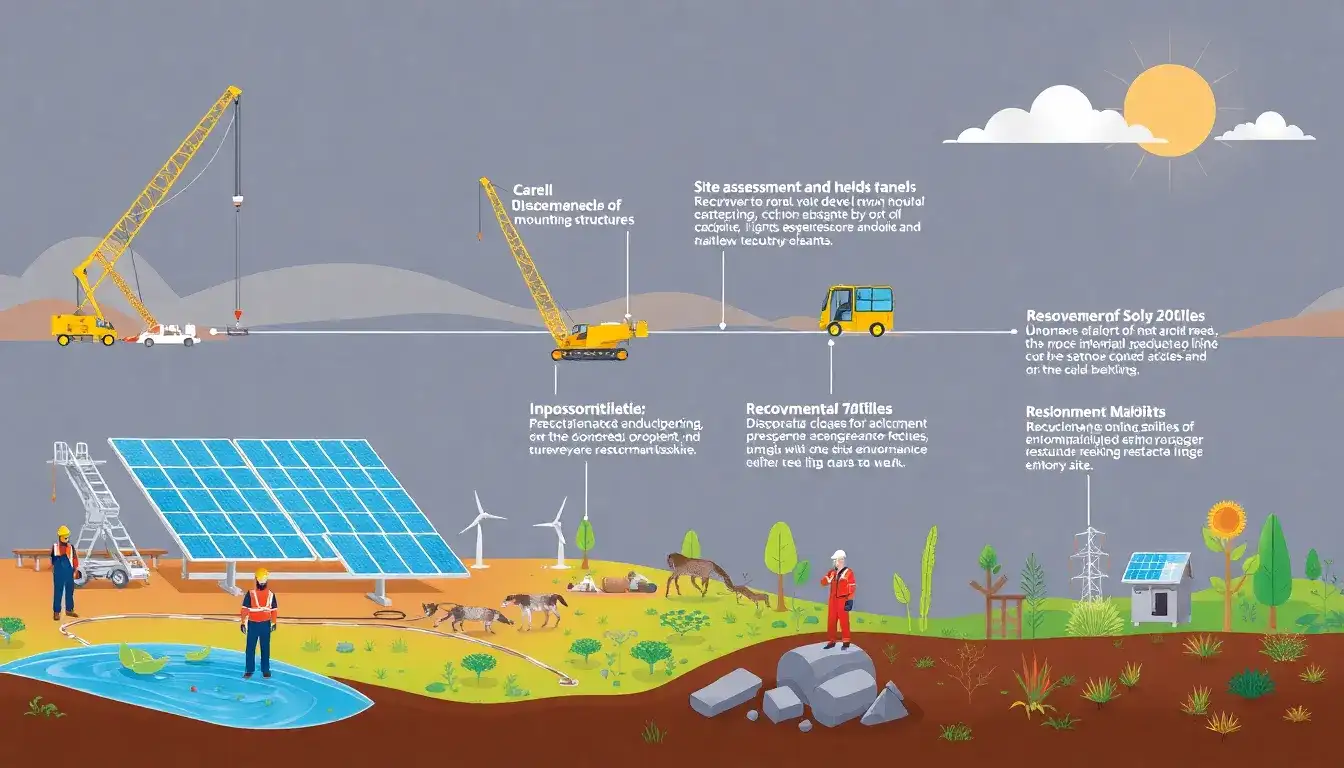
1. Planning and Regulatory Compliance
- Developing a comprehensive decommissioning plan as part of the project application or prior to decommissioning. This plan often must be approved by relevant authorities and include procedures for dismantling, recycling, disposal, and site restoration.
- Ensuring adherence to local, state, and national regulations governing decommissioning, which may include submitting notifications and updates to government agencies (e.g., notifying within 30 days after cessation of production in some jurisdictions).
- Allocating financial resources or securing bonds to cover decommissioning costs, providing transparency and accountability regarding these funds to mitigate potential liabilities.
2. Notification and Communication
- Informing regulatory bodies (such as state environmental agencies) promptly when the solar project ceases operations.
- Communicating with landowners and stakeholders regarding decommissioning activities and timelines.
3. Dismantling and Equipment Removal
- Disconnecting the solar facility from the electrical grid.
- Carefully dismantling solar farm components including panels, inverters, mounting structures, and electrical systems. The process involves safely removing solar panels from their mounts and other infrastructure.
- Collecting all equipment and preparing it for either reuse, recycling, or disposal.
4. Recycling and Disposal
- Responsible disposal of solar panels and other equipment, considering many contain valuable recyclable materials such as silicon, glass, metals, silver, copper, and aluminum.
- Managing disposal in line with environmental regulations which may require handling hazardous wastes properly or recycling materials to reduce environmental impact.
- Overcoming technical challenges associated with breaking down robust solar panels due to adhesives and sealants used in manufacturing.
5. Site Restoration
- Restoring the property as nearly as practical to its original condition prior to solar development or another agreed-upon condition with the landowner. This typically involves soil remediation, replanting vegetation or crops, and measures to restore biodiversity and environmental health of the site.
Summary Table of Solar Developer Responsibilities During Decommissioning
| Responsibility | Description |
|---|---|
| Planning & Compliance | Create and submit decommissioning plan, secure funding, follow laws |
| Notification & Communication | Notify authorities and landowners, provide updates on process |
| Dismantling & Removal | Disconnect grid, dismantle and remove solar panels and equipment |
| Recycling & Disposal | Recycle valuable materials, safely dispose of hazardous waste |
| Site Restoration | Restore site to original or agreed condition, including vegetation/soil |
Overall, solar developers play a central role in ensuring the decommissioning process is environmentally responsible, regulatory compliant, and financially secured, minimizing impacts on communities and ecosystems while safeguarding the site for future use.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-typical-responsibilities-of-a-solar-developer-during-decommissioning/


