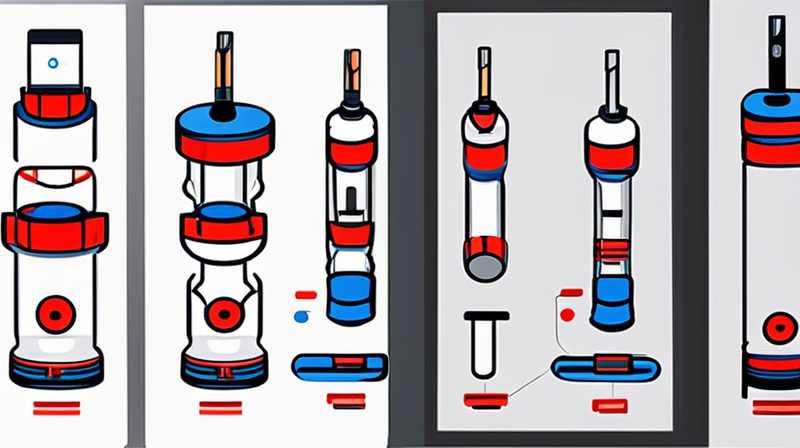
To successfully disassemble a solar solenoid valve body, follow these essential steps: 1. Gather necessary tools and safety gear, 2. Disconnect power supply to prevent accidents, 3. Detach the valve from its mounting location, 4. Carefully remove the solenoid cover and components, 5. Take note of the arrangement of inner parts for reassembly, 6. Clean or replace seals to ensure optimal performance.
When disassembling a solar solenoid valve body, attention to detail and proper technique are essential to avoid damage and ensure a successful reassembly.
1. INTRODUCTION TO SOLENOID VALVES
Solar solenoid valves serve an essential role in directing the flow of fluids within various applications, particularly in irrigation systems that rely on solar energy. These valves employ electromagnetic mechanisms to control fluid movement, making them crucial for efficient operation. Understanding the construction and functionality of these devices is vital for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
The solenoid valve body comprises several integral components, including coils, springs, and various seals. Each part contributes to the overall functionality, and disassembling the valve requires knowledge of how these components interact. Having a clear understanding of their arrangement and purpose will pave the way for a successful disassembly process.
2. TOOLS REQUIRED FOR DISASSEMBLY
Before attempting to disassemble a solar solenoid valve, it is imperative to gather the appropriate tools to ensure efficiency and safety during the process. 1. Wrenches and screwdrivers are essential for loosening fittings, 2. Pliers may assist in gripping and pulling components apart, 3. A multimeter is advisable for testing electrical systems, 4. Cleaning materials such as brushes and cloths aid in maintaining components.
The choice of tools can significantly impact the ease with which the solenoid valve can be disassembled. For example, utilizing a precise torque wrench can help in safely loosening any tightly fitted parts without causing damage. Moreover, a comprehensive toolset can prevent frustration when encountering different types of screws or fittings.
3. PREPARATION FOR DISASSEMBLY
Proper preparation plays a crucial role in the successful disassembly of the solar solenoid valve body. Safety precautions should include wearing gloves and goggles to protect against potential hazards during the process. Additionally, ensuring that the system’s power supply is disconnected minimizes risks related to electrical shock.
Before initiating disassembly, take the time to document or photograph the valve’s current assembly state. This record will provide invaluable guidance when reassembling the valve, ensuring that every component returns to its correct position. Furthermore, familiarizing oneself with the valve’s specifications and user manual can offer insights into common pitfalls and troubleshooting techniques.
4. REMOVING THE VALVE FROM ITS MOUNTING
The initial step in disassembly involves detaching the valve from its mounting location. This requires adequately assessing how the valve is secured, whether it’s through bolts, brackets, or clamps. Using the appropriate tools, carefully remove any fasteners holding the valve in place. It is crucial to take caution during this stage to prevent damaging the piping or surrounding infrastructure.
Once the valve is detached, inspect it for any visible signs of wear or damage, which may indicate underlying issues that contributed to malfunctions. This inspection serves as an opportunity to address potential problems while the valve is disassembled.
5. DISCONNECTING THE SOLENOID COIL
With the valve removed from its mounting position, attention now turns to the solenoid coil. This component is often secured by screws or clips, which may require careful handling to avoid breaking or distorting the coil. 1. Start by marking the wires connected to the coil to avoid confusion during reassembly, 2. Unscrew or unclamp the coil gently to separate it from the valve body.
It is advisable to measure the coil’s electrical resistance at this stage using a multimeter; this can provide insights into the coil’s health and functionality. If the coil indicates an open circuit or significantly deviates from the specified resistance range, it may be time for replacement.
6. REMOVING INTERNAL COMPONENTS
Upon removing the solenoid coil, the next step involves accessing the internal components of the valve body. These often include springs, plungers, and seals that work together to facilitate the valve’s operation. 1. Note the arrangement of these parts—this is crucial for reassembly, 2. Use pliers to carefully pull out the plunger, ensuring that no small components slip away unnoticed.
Cleaning the internal components during this stage is beneficial, particularly the valve seat and sealing areas where debris can accumulate. Employ appropriate cleaning solutions that are compatible with the materials, ensuring no residues are left behind that could affect future functioning.
