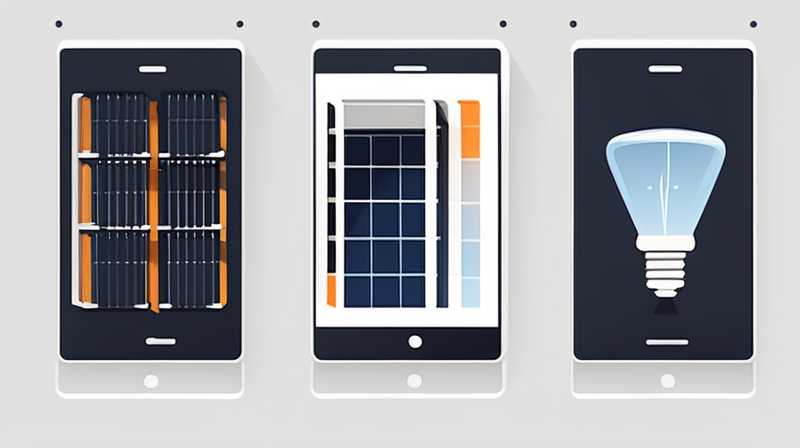
1. LED bulbs are widely regarded as the most efficient option for solar lights due to their low energy consumption and long lifespan, 2. CFL bulbs provide decent illumination but are less effective in colder temperatures, 3. Incandescent bulbs, while inexpensive, are highly inefficient and not recommended for solar applications, 4. Choosing the right bulb depends on factors such as brightness, energy efficiency, and environmental conditions.
When considering the optimal bulb for solar lights, efficiency, longevity, and adaptability to various weather conditions are paramount. The most preferred option often falls upon LED (Light Emitting Diode) bulbs, celebrated for their remarkable energy efficiency. LED technology consumes a fraction of the power that traditional incandescent bulbs require, translating to longer operation times on solar energy. Moreover, their durability and resilience against harsh elements ensure that they can withstand outdoor usage for extended periods. The luminous efficacy exhibited by LED bulbs allows them to produce substantial light while remaining energy efficient, thereby maximizing the utility of the solar panel.
CFL (Compact Fluorescent Lamp) bulbs emerge as another contender in the realm of solar lighting. They generate a magnificent amount of light and exhibit a longer lifespan than incandescent alternatives. However, they are typically less efficient in colder climates and may take time to warm up, rendering them less ideal for areas that experience significant temperature fluctuations. Furthermore, the presence of mercury in CFLs poses environmental challenges concerning disposal and degradation over time. Thus, while CFLs may provide benefits in specific circumstances, their overall utility may diminish when evaluating long-term use in solar applications.
Incandescent bulbs, while historically popular, stand as a less favorable choice for solar installations. Their energy consumption is strikingly high compared to both LED and CFL options, resulting in poor performance when powered by solar energy. In addition, their fragility and vulnerability to breakage during outdoor application detract from their viability in solar lighting systems. When prioritizing energy conservation and performance, incandescent bulbs fall short, limiting their effectiveness in environments that rely on sustainable energy sources.
Evaluating the bulb options for solar lights involves considering specific needs and conditions. Factors such as brightness levels, energy efficiency, ambient temperatures, and environmental impacts must all be factored into the decision-making process. Moreover, users must assess their individual lighting requirements based on the intended use and geographical location, as these aspects can greatly influence the effectiveness of the selected bulb technology.
1. LED BULBS: THE PREFERRED OPTION
When delving into the specifics of LED bulbs, several advantages come into focus. They operate with a significantly lower wattage compared to their incandescent counterparts, which allows solar lights to function more effectively. For instance, an LED bulb can produce an equivalent brightness level of 800 lumens while consuming merely 10 watts. This stark contrast to incandescent bulbs, which may require 60 watts for the same output, showcases how LED bulbs excel in energy efficiency.
Moreover, LED technology offers exceptional operational longevity. Many LEDs are rated for up to 50,000 hours of use, which extends far beyond the typical 1,000 hours for incandescent bulbs and the 10,000 hours for CFLs. This longevity not only lowers replacement costs but also enhances the ecological benefits associated with less frequent disposals. The durability of LEDs allows them to withstand fluctuations in temperature and adverse weather conditions, positioning them as the optimal choice for solar lighting applications.
2. CFL BULBS: A DECENT CHOICE?
CFL bulbs, while somewhat overshadowed by LEDs, still possess qualities that merit consideration in certain contexts. Their higher lumen output can be advantageous for applications requiring more intense illumination. Furthermore, their initial cost usually remains lower than that of LED bulbs, making them accessible options for users with budget constraints.
