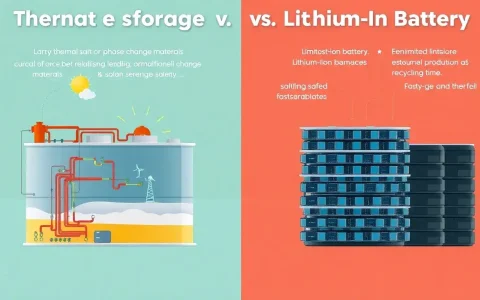
1. Energy storage systems can significantly lower energy expenses for Nigerian households through various mechanisms. 2. These systems enhance energy efficiency by optimizing the use of renewable sources, thereby reducing reliance on more costly fossil fuels. 3. Additionally, energy storage enables households to store excess energy generated during low-demand periods, which can be utilized during peak times when costs surge. 4. Finally, the implementation of smart technologies in conjunction with energy storage allows for better energy management, leading to further reductions in overall costs.
1. INTRODUCTION TO ENERGY STORAGE IN NIGERIA
Nigerian households face enduring challenges regarding energy access and reliability. In a country where power outages are commonplace and the cost of energy surges intermittently, innovative solutions are increasingly sought. Energy storage systems, particularly, stand out as a viable mechanism to alleviate financial burdens linked to energy consumption. With renewable sources such as solar and wind becoming more prevalent, understanding how to capture and utilize this energy effectively can lead to a transformative shift in household energy management.
Energy storage technology has advanced significantly over the past few years, making it more accessible than ever. By integrating systems like batteries into household architectures, families can reduce their dependence on centralized grids and the volatile costs associated with them. The rise of these technologies resonates not only with environmental aspirations but also with economic necessities, creating a strong foundation for households to thrive.
2. UNDERSTANDING ENERGY STORAGE TECHNOLOGIES
2.1 Overview of Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage encompasses a variety of technologies that allow the capture and later release of energy. Common solutions include lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, and even mechanical systems like pumped hydro storage. Each technology comes with unique characteristics, advantages, and challenges tailored to specific environments and energy demands.
Lately, lithium-ion batteries have dominated the market due to their high energy density and decreasing costs. With ongoing advancements in technology, their integration into residential settings has become more feasible and effective. Such batteries allow households to store surplus energy collected from solar panels during the day and utilize it during hours when energy costs are heightened.
2.2 Benefits of Energy Storage Technologies
The significant benefits of adopting energy storage technologies affect various aspects of household energy consumption. Energy independence is one primary advantage; by storing energy generated from renewable sources, households can shield themselves from fluctuations in energy prices. This capability proves essential in Nigeria, where energy costs can vary dramatically, making predictable budgeting challenging for families.
Furthermore, energy storage improves grid stability, particularly in locations with intermittent renewable generation. During peak demand times, stored energy can be dispatched to meet higher consumption needs, thereby stabilizing local grids. Households employing energy storage solutions can therefore play a crucial role in enhancing the resilience of their energy systems while driving down costs.
3. ECONOMIC IMPLICATIONS OF ENERGY STORAGE
3.1 Cost Reduction through Energy Storage
The integration of energy storage technologies fundamentally changes the economic landscape for Nigerian households. By mitigating peak demand charges, families can avoid exorbitant costs prevalent during high consumption hours. During such times, stored energy offers a cost-effective alternative to purchasing energy at peak prices.
When households harness energy storage systems, they reap the benefits of grid independence. Storing energy during low-cost periods allows consumers to minimize reliance on costly utility supplies, significantly lowering monthly bills. Additionally, energy independence brings empowerment and autonomy, enabling households to take control of their energy expenses.
3.2 Long-Term Financial Benefits
While the initial investment in energy storage technology may seem substantial, the long-term financial benefits often surpass these initial costs. Through decreased energy expenditures, households can recover their investments over time. Moreover, many governments or institutions incentivize the adoption of renewable technologies, further easing financial burdens.
As energy storage systems continue to proliferate, competition within the market may drive down prices. Over time, as technologies mature and production scales up, household energy storage systems may become even more affordable and accessible. For families in Nigeria, this means an increasingly feasible way to secure energy independence and stability in their financial planning.
4. RENEWABLE ENERGY AND ENERGY STORAGE SYNERGY
4.1 The Role of Renewable Energy
The incorporation of renewable energy sources is naturally complementary to energy storage systems. Solar and wind energy generation fluctuates based on environmental conditions, necessitating efficient storage solutions to maximize their use. By deploying solar panels combined with energy storage technologies, households can capture excess energy during sunny or windy periods.
This synergy not only stabilizes energy supply but also reinforces the economic rationale behind investments in renewables. Households can effectively harness and store renewable energy, reducing overall reliance on non-renewable sources, which are often subject to erratic price shifts. This transition promotes sustainability while combating the financial implications linked to fossil fuel dependency.
