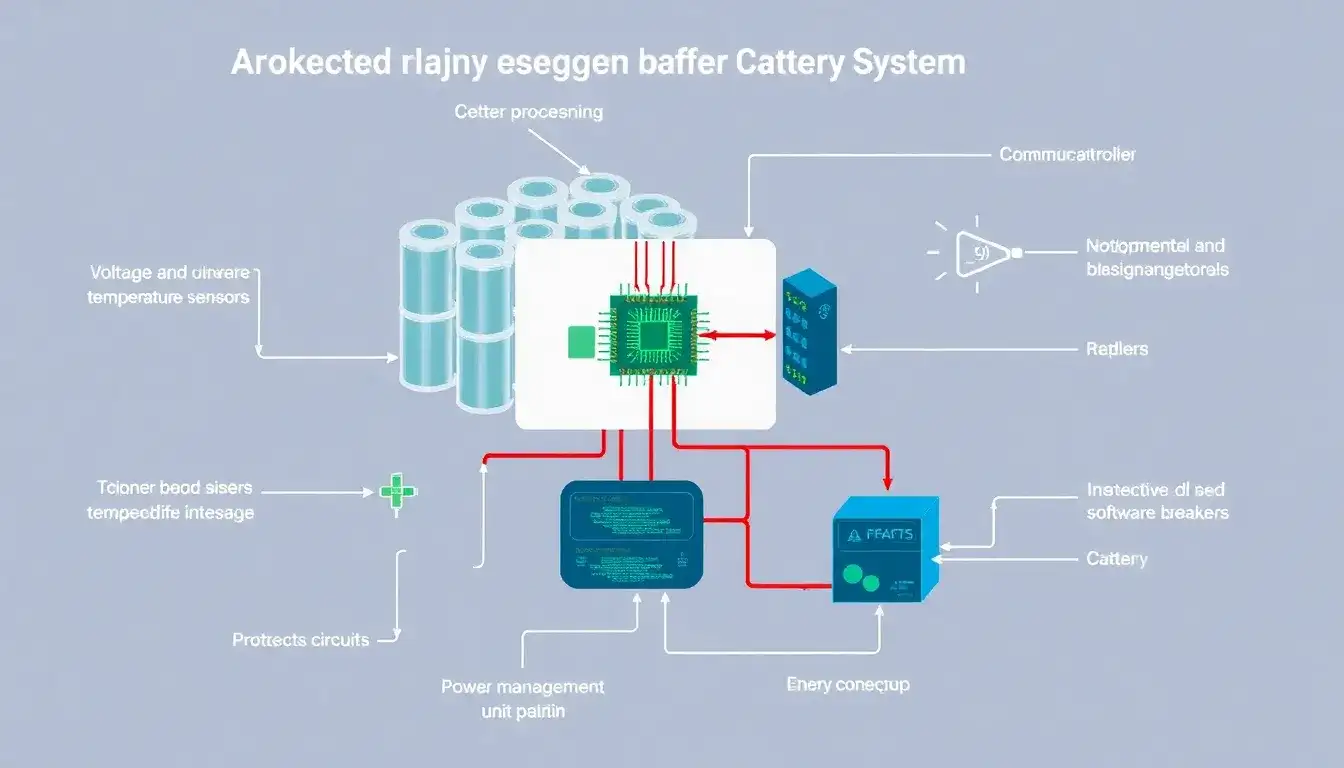
A Battery Management System (BMS) in a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) is a crucial component that ensures the safe and efficient operation of the battery cells. The main components of a BMS typically include:
- Sensing Components:
- Voltage Sensors: Monitor the voltage of individual battery cells to prevent overcharging or deep discharge.
- Current Sensors: Measure the electric current flowing in and out of the battery, helping calculate state of charge (SoC) and detect adverse conditions like overcurrent.
- Temperature Sensors: Track the temperature of battery cells to avoid overheating and ensure optimal performance.
- Battery Controller:
This acts as the brain of the BMS, processing data from sensors and executing control algorithms to manage charging and discharging operations. It often includes a microcontroller or digital signal processor (DSP) for processing tasks. - Control Algorithms:
These are software programs that analyze sensor data and adjust operations accordingly. Examples include algorithms for charging rate adjustments and SoC estimation. - Communication and Interface Systems:
These enable the BMS to communicate with other components of the BESS, such as the Energy Management System (EMS) and Power Conversion System (PCS), ensuring coordinated operation. - Protection Mechanisms:
Functionalities like disconnecting the battery during anomalies (e.g., overvoltage, overcurrent) to ensure safety.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-main-components-of-a-bms-in-a-bess/


