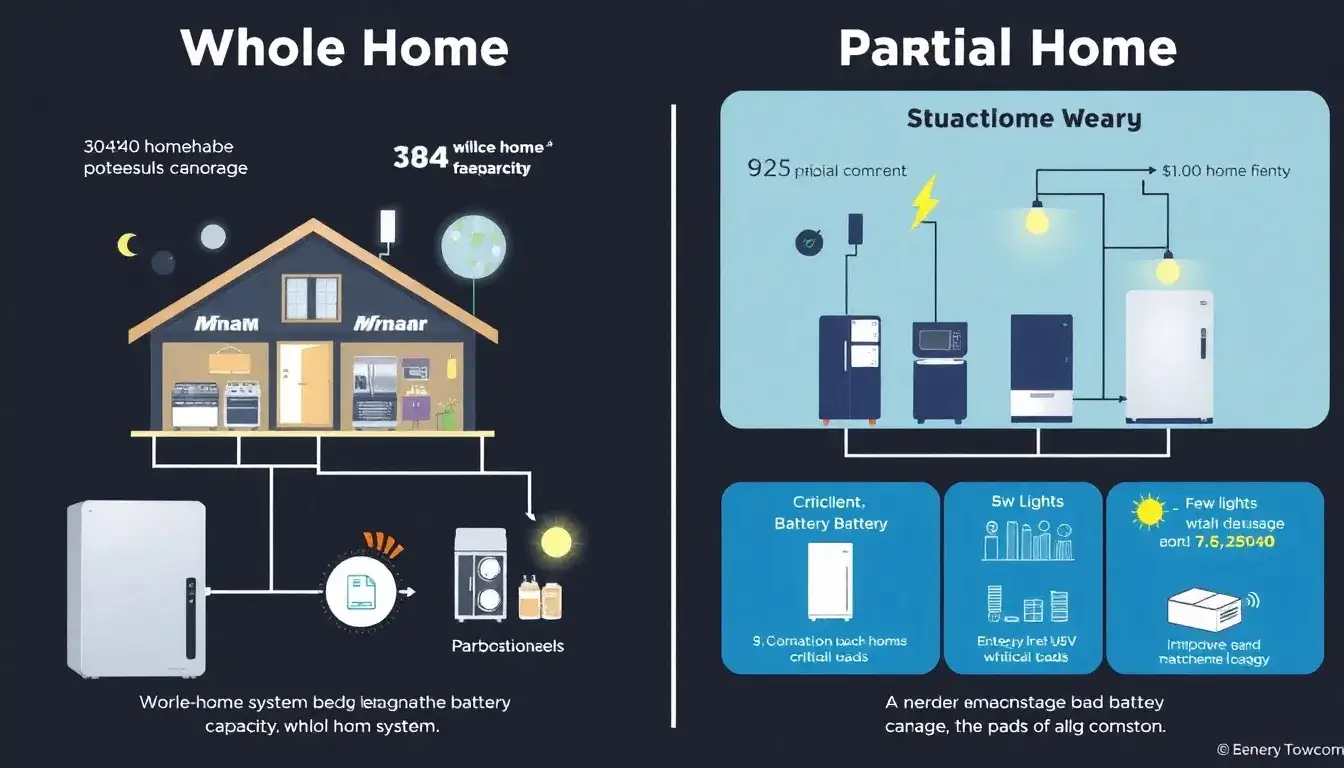
The main differences between whole-home and partial-home battery backup systems can be summarized as follows:
Whole-Home Battery Backup Systems
- Comprehensive Coverage: These systems power the entire home during an outage, ensuring all appliances and devices remain operational.
- Higher Cost: More expensive due to the need for larger batteries and possibly multiple inverters.
- Increased Energy Storage: Requires substantial battery capacity, typically around 30 kWh or more, to support all home systems.
- Convenience and Continuity: Provides uninterrupted power to HVAC systems, entertainment setups, and all appliances without manual switching.
- Increased Property Value: Attractive to potential home buyers, especially in areas prone to power outages.
- Scalability: Allows for future expansion with additional storage if needed.
Partial-Home Battery Backup Systems
- Essential Load Support: Only powers critical circuits and appliances such as refrigerators, lighting, and essential outlets.
- Lower Cost: More affordable with smaller batteries and often a single hybrid inverter.
- Smaller Energy Storage: Typically requires about 10 to 15 kWh of battery capacity.
- Flexibility: Allows users to choose which appliances to prioritize during an outage.
- Simplicity: Installation is generally easier and quicker due to fewer circuits.
- Manual Management: May require manual control of power distribution or load management to ensure efficient energy use.
In summary, whole-home backup systems offer comprehensive power during outages but at a higher cost and complexity, while partial-home systems are more economical, prioritizing essential loads and requiring less energy storage.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-main-differences-between-whole-home-and-partial-home-battery-backup-systems/


