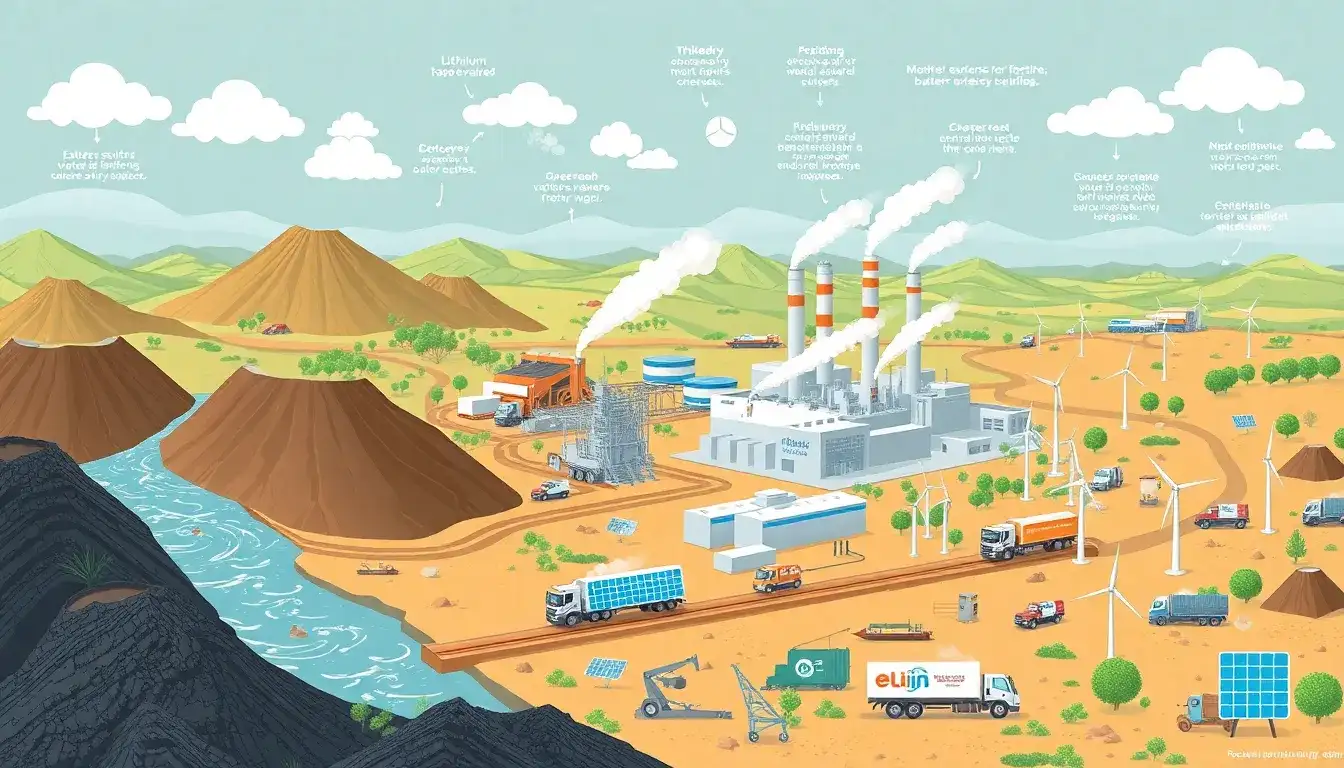
The main sources of emissions in the production of electric vehicle (EV) batteries are as follows:
- Mining and Processing of Raw Materials:
- Critical minerals such as lithium, nickel, manganese, cobalt, and graphite are key components of EV batteries. Their mining and processing emit significant greenhouse gases (GHGs), particularly due to energy-intensive refining processes.
- For lithium, hard rock mining can emit up to 15 tonnes of CO2 per tonne of lithium mined.
- Energy Used in Manufacturing:
- The production process requires high temperatures (800 to 1,000°C), which are often achieved by burning fossil fuels, contributing to CO2 emissions.
- The use of renewable energy sources can significantly reduce the carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
- Battery Chemistry and Production Technology:
- Different battery chemistries, such as Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) and Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), have varying emission contributions. For NMC, critical minerals processing accounts for 55% of emissions, while for LFP, manufacturing is a larger contributor.
- Transportation and Supply Chain:
- Sourcing decisions, including transportation routes and energy sources used in the supply chain, impact overall emissions.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-main-sources-of-emissions-in-the-production-of-ev-batteries/


