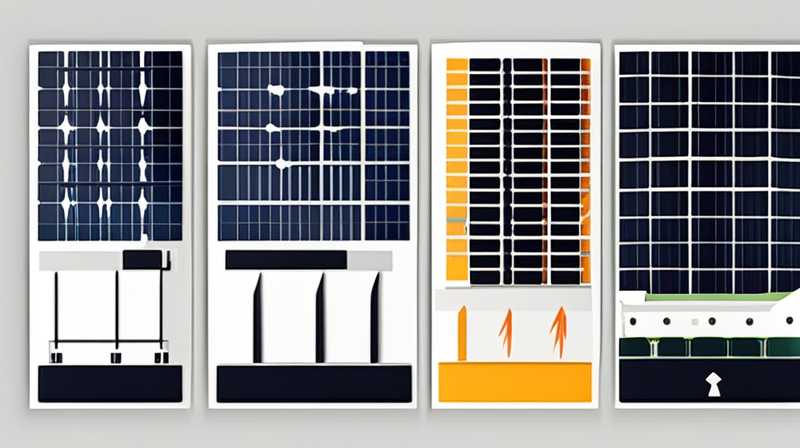
How many grid lines does a solar panel have now? The general range for grid lines on solar panels typically falls between 60 and 72 grid lines, depending on the specific design of the module. 1. The grid lines, also known as busbars, serve a crucial role in collecting and distributing the electric current generated by the solar cells, ultimately impacting efficiency and performance. 2. The number of grid lines influences the overall surface area of the solar panel, which affects the amount of sunlight captured. 3. Advances in manufacturing techniques have allowed for variations in grid line configurations, optimizing energy output while reducing material costs.
1. SIGNIFICANCE OF GRID LINES
When discussing solar panels, the importance of grid lines becomes clear. They are integral to the functionality of photovoltaic systems. Primarily serving to facilitate the transport of electricity generated by solar cells, these lines collect the electric current produced from each cell. They are usually made from conductive metals like silver, ensuring minimal resistance as the electricity travels through. This configuration is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of solar panels. In recent years, innovations in manufacturing technologies have led to varied designs in the grid line structure, which can enhance overall energy conversion.
Moreover, the arrangement and number of grid lines can impact the aesthetic appearance of solar panels. Traditional designs, featuring a typical pattern of 60 or 72 grid lines, often result in a familiar look. However, newer models may reduce the number of lines, promoting a sleeker appearance while maintaining performance. This change can appeal to potential consumers looking for more visually appealing options.
2. EVOLUTION OF SOLAR PANEL DESIGN
The landscape of solar technology has rapidly advanced, resulting in significant changes in solar panel designs, including the number of grid lines. In the past, panels usually contained higher quantities of busbars, which could lead to efficiency losses due to shading and resistance issues. With increased understanding and technological advancements, manufacturers have developed panels with fewer but more strategically placed busbars. This alteration enhances performance while reducing the material costs associated with production.
Recent innovations have led to the introduction of half-cell technology. Utilizing smaller cells within the panel, these designs enable manufacturers to optimize both the number of grid lines and the overall efficiency. By dividing each cell in half, these configurations can generate more power per square meter while minimizing shading effects. This evolution has resulted in greater energy production capabilities and has contributed positively to the solar industry’s growth.
3. IMPACT ON ENERGY PRODUCTION
The interaction between grid lines and energy production cannot be understated. As solar panels with more effective grid line configurations perform better, the energy output can be enhanced. Grid lines are not merely structural components; they directly affect current collection efficiency. More busbars mean more pathways for electrons to flow, reducing the chances for resistive losses that typically accompany longer routes.
Electrical limitations tied to current generation may pose a challenge when panels are subjected to shading or obstructions. Therefore, the number and placement of grid lines directly influence performance, especially in less-than-ideal conditions. The latest technologies have aimed to mitigate these effects by incorporating grid line designs that minimize the shadows cast by the busbars themselves. Advanced options in solar panel technology facilitate improved energy capture and conversion, leading to better performance rates over the lifespan of the system.
4. FUTURE OF SOLAR PANEL GRID LINES
Looking ahead, the solar industry is likely to witness ongoing developments in grid line configurations. As research continues to explore the optimal balance between aesthetic appeal, efficiency, and material use, manufacturers will refine their designs further. The emergence of advanced materials, including transparent conductors and innovative alloys, may further influence future configurations. These materials can enhance performance while minimizing visual impact, leading to more possibilities for solar integration in various architectural designs.
With the ongoing push toward sustainability, the quest for higher energy conversion efficiency ensures that grid lines will play a critical role in future innovations. Companies that invest in R&D will likely spearhead these advancements, striving for designs that optimize electricity generation while maintaining environmental goals. As energy demands continue to rise and technology matures, the number and configuration of grid lines on solar panels will likely evolve, ensuring their effectiveness in meeting the world’s energy needs.
FAQs
WHAT ARE SOLAR PANEL GRID LINES?
Grid lines, often called busbars, are conductive strips on solar panels designed to collect and transport the electric current generated by solar cells. These metal strips primarily serve to connect individual cells and enable efficient flow of electrons, vital for overall solar panel performance. The material used for these lines is typically high-conductivity metals such as silver, ensuring low resistance and effective current distribution. Various designs have emerged in recent years that minimize the number of grid lines while maintaining efficiency, greatly enhancing aesthetic appeal and performance. In summary, grid lines are essential components enabling the function of solar technology, directly linked to its effectiveness in energy generation.
HOW DOES THE NUMBER OF GRID LINES AFFECT SOLAR PANEL EFFICIENCY?
Efficiency in solar panels is significantly influenced by the configuration of grid lines. Panels with more busbars can collect and distribute more electricity effectively, reducing resistive losses. However, a larger number of grid lines can lead to shading issues, which may negatively impact performance, especially under indirect light conditions. The optimization of grid line layouts, striking a balance between maximizing current collection and minimizing shading effects, is crucial. Recent innovations, such as half-cell technology, enhance energy production while minimizing costs by limiting the number of busbars needed without compromising efficiency. Ultimately, the sophistication of grid line design is vital to achieving superior solar performance.
WHAT TECHNOLOGIES ARE EMERGING IN SOLAR PANEL DESIGN?
As the solar industry continues to advance, various technologies are emerging with the potential to transform the design of solar panels. Innovations include bifacial solar panels, which harness sunlight from both sides, and half-cell technology, where the cells are divided to operate more efficiently. The utilization of transparent conductive materials is also becoming more prevalent, allowing manufacturers to create panels that blend seamlessly with building designs. These innovations aim not only to improve energy conversion efficiencies but also to enhance the aesthetic appeal of solar solutions. Continuous research and development in manufacturing processes and materials promise to pave the way for further advancements in solar technologies.
Emphasizing the role of grid lines provides crucial insight into solar panel technology. The current standard mostly sees panels designed with 60 to 72 grid lines showcasing advanced configurations. As research evolves, tailored designs optimizing energy production while considering aesthetics are necessary. Enhancements in materials and technology will be key to influencing new designs, streamlining the grid line configuration to boost both operational efficiency and visual appeal. This adaptability remains paramount to meeting global energy demands and supporting sustainable initiatives, encouraging further growth in the solar industry. As attention to technology continues to increase, the exploration of various configurations ensures an exciting future where solar panels evolve to meet the challenges of sustainable energy generation.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-many-grid-lines-does-a-solar-panel-have-now/


