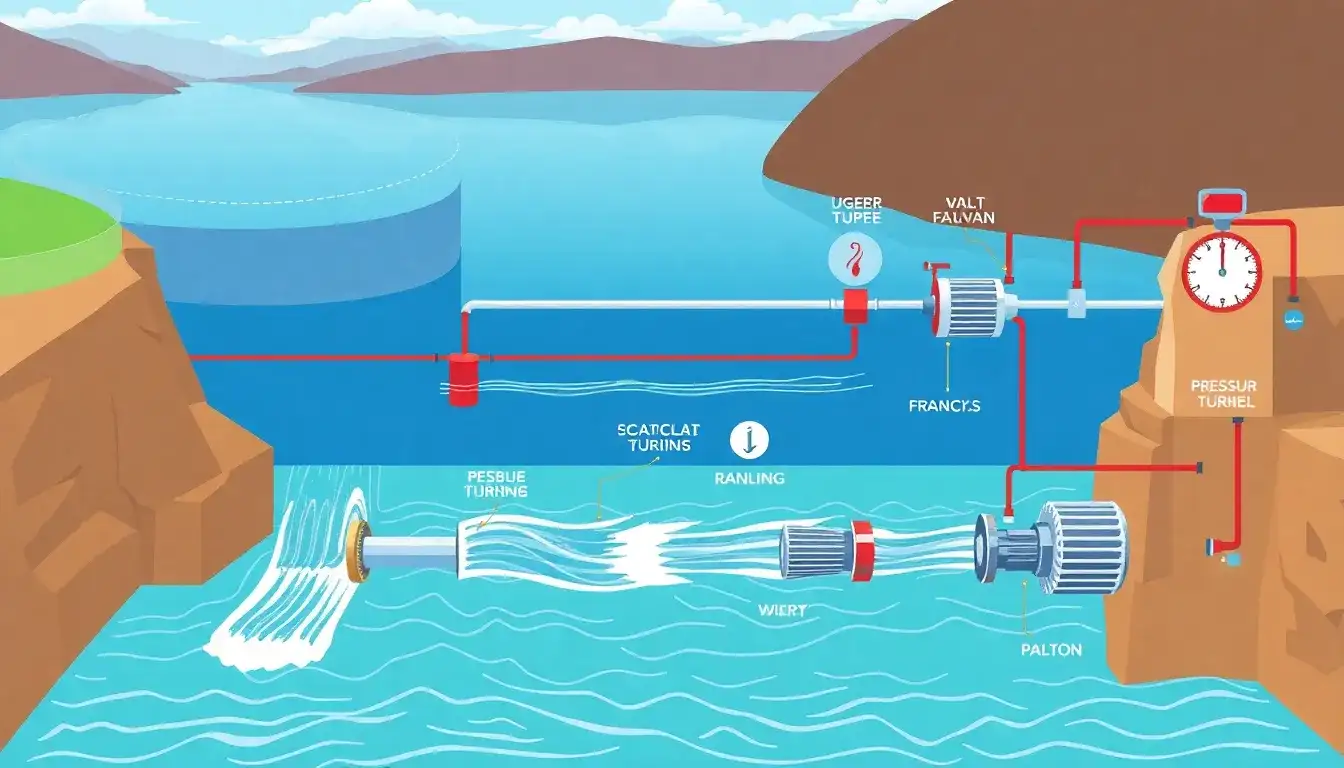
Pumped hydroelectric energy storage systems rely heavily on reversible Francis turbines for their operational efficiency and response characteristics. Here’s how turbine type impacts response time:
- Reversible turbine design:
Francis turbines (the most commonly used) allow a single unit to act as both pump and turbine through directional rotation and flow control. This eliminates the need to switch between separate pump/turbine systems, enabling faster mode transitions. - Grid response capabilities:
- Frequency stabilization: Reversible turbine-generators detect grid frequency deviations and respond in seconds, adjusting power output by releasing water through the turbine.
- Ancillary services: They provide spinning reserve (ready-to-deploy capacity) and black start capability (restarting dead grids) due to immediate mechanical energy conversion.
- Variable speed operation:
Modern systems use adjustable-speed turbines that optimize energy conversion efficiency in both pumping and generation modes. While this primarily affects round-trip efficiency, precise speed control enhances the ability to match grid demands rapidly.
For comparison:
| Feature | Francis Turbines | Impulse Turbines |
|---|---|---|
| Role in PSH | Primary choice due to reversibility | Rarely used |
| Response Time | Seconds to minutes | N/A (unsuitable for PSH) |
The turbine’s reversibility and hydraulic design enable sub-minute response times for ancillary grid services, making Francis turbines crucial for fast-reacting energy storage. Pumped storage plants using these turbines can transition from standby to full generation in <2 minutes.
While the source doesn’t specify exact transition times, industry standards for modern PSH plants using Francis turbines typically achieve 1-2 minute response times for grid services, as referenced in general hydropower literature. The cited source confirms the operational principles enabling this capability.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-role-does-the-type-of-turbine-used-play-in-the-response-time-of-pumped-hydroelectric-energy-storage/


