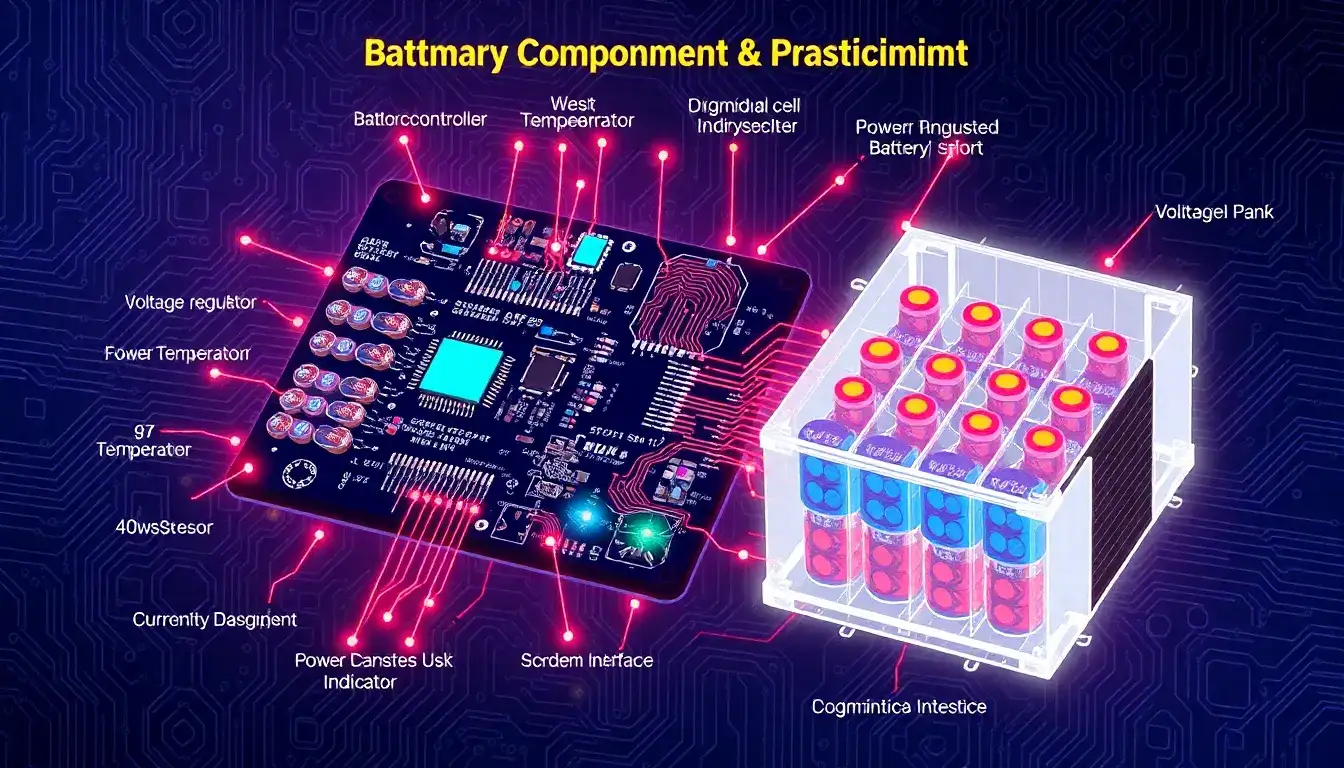
- Cell Monitoring Unit:
- This unit is responsible for monitoring the voltage and temperature of individual cells in the battery pack. It ensures safe operation by detecting improper conditions such as overcharging or deep discharging.
- Control Unit:
- Often implemented as a microcontroller, this unit processes data from sensors and controls the BMS’s functions, ensuring the system stays within safe operating limits.
- Sensing Components:
- Voltage Sensors: Monitor the voltage levels of each cell.
- Current Sensors: Track the current flowing into or out of the battery, crucial for state of charge calculations.
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor the battery temperature to prevent overheating.
- Balancing Circuit:
- Ensures that all cells in the battery pack have uniform voltage levels to prevent overcharging or undercharging.
- Protection Circuitry (Cutoff FETs):
- These protect the battery from overcharge, over-discharge, short circuits, and excessive currents by disconnecting the battery pack.
- Thermal Management System:
- Controls the temperature of the battery to maintain efficiency and safety.
- Communication Interface:
- Allows the BMS to communicate with external systems such as chargers or control units.
- State Machine/Real-time Clock (RTC):
- Some BMS systems include these for scheduling, timing functions, and executing state-based logic.
These components work together to optimize battery performance, ensure safety, and prolong battery life.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-main-components-of-a-battery-management-system/