4.2 Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Utilizing energy storage technologies to leverage renewable energy enables households to maximize energy efficiency. By optimizing storage and usage patterns, households can effectively cut energy waste and enhance their energy independence. Such measures improve household financial health while nurturing a sustainable environment.
As more Nigerian households embrace solar energy generation alongside storage technologies, a ripple effect occurs within communities. As shared knowledge and practices develop, more families can participate in the transition towards a more resilient energy infrastructure. This communal movement fosters a culture of sustainability and encourages heightened adoption of energy-efficient practices.
5. POLICY FRAMEWORK AND SUPPORT FOR ENERGY STORAGE
5.1 Regulatory Environment
The Nigerian government recognizes the potential of energy storage solutions in addressing energy inefficiencies and driving economic benefits. Recent policies have aimed at promoting renewable energy initiatives, yet further framework development is necessary to streamline energy storage adoption. Clear regulatory pathways will encourage innovation and investment in this vital sector.
Beyond regulatory incentives, financial mechanisms offering subsidies, rebates, or tax credits for energy storage installations can significantly bolster adoption rates. Such initiatives lower the financial barriers associated with energy storage technologies, stimulating both market growth and consumer interest. By creating an enabling environment, policymakers can ensure that energy storage proliferates within households across Nigeria.
5.2 Future of Energy Storage Policies
The future of energy storage will depend largely on coordinated efforts among governments, industries, and communities. As households increasingly adopt energy storage solutions, tailored policies must address the specific needs and challenges faced in Nigerian contexts. This collaboration will facilitate efficient energy management and create new economic opportunities.
Investments in research and development are paramount for creating improved energy storage technologies. Innovations will drive down costs, enhance efficiency, and lead to breakthrough solutions that further transform household energy economics. Emphasizing collaborative advancements within the sector shall create a sustainable energy future benefiting all Nigerians.
6. REAL-LIFE EXAMPLES OF ENERGY STORAGE IN NIGERIA
6.1 Case Studies
Analyzing successful integrations of energy storage technologies showcases the potential outcomes possible for Nigerian households. In certain communities, the combination of solar power systems and energy storage has led to significant decreases in energy costs. Such case studies highlight how energy storage can facilitate the transition to a more resilient energy ecosystem.
Another growing area involves commercial operations leveraging energy storage for cost reductions. By shifting consumption patterns, these businesses report considerable savings on their energy bills while enhancing operational efficiency. These success stories serve as models for households to consider as they investigate potential energy storage implementations.
6.2 Community Adaptations and Ecosystem Benefits
The gradual acceptance of energy storage technologies fosters a strong sense of community engagement and action. As families band together to adopt sustainable energy solutions, shared resources can lead to collective benefits. Communities that integrate energy storage initiatives experience enhanced energy resilience, better access to economic opportunities, and environmental stewardship.
Furthermore, as energy storage systems are incorporated into neighborhoods, the overall demand for fossil fuels diminishes. This transition contributes to reduced emissions and initiates progress toward a sustainable future for Nigeria. Ultimately, these collective adaptations position households not just to save money, but to contribute positively to the fabric of their communities and the environment.
6.3 Education and Capacity Building
Awareness and education around energy storage play critical roles in successful adoption within households. Programs aimed at informing families about the benefits and workings of energy storage systems can dispel misconceptions and inspire action. Educational initiatives empower individuals to make informed energy decisions.
As communities prioritize capacity-building efforts, local technicians will become better equipped to install and maintain energy storage systems. This localized expertise ensures the sustainability of energy storage solutions while bolstering the local economy through job creation. The virtuous cycle of education and empowerment moves Nigeria closer to realizing its energy transformation potential.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
WHAT EXACTLY IS ENERGY STORAGE?
Energy storage refers to the capture and retention of energy for later use, encompassing various technologies designed to address energy supply and demand discrepancies. Common methods include batteries, flywheels, compressed air, and even thermal energy storage systems. The primary objective of energy storage is to optimize energy usage by storing surplus energy produced when demand is low and releasing it during peak demand. This capability enhances overall system efficiency and resilience while potentially reducing costs associated with energy consumption.
In the context of Nigeria, energy storage can significantly improve household energy management. Utilizing energy storage allows families to mitigate reliance on traditional power sources, particularly during grids’ peak load periods. This shift is vital given Nigeria’s energy challenges, characterized by erratic supply and rising costs. As households leverage energy storage, they can attain greater independence and sustainability in their energy consumption practices.
HOW DOES ENERGY STORAGE LOWER ENERGY COSTS?
Energy storage imparts cost savings primarily through peak-load management. By storing energy during times when prices are low and utilizing it during peak demand hