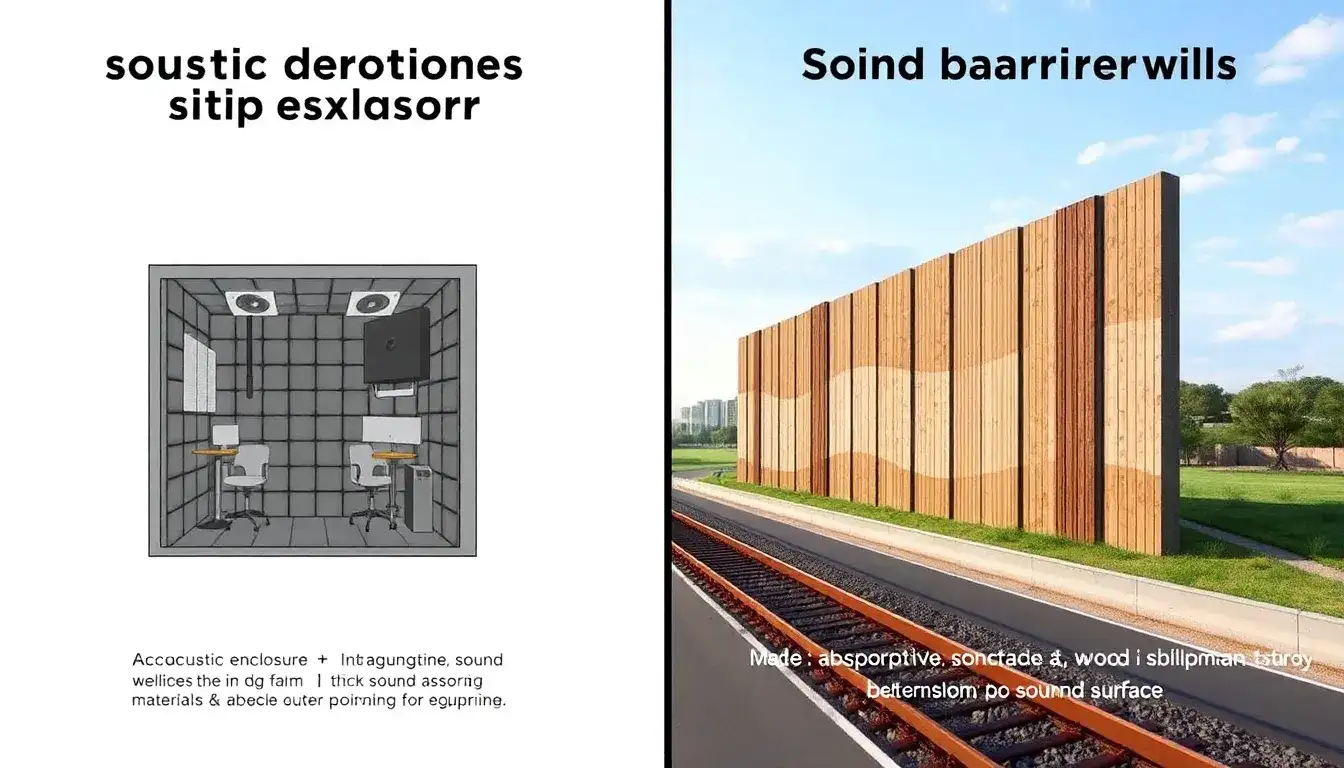
Acoustic enclosures and sound barrier walls differ fundamentally in their design approach, application, and noise control mechanisms.
Design Differences Between Acoustic Enclosures and Sound Barrier Walls
1. Structural Design and Form:
- Acoustic Enclosures are often fully or partially enclosed structures designed to surround a noise source. They can be complete boxes or partial enclosures such as 4 walls without a ceiling, 2 walls with a base and ceiling, or 3 walls depending on the needs. This design aims to enclose the noise generation point closely to contain and suppress noise.
- Sound Barrier Walls are generally large vertical panels or walls placed between the noise source and the receiver, intended to block or deflect sound waves from traveling directly to the sensitive area. They do not enclose the noise source but create a physical barrier to sound propagation.
2. Noise Control Mechanisms:
- Acoustic enclosures primarily reduce noise by physically enclosing the source, adding layers of sound-absorbing materials inside the enclosure to dampen and absorb noise, preventing it from escaping into the environment.
- Sound barrier walls reduce noise mainly by blocking the direct path of sound waves and either reflecting or absorbing sound. Absorptive sound barrier walls use porous materials that absorb sound energy, significantly reducing reflected noise and overall sound pollution, whereas reflective barriers bounce sound away, which can sometimes increase noise in unintended directions.
3. Coverage and Application Context:
- Acoustic enclosures focus on specific noise sources like generators, compressors, transformers, or machinery. They are customized modular structures, sometimes without full closure (e.g., without ceiling or base), tailored to the noise profile and spatial constraints.
- Sound barrier walls are generally used to mitigate environmental noise over larger areas, such as along highways or around industrial sites, and are designed to be permanent installations separating noisy areas from residential or quiet zones.
4. Material and Construction:
- Acoustic enclosures often use modular acoustic panels designed for sound absorption and internal noise suppression, sometimes addressing low-frequency noise specifically (e.g., transformer enclosures).
- Sound barrier walls use materials ranging from concrete, wood, and metal to advanced PVC and composite materials. Modern sound barriers often emphasize absorptive materials to minimize noise reflection and improve overall noise reduction effectiveness.
Summary Table
| Feature | Acoustic Enclosure | Sound Barrier Wall |
|---|---|---|
| Design Form | Enclosures (full or partial) around noise source | Vertical walls positioned between source and receiver |
| Noise Control Method | Enclosure and absorption around source | Blocking, absorption, or reflection of sound waves |
| Typical Application | Specific machinery or equipment noise control | Environmental noise control (roads, industrial sites) |
| Material Types | Acoustic panels, modular, absorptive materials | Concrete, wood, metal, PVC; absorptive or reflective |
| Coverage | Surrounds noise source, sometimes partial coverage | Between source and receiver, open environment |
In essence, acoustic enclosures are designed to surround and absorb noise directly at the source, often in modular and partially enclosed formats, while sound barrier walls act as physical barriers blocking or absorbing sound along transmission paths in open environments.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-main-differences-in-design-between-acoustic-enclosures-and-sound-barrier-walls/