7. INSPECTING AND REPLACING SEALS
Seals within the solenoid valve are critical for maintaining leaks and preserving pressure within the system. After removing the components, conduct a thorough inspection of all seals and O-rings to assess their condition. If any signs of wear, cracking, or deformation are evident, replacing them is imperative for optimal performance.
During replacement, carefully select seals that match the specifications of the original parts. Using mismatched seals can lead to leaks or malfunctions after reassembly, negating the benefits of the disassembly process. Proper lubrication of new seals before installation can ensure a snug fit and prevent future leakage.
8. ASSEMBLING BACK THE VALVE
Once all components are cleaned, inspected, and replaced as necessary, proceed with reassembling the valve. Start with the internal components, paying careful attention to the order and orientation of each part, 1. Gradually reinsert the plunger and any springs, ensuring they seat correctly, 2. Replace the seals and O-rings to provide adequate closure.
Following the internal assembly, reattach the solenoid coil, fastening it securely according to the original configuration. This step requires careful handling, as excessive force can damage the coil or compact elements incorrectly.
9. RECONNECTING THE VALVE AND TESTING
Once the valve has been reassembled correctly, it must be mounted back into its original position. You will need to securely fasten it, ensuring that all connections are tight and leak-proof. Before reconnecting power to the system, it’s wise to conduct a pre-test by examining the valve visually for any signs of improper assembly.
Upon ensuring everything is in place, reconnect the power supply and activate the system. Observing the valve’s operation in real-time is vital; listen for any abnormal sounds and check for leaks around the connections. A proper functioning valve will operate smoothly without unusual noises or interruptions in flow.
10. MAINTENANCE TIPS FOR SOLENOID VALVES
Post-disassembly, implementing a routine maintenance schedule can greatly extend the life of the solar solenoid valve. Regular inspections should include visual checks for signs of wear, leaks, or corrosion, as well as functional tests to confirm the proper operation of the solenoid. 1. Establish a routine for cleaning the valve body and internal components, 2. Ensure that connections, both electrical and fluidic, are tight and secure.
Documenting your maintenance activities can help track the valve’s performance over time, allowing for proactive measures before significant issues arise. A well-maintained valve can significantly enhance the efficiency of a solar energy system, promoting sustainability and reliability in fluid management.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
WHAT IS A SOLENOID VALVE?
A solenoid valve is a type of electromechanical valve that uses an electric current to control the flow of fluids. It consists of a coil, plunger, and various seals that work together to open or close the valve based on electrical signals. Solenoid valves are widely used in various applications, including irrigation systems, HVAC, and automotive industries. Their ability to automate fluid control makes them a popular choice for systems controlled through electrical inputs.
The operation of the valve is straightforward; when an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field, causing the plunger to move and either open or close the flow path. The design can vary based on the application and intended fluid type, influencing parameters like pressure ratings and flow capacity. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity of solenoid valves.
HOW DO I KNOW IF MY SOLENOID VALVE IS FAULTY?
Identifying a faulty solenoid valve can be achieved through several diagnostic methods. Common symptoms of a malfunction may include the valve failing to open or close, unusual noises during operation, or visible leaks around the valve body. To check the functionality, first, ensure that power is supplied to the solenoid; using a multimeter, measure the electrical resistance of the coil. If the resistance reading deviates significantly from the manufacturer’s specifications or indicates an open circuit, the coil may need replacement.
Additionally, visually inspecting for debris accumulation or external damage can provide insights into the valve’s condition. If internal components are not sealing correctly, this may also contribute to system inefficiencies or failures. Regular testing and maintenance schedules can help to identify issues before they lead to major operational problems.
WHAT ARE COMMON CAUSES OF SOLENOID VALVE FAILURE?
Several factors can contribute to the failure of a solenoid valve, including contamination, electrical issues, overheating, and mechanical wear. Contaminants, such as dirt and debris, can obstruct moving parts, leading to malfunctions. Inadequate electrical supply can prevent the solenoid from operating correctly, while overheating may occur due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures or incorrect wiring.
Mechanical wear is a natural process that can lead to the degradation of seals and internal components over time. Regular inspections and maintenance can mitigate these risks by ensuring that the system remains free of contaminants and that electrical connections are secure. Understanding these potential causes can aid in preventative strategies and enhance the overall lifespan of the solenoid valve.
Completing the process of disassembling a solar solenoid valve body requires careful attention to detail and adherence to best practices throughout the entire procedure. Proper preparation involves gathering the appropriate tools and ensuring safety before initiating disassembly. A systematic approach ensures that the internal components are correctly accessed, inspected, and replaced as necessary. Assembling the valve back in the correct order is crucial, and routine maintenance post-reassembly will promote a longer lifespan and efficiency. By familiarizing oneself with the inner workings of solenoid valves and implementing a diligent maintenance schedule, one can significantly improve overall operational reliability and effectiveness in fluid control systems. Following these guidelines allows for better management of both solar energy applications and fluid dynamics while ensuring a sustainable approach to usage and maintenance.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-to-disassemble-the-solar-solenoid-valve-body/


