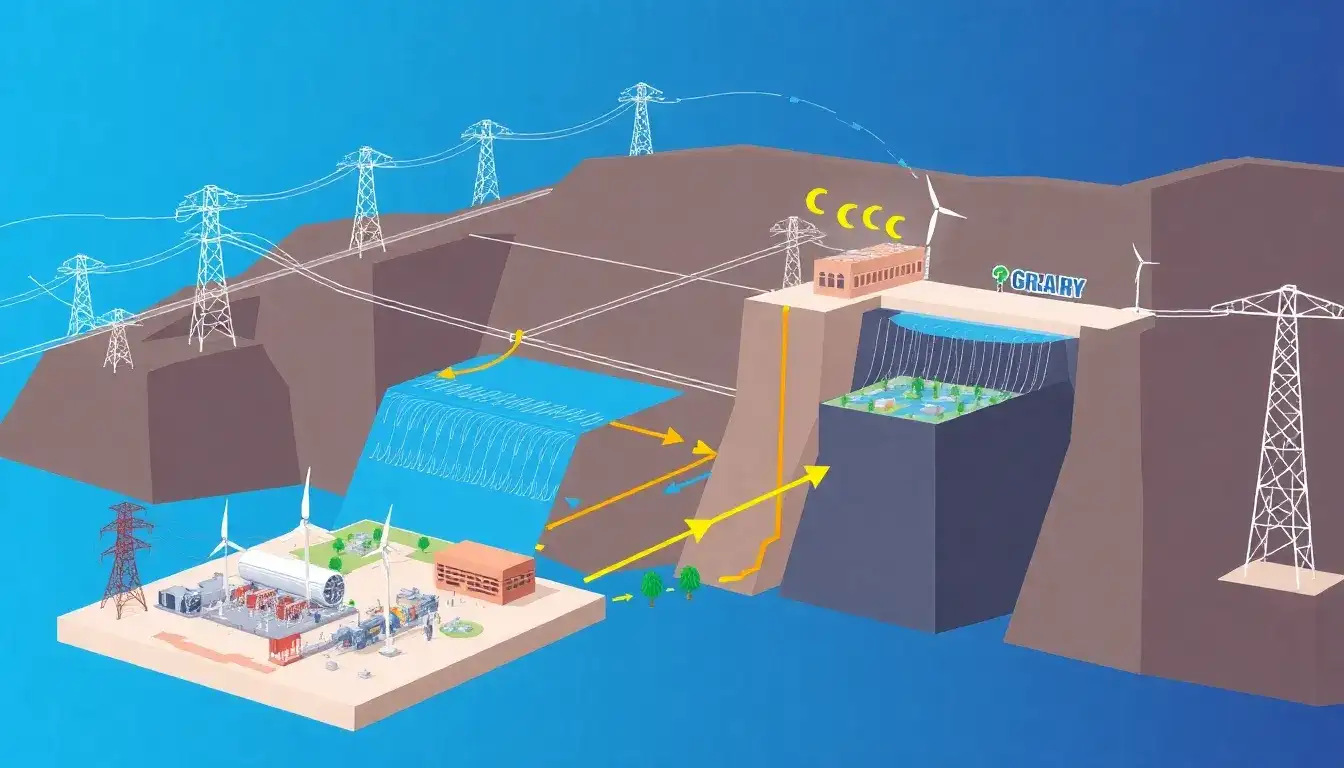
The electricity grid plays a crucial role in the operation of pumped hydroelectric storage (PHS), which is a form of energy storage that supports grid stability and reliability through several key functions:
Key Roles of the Electricity Grid in PHS Operation
- Supplying Excess Energy: The grid provides excess electricity, often from renewable sources like solar and wind, or from base-load sources during low-demand periods. This excess energy is used to pump water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir, storing energy as gravitational potential energy.
- Demand Management: During peak demand periods, when the grid requires more electricity, the stored water is released from the upper reservoir through turbines. This process generates electricity to meet the increased demand, helping to stabilize and balance the grid.
- Grid Stability and Flexibility: PHS systems offer rapid response times, allowing them to quickly adjust electricity supply to match changes in demand or sudden disruptions, thereby maintaining grid stability.
- Supporting Renewable Integration: By storing energy generated from intermittent renewable sources during low-demand periods, PHS helps ensure their output can be utilized effectively during high-demand times, facilitating the integration of more renewable energy into the grid.
- Economic Benefits: The grid facilitates the economic efficiency of PHS by allowing the sale of stored energy during peak demand periods when electricity prices are highest. This can offset the energy losses inherent in the pumping process.
Overall, the electricity grid is essential for the operation of pumped hydroelectric storage, as it provides both the excess energy needed for storage and the demand that PHS supplies during peak periods.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-role-does-the-electricity-grid-play-in-the-operation-of-pumped-hydroelectric-storage/


