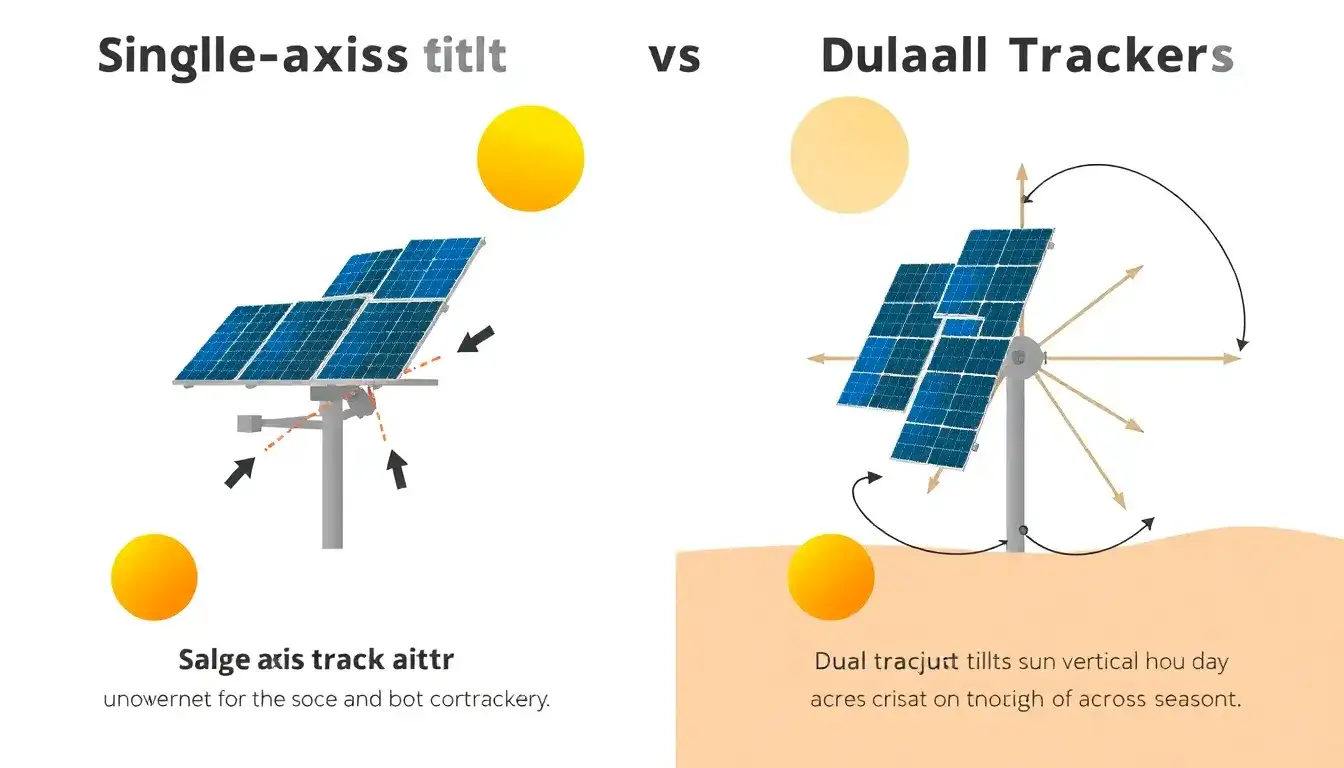
The key differences between single-axis and dual-axis solar trackers can be understood across several dimensions: movement capabilities, energy efficiency, complexity, cost, maintenance, and ideal geographic application.
Movement and Tracking Capability
- Single-axis trackers rotate solar panels around one axis, usually aligned east-to-west, allowing panels to follow the sun’s path horizontally throughout the day. Variants include horizontal, tilted horizontal, vertical, and vertical-tilted axes that optimize solar exposure based on latitude and seasonal changes but only along one axis.
- Dual-axis trackers have two degrees of freedom: they rotate panels horizontally (east-west) and vertically (up-down) to track the sun’s position more precisely throughout the day and across seasons. This dual movement ensures panels are almost always perpendicular to the sun’s rays, maximizing exposure.
Energy Efficiency and Production
- Single-axis trackers can increase solar energy generation by about 25% to 35% over fixed systems.
- Dual-axis trackers boost energy production by an additional 5% to 15% beyond single-axis systems, roughly translating to 30% to 40% more than fixed installations in total. This is because their ability to track both the sun’s daily and seasonal position improves sunlight capture.
Complexity and Cost
- Single-axis trackers are mechanically simpler with fewer moving parts, resulting in lower upfront costs and less complexity in design and installation.
- Dual-axis trackers are more complex due to the additional motor and control mechanisms needed for two-axis movement, which increases initial costs and requires more sophisticated control software.
Maintenance and Reliability
- Single-axis trackers tend to be more reliable with lower maintenance requirements, as fewer mechanical parts mean less chance of failure or downtime. They typically have a longer lifespan.
- Dual-axis trackers require more maintenance and can experience more frequent downtime due to their mechanical complexity and increased wear and tear. They might also be less reliable over long periods.
Geographic Application
- Single-axis trackers work well in locations where the sun’s path is relatively consistent, such as equatorial or desert regions with a high sky clearness index.
- Dual-axis trackers are beneficial in locations with significant seasonal variations in sun angle or where maximum energy capture is crucial despite higher costs and maintenance.
Summary Table of Key Differences
| Feature | Single-Axis Trackers | Dual-Axis Trackers |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | One rotational axis (usually east-west) | Two rotational axes (horizontal + vertical) |
| Energy Gain | +25% to +35% over fixed arrays | +30% to +40% over fixed arrays |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, simpler mechanics | Higher complexity, advanced mechanics |
| Cost | Lower capital cost | Higher capital cost |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance, higher reliability | Higher maintenance, potentially lower reliability |
| Ideal Location | Regions with stable sun angles | Regions with variable sun angles or higher energy needs |
In conclusion, single-axis solar trackers are cost-effective, simpler, and reliable, making them suitable for many solar projects, especially where budget and maintenance are concerns. Dual-axis trackers provide the highest solar exposure and energy output by more accurately following the sun but at the expense of higher cost, complexity, and maintenance needs. The choice depends on project goals, location, and budget.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-key-differences-between-single-axis-and-dual-axis-solar-trackers/


