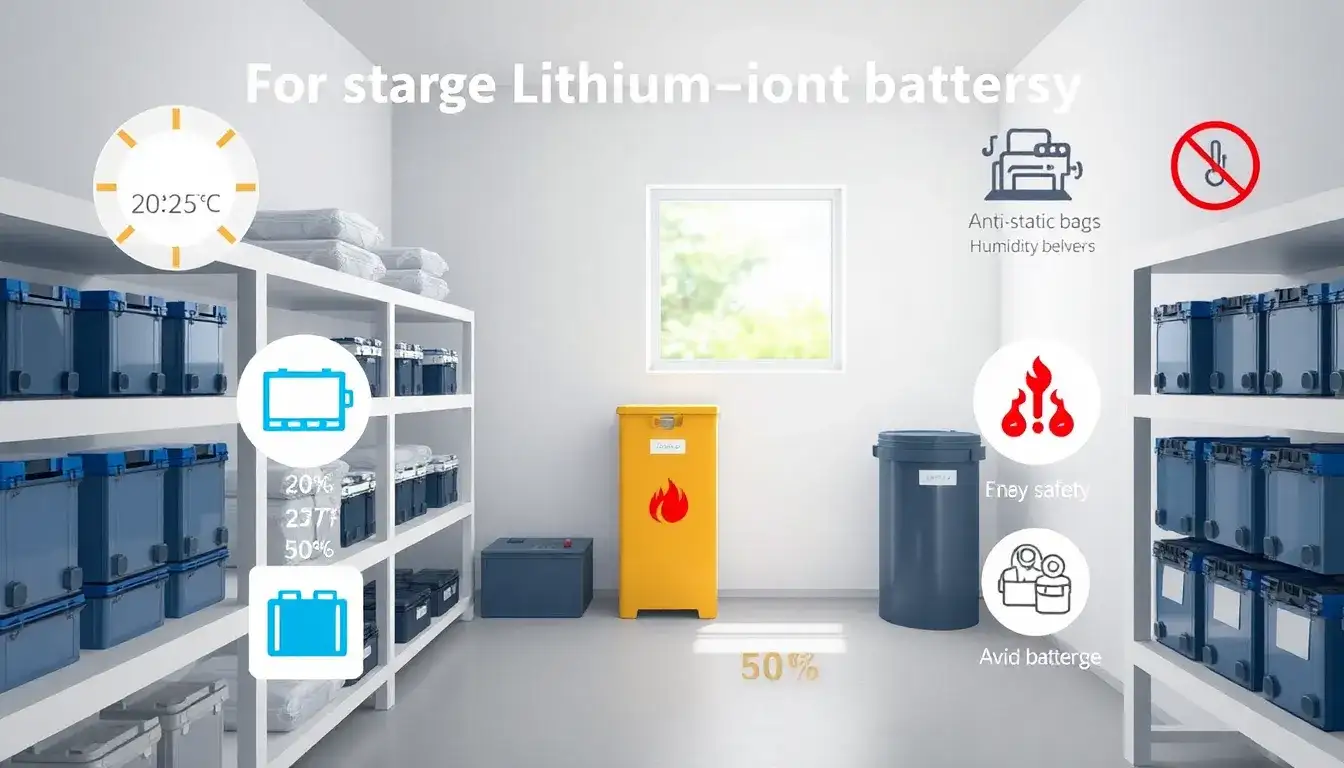
Storing lithium-ion batteries safely and effectively requires adherence to several best practices. These practices help prevent hazards like fires, explosions, and damage to the batteries. Here are key recommendations for storing lithium-ion batteries:
Best Practices for Storing Lithium-Ion Batteries
1. Charge Level
- Storage Charge Level: Store lithium-ion batteries with a charge between 40% and 60% capacity. This reduces stress on the cells and minimizes the risk of degradation or thermal runaway.
- Recharge Regularly: For long-term storage, inspect batteries every three months and recharge them as needed to maintain the optimal charge level.
2. Environmental Conditions
- Temperature: Store batteries in a cool, dry place with temperatures between 40°F and 77°F (4°C to 25°C) for short-term storage. For long-term, maintain temperatures between 50°F and 86°F (10°C to 30°C).
- Ventilation: Ensure good airflow to prevent hothouses or humid conditions, which can cause overheating and damage.
- Avoid Direct Sunlight and Heat Sources: Keep batteries away from direct sunlight, heaters, or ignition sources to prevent excessive heat buildup.
3. Handling and Storage
- Non-Combustible Surfaces: Never charge or store batteries on soft or combustible surfaces like fabric or wood. Instead, use metal or concrete surfaces.
- Dedicated Storage: Use a non-conductive container or fireproof storage unit to prevent accidental short circuits and protect against thermal runaway.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Ensure batteries are not touching each other to reduce the risk of fire spreading.
4. Battery Condition
- Inspect Before Storage: Check batteries for damage before storing them. Damaged batteries should be disposed of properly and not stored.
- Dispose of Damaged Batteries: Safely dispose of any dropped, swollen, or visibly damaged batteries through proper recycling channels.
5. Chargers
- Use Correct Chargers: Always use manufacturer-approved chargers that match the battery’s voltage and capacity specifications to avoid overcharging or overheating.
6. Leak Containment
- Prepare for Leaks: Although rare, damaged batteries can leak flammable electrolyte. Use containment solutions like bunded cabinets or drip trays to manage spills.
By following these best practices, you can ensure safe and effective storage of lithium-ion batteries, minimizing risks and prolonging their lifespan.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-best-practices-for-storing-lithium-ion-batteries/


