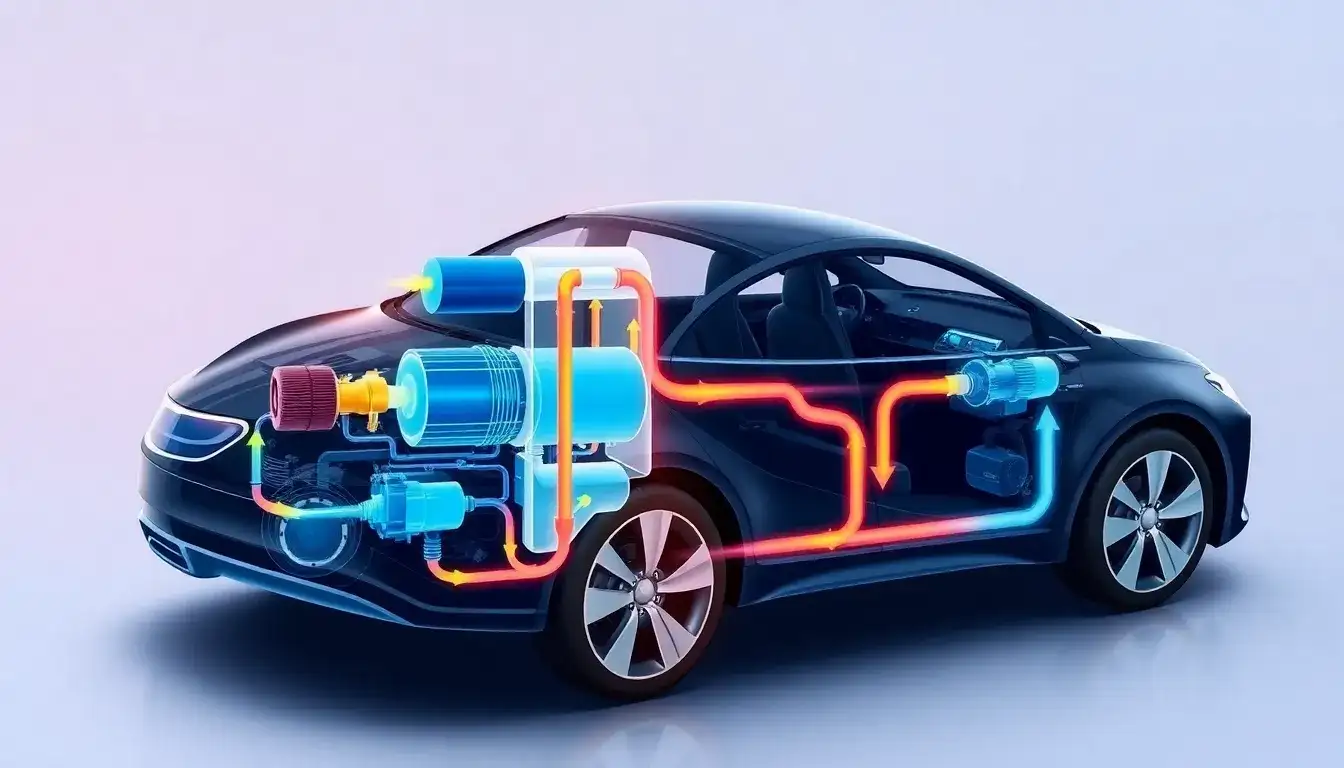
The refrigerant loop plays a crucial role in the thermal management of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in maintaining optimal temperatures for the batteries and cabin. Here are some key aspects of its function:
Key Components and Functions
- Components: The refrigerant loop typically includes a compressor, condenser, liquid receiver, expansion valves, a chiller, and an evaporator.
- Cooling in Cold Loop Mode: In cold weather, the refrigerant loop cools the cabin air and the batteries. The chiller is used to cool the coolant, which in turn cools the batteries, while the evaporator cools the cabin air.
- Heating in Heat Pump Mode: In heat pump mode, the refrigerant loop can heat the cabin by passing the refrigerant through an inner condenser to warm the cabin air.
- Active vs. Passive Cooling: The refrigerant loop is part of an active cooling system where the chiller rejects heat from the coolant to the refrigerant. This heat is then dissipated to the ambient air through a condenser, which is enhanced by fans to increase airflow.
Importance in EV Thermal Management
- Temperature Regulation: It helps maintain the batteries and power electronics within safe operational temperatures, ensuring efficiency and longevity.
- Adaptability: The refrigerant loop’s ability to switch between cooling and heating modes (cold loop and heat pump modes) allows it to adapt to various environmental conditions, improving vehicle performance across different climates.
Overall, the refrigerant loop is essential for managing both the cabin temperature and the battery temperature, ensuring that the electric vehicle operates efficiently under all conditions.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-role-does-the-refrigerant-loop-play-in-ev-thermal-management/


