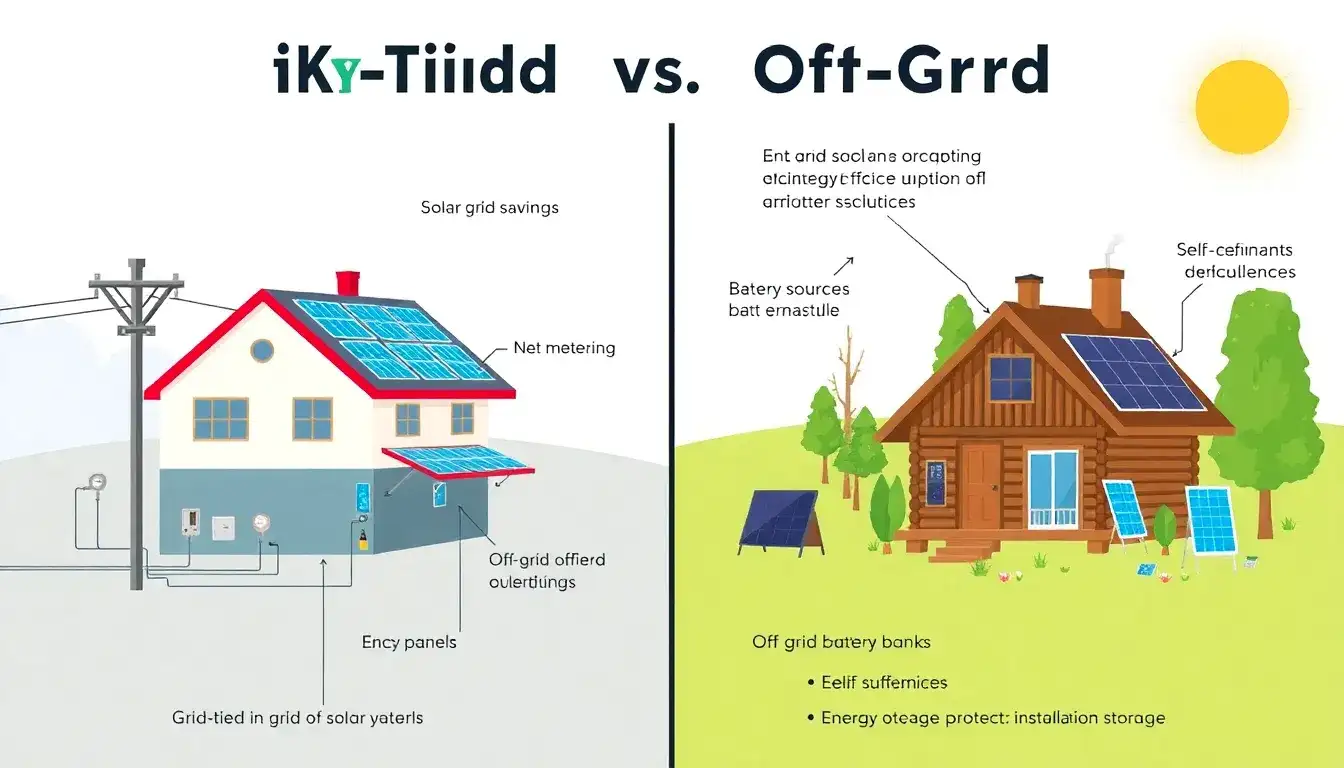
Key Factors to Consider
1. Location and Access to the Grid
- Grid-Tied Systems: Suitable for locations connected to the utility grid, providing continuous access to electricity.
- Off-Grid Systems: Ideal for remote areas without access to the grid, offering complete independence.
2. Energy Independence
- Grid-Tied Systems: Dependent on the grid for backup power, vulnerable to outages.
- Off-Grid Systems: Allows for self-sufficiency, unaffected by grid outages but relies on solar and battery power.
3. Cost Considerations
- Grid-Tied Systems: Generally less expensive, as they do not require battery storage.
- Off-Grid Systems: More costly due to the need for extensive battery storage to ensure continuous power availability.
4. Energy Efficiency and Excess Power Handling
- Grid-Tied Systems: Utilizes net metering to export excess energy to the grid for credits.
- Off-Grid Systems: Excess energy is stored in batteries for later use.
5. Maintenance and Complexity
- Grid-Tied Systems: Typically simpler to install and maintain with fewer components.
- Off-Grid Systems: Requires more complex energy management and maintenance due to battery banks.
6. Electricity Bills and Savings
- Grid-Tied Systems: Reduces electricity bills via net metering but may incur some grid connection fees.
- Off-Grid Systems: Eliminates electricity bills but requires significant upfront investment in equipment.
7. Backup Power During Outages
- Grid-Tied Systems: Needs additional investment (like batteries) to provide backup power during grid outages.
- Off-Grid Systems: Offers inherent backup power capabilities through stored energy in batteries.
Ultimately, the choice between a grid-tied and off-grid solar system depends on your specific energy needs, budget constraints, and grid accessibility.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-key-factors-to-consider-when-choosing-between-grid-tied-and-off-grid-solar-systems/


