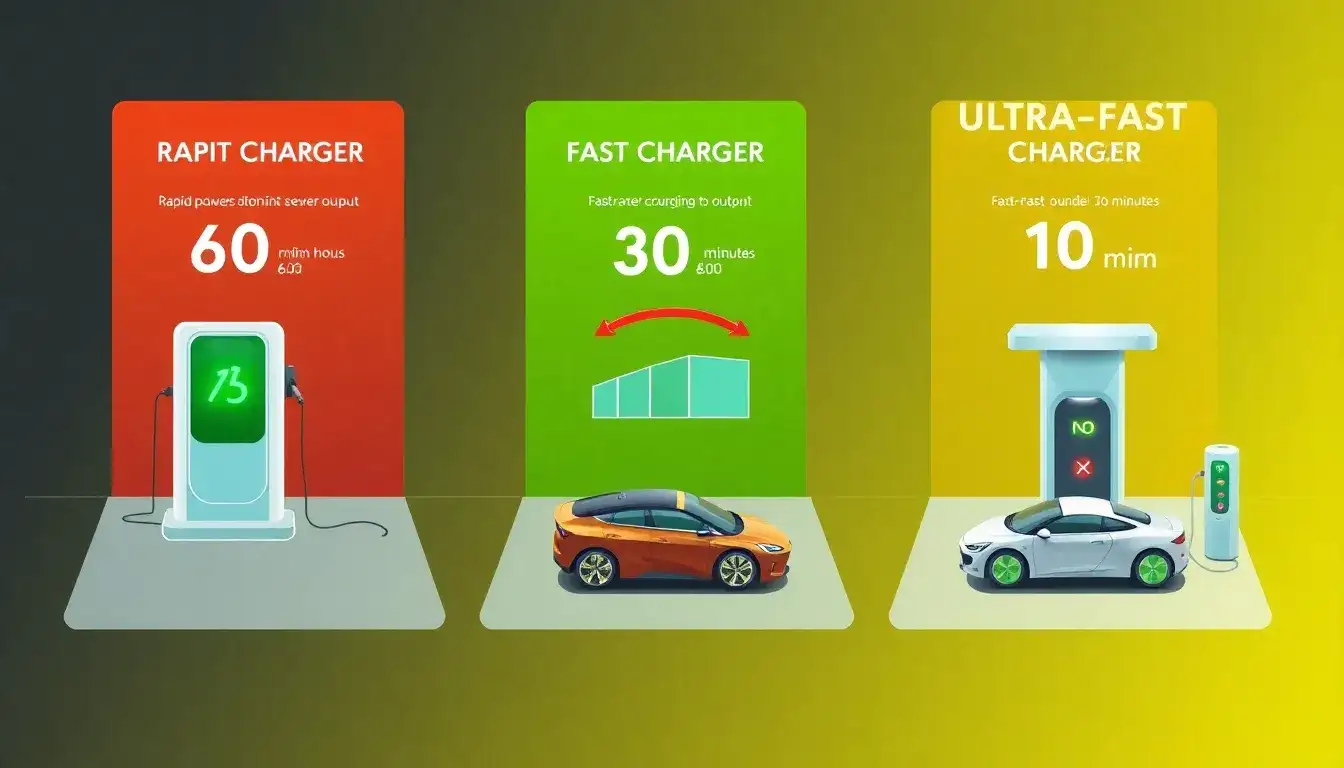
Fast Chargers
- Power Output: Usually between 7 kW and 22 kW.
- Charging Time: Typically takes between 1 to 4 hours to charge an EV.
- Charging Method: Often use AC (Alternating Current).
- Use Case: Suitable for daily charging needs such as at home, work, or while shopping; convenient for topping up rather than full rapid charges.
- Cost and Impact: More cost-effective and gentle on the battery, causing minimal wear.
- Availability: Widely available in urban and residential areas.
Rapid Chargers
- Power Output: Generally between 50 kW and 149 kW (sometimes cited as 25 kW to 150 kW+).
- Charging Time: Can charge an EV up to 80% in about 30 to 60 minutes.
- Charging Method: Use DC (Direct Current) for faster charging, with connectors like CHAdeMO, CCS, or Tesla-specific connectors.
- Use Case: Ideal for long-distance travel or quick top-ups on road trips, offering significantly faster charging than fast chargers.
- Cost and Impact: Typically more expensive per charge and may contribute to faster battery wear if used frequently.
- Availability: Less common than fast chargers but increasing, especially at highway stops and service stations.
Ultra-Fast (Ultra-Rapid) Chargers
- Power Output: 150 kW and above, with some ultra-rapid chargers delivering up to 350 kW.
- Charging Time: Can charge an EV battery in approximately 15 to 20 minutes, significantly reducing downtime.
- Use Case: Designed for very fast top-ups during long journeys or where minimal charging time is critical.
- Cost and Impact: Highest cost and energy demand among the three, with concerns over potential battery degradation due to the high charging speeds.
- Availability: Still relatively limited but expanding with growing EV infrastructure.
Summary Table
| Feature | Fast Charger | Rapid Charger | Ultra-Fast (Ultra-Rapid) Charger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | 7 kW – 22 kW | 50 kW – 149 kW (25-150 kW+) | 150 kW and above (up to 350 kW) |
| Charging Time | 1 – 4 hours | 30 – 60 minutes | 15 – 20 minutes |
| Charging Method | AC | DC | DC |
| Typical Use Case | Daily charging, short stops | Long-distance travel, quick top-ups | Rapid top-ups during long trips |
| Cost per Charge | Lower | Higher | Highest |
| Battery Impact | Minimal wear | Potential for battery wear | Higher potential battery wear |
| Availability | Widely available | Increasing, mainly at highways | Limited but expanding |
In essence, the charging categories reflect a trade-off between charging speed, cost, and potential impact on battery health, with fast chargers being suitable for routine use, rapid chargers for quicker top-ups especially on journeys, and ultra-fast chargers offering the fastest charge times for long-distance travel scenarios.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-differences-between-rapid-chargers-fast-chargers-and-ultra-fast-chargers/


