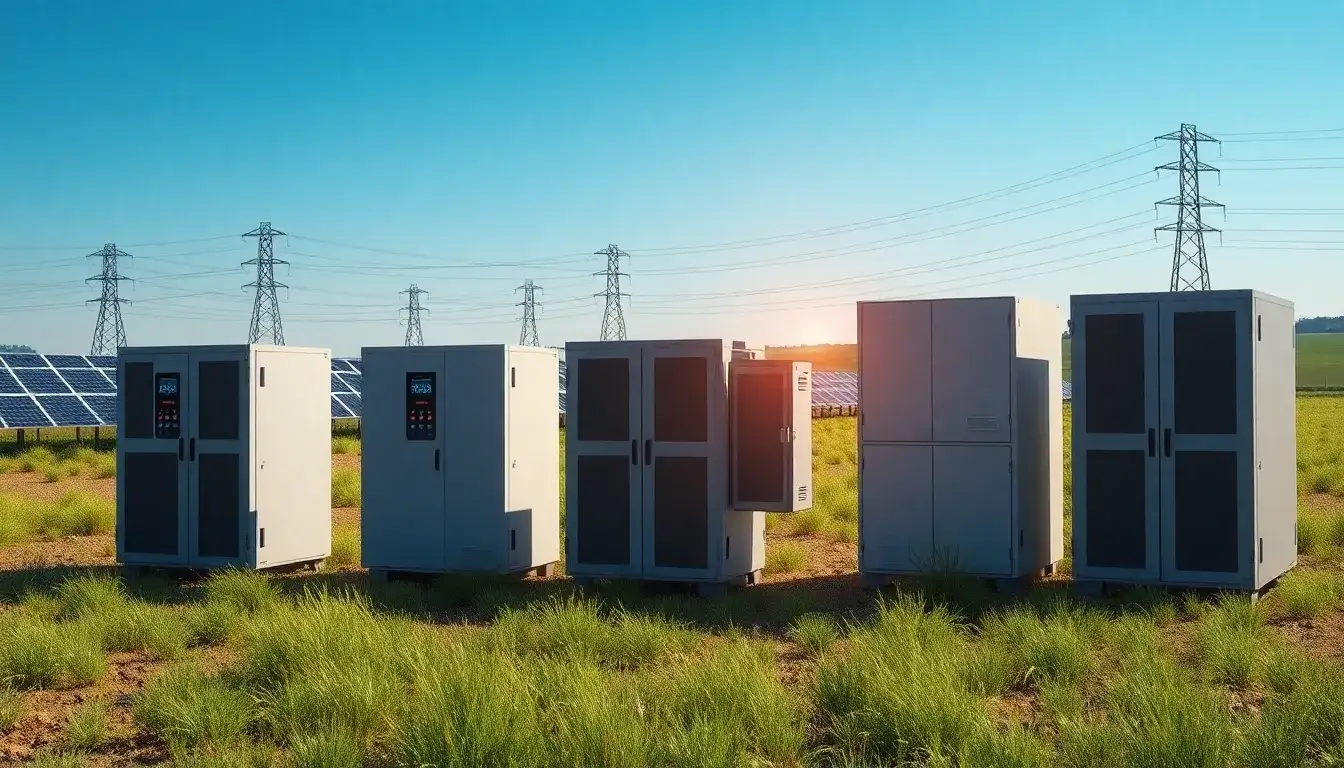
Inverters play a crucial role in the operation of utility-scale battery storage systems. Here’s how they contribute to the overall functionality:
Function of Inverters in Utility-Scale Battery Storage
- Bidirectional Conversion: Inverters, often referred to as power conversion systems (PCS) or bi-directional inverters, facilitate the conversion of electricity between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). During charging, they convert AC power from the grid into DC to store in the batteries. When discharging, they convert the DC power stored in the batteries back into AC so it can be fed into the grid.
- Grid Integration: The primary function of inverters is to ensure that the output from the battery storage system matches the grid’s specifications. This involves creating a smooth AC waveform that aligns with the grid’s frequency and voltage, ensuring seamless integration and avoiding disruptions.
- Operational Flexibility: Inverters are essential for managing energy flow in both grid-tied and off-grid applications. They enable utility-scale batteries to interact with the grid dynamically, providing support during peak demand periods and stabilizing the supply to maintain grid reliability.
- Efficiency and Scalability: Utility-scale inverters are designed to maximize efficiency and can handle large volumes of energy. This scalability is vital for utility-scale battery systems, as it allows them to support extensive areas and large populations effectively.
In summary, inverters are critical for converting energy types, integrating with the grid, and ensuring operational flexibility and efficiency in utility-scale battery storage systems.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-role-do-inverters-play-in-the-operation-of-utility-scale-batteries/