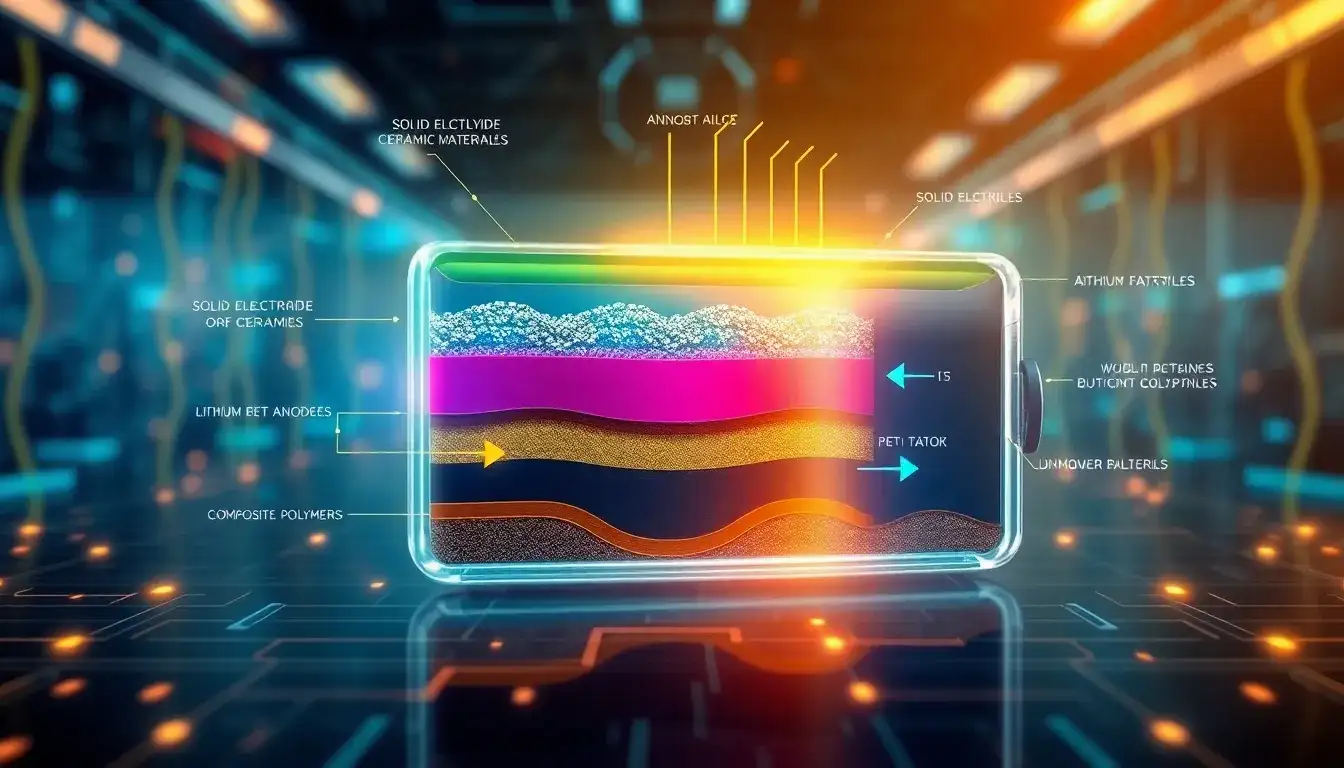
Solid-state batteries utilize various materials to enhance their performance, safety, and efficiency compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The main materials include:
Materials Used in Solid-State Batteries
- Solid Electrolytes:
- Ceramic Oxides: These provide high thermal stability and are non-flammable, reducing fire risk and improving safety.
- Sulfides: Considered for high ionic conductivity and potential for high-performance batteries.
- Phosphates: Used for their stability and chemical inertness.
- Solid Polymers: Organic electrolytes that are easier to process but may require heating for improved conductivity.
- Anode Materials:
- Lithium Metal: Offers high charge capacity, increasing energy density.
- Carbon Materials:
- Carbon Nanotubes: Known for their high surface area and excellent electrochemical performance.
- Silicon Materials: Such as silicon nanowires, which provide high specific capacity though prone to volume expansion.
- Cathode Materials:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2): High energy density but with safety concerns.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4): Offers better safety and longer life but lower energy density.
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Oxide (LiNiCoO2): Known for high energy density and long cycle life, though costly.
Enhancements from Materials
- High Energy Density: Solid-state batteries can achieve up to 350 Wh/kg, benefiting from lithium metal anodes.
- Improved Safety: Non-flammable solid electrolytes reduce the risk of thermal runaway and fires.
- Faster Charging: Solid electrolytes enable quicker ion transfer, potentially reducing charging times.
These materials and designs contribute to solid-state batteries offering enhanced performance, safety, and efficiency compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-materials-are-used-in-solid-state-batteries-to-enhance-their-performance/


