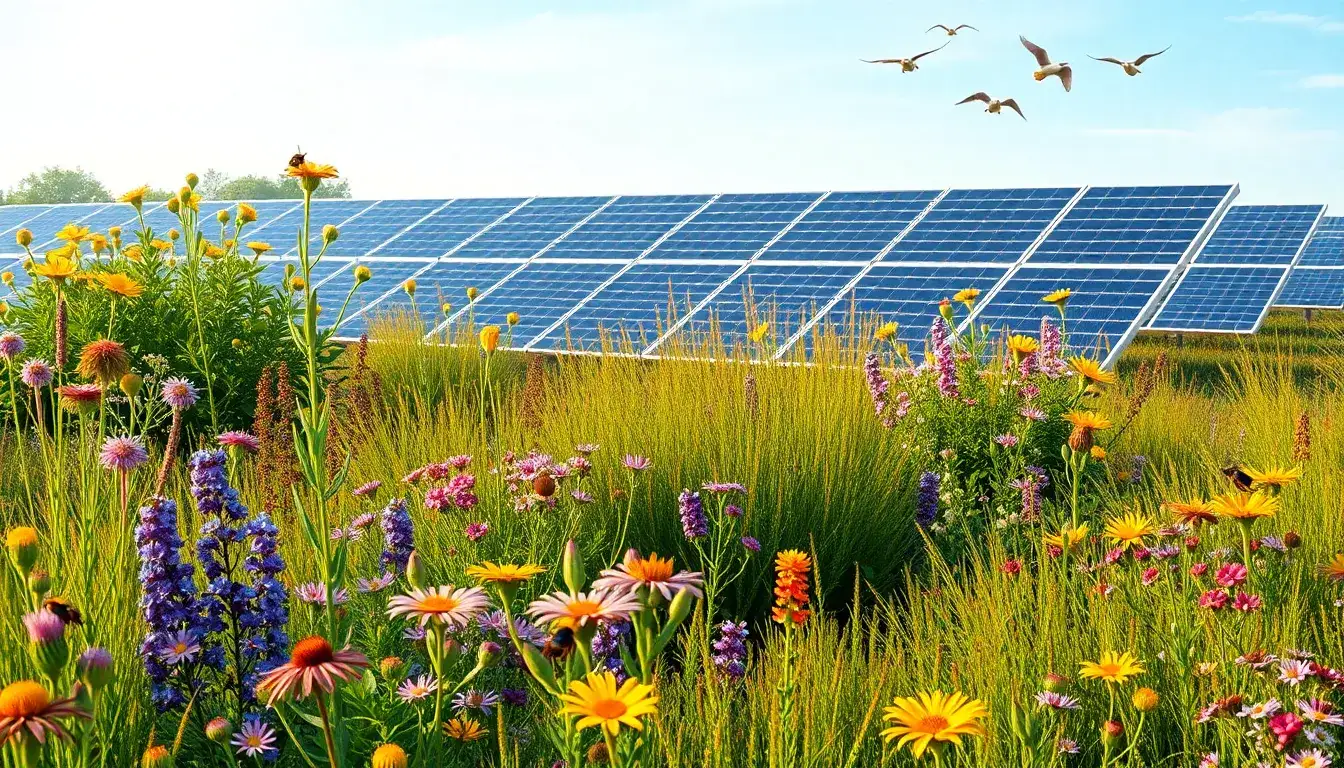
When designing solar arrays to enhance biodiversity, choosing the right native plants is crucial. These plants should support local wildlife, particularly pollinators, and help restore native ecosystems. Here are some guidelines and examples of native plants that can be effective:
Criteria for Selecting Native Plants
- Pollinator Support: Choose plants that are rich in nectar and pollen to attract bees, butterflies, and other pollinators.
- Local Adaptation: Use plants that are native to the specific region to ensure they thrive in local conditions and support regional wildlife.
- Low Maintenance: Select plants that require less watering and mowing to reduce maintenance costs.
Examples of Native Plants
- Milkweed (for monarch butterflies)
- Purple Coneflower (for bees and butterflies)
- Black-eyed Susan (for bees and butterflies)
- Little Bluestem and Big Bluestem (native grasses that support a wide range of insects)
Design Considerations for Solar Arrays
- Raised Panels: Elevate solar panels to allow sunlight to reach the plants below and ensure sufficient space for vegetation.
- Native Wildflowers and Grasses: Plant a mix of native wildflowers and grasses to mimic natural habitats and support biodiversity.
- Soil Conservation: Use native plants to stabilize soil and prevent erosion, improving overall ecosystem health.
By incorporating these types of native plants into solar array designs, you can create environments that enhance biodiversity, support pollinators, and even reduce maintenance costs over time.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/what-are-the-best-native-plants-to-use-in-solar-arrays-for-enhancing-biodiversity/