However, while CFL bulbs contribute to energy savings and environmental conservation when compared to incandescent options, they still demand a careful evaluation of their limitations. A pivotal downside is their reduced efficiency at lower temperatures. In regions where nighttime temperatures drop significantly, CFLs may dim or fail to perform optimally, potentially leading to inadequate lighting during key hours.
3. INCANDESCENT BULBS: OUTDATED TECHNOLOGY
As the least favorable option, incandescent bulbs have faced criticism due to their substantial energy requirements. They emit a warm light often desired for aesthetic reasons, but this comes at the cost of efficiency. When assessing their role in solar applications, the reliance on solar energy becomes critically undercut by their high operational demands.
Furthermore, the environmental implications of incandescent bulbs extend beyond their energy consumption. The lifecycle analysis reveals a greater carbon footprint due to their shorter lifespan and the increased frequency of replacements required. In scenarios where sustainability is prioritized, incandescent bulbs represent an outdated choice that offers negligible advantages compared to modern alternatives.
4. ADDITIONAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER
Choosing the right kind of bulb for solar lights involves understanding the operational environment and individual lighting requirements. The geographic location can profoundly affect the performance of each bulb type. For instance, regions with consistently mild climates may find that both LEDs and CFLs operate efficiently, whereas colder areas necessitate a more careful selection where LEDs would undoubtedly provide superior performance.
Additionally, the intensity and duration of solar exposure influence the efficiency of solar light systems. Locations with abundant sunlight and longer daylight hours can harness solar energy more effectively, allowing for robust usage of LED bulbs. Conversely, areas that experience persistent cloud cover may prompt users to evaluate different bulb technologies based on yield and lifecycle costs.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
WHICH BULB TYPE IS THE MOST COST-EFFECTIVE FOR SOLAR LIGHTS?
The financial implications of selecting a bulb type can be assessed across various dimensions, encompassing initial purchase price, energy consumption, and longevity. LED bulbs generally present the most cost-effective solution in the long run. Though they often demand a higher upfront investment, their remarkable lifespan and energy efficiency translate to reduced electricity bills over time. Conversely, CFL bulbs may appear less expensive initially but often do not yield comparable savings when accounting for their shorter lifespan and reduced efficiency in colder conditions. Consequently, the total cost of ownership should prioritize LEDs, leading to substantial savings while providing durable and bright solar lighting.
CAN SOLAR LIGHTS WORK WITH INCANDESCENT BULBS?
Technically, solar lights can function with incandescent bulbs; however, such a configuration is ill-advised. The high power demands of incandescent bulbs predominantly negate the effectiveness of solar systems. Not only will these bulbs limit operational hours substantially due to inadequate energy output, but they may also lead to rapid depletion of the energy stored in the solar batteries. Additionally, the increased heat generated by incandescent bulbs poses a risk to the integrity of the solar light’s components. Therefore, it is highly recommended to stick with more energy-efficient options such as LEDs or CFLs to obtain optimal performance from solar lighting solutions.
ARE LED BULBS WEATHER-RESISTANT FOR SOLAR APPLICATIONS?
LED bulbs are usually constructed to withstand a variety of weather conditions, making them suitable for outdoor solar lighting applications. Many manufacturers create LED bulbs that are either fully sealed or equipped with durable housing resistant to moisture, dust, and temperature variations. Such designs ensure that even in harsh climates, LED bulbs maintain efficient operation without succumbing to environmental degradation. Moreover, their longevity and resilience reduce the necessity for frequent replacements, making them an ideal choice for solar-powered lights exposed to nature.
LED bulbs serve as the benchmark in energy-saving technology, revolutionizing solar lighting applications across diverse landscapes. CFL bulbs offer a viable alternative in specific scenarios, while incandescent bulbs remain largely impractical for solar energy use. When selecting optimal lighting solutions, each type’s characteristics, advantages, and limitations come into sharper focus. By understanding these intricacies, users can empower themselves to make informed choices that align with both their individual lighting needs and broader sustainability considerations. With the ongoing advancements in energy technology, a great deal of innovation continues to enhance solar lighting systems, driving new developments that encapsulate weighty considerations of environmental responsibility, economic factors, and aesthetic appeal. Choosing the right type of bulb for solar lights is thus an essential decision that extends beyond mere illumination; it encompasses a commitment to sustainable practices and ongoing energy efficiency. Moreover, as we navigate the intersection of technology and ecological awareness, the options available will continue to evolve, ensuring that solar lighting remains a crucial component of future energy strategies.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-kind-of-bulb-is-good-for-solar-lights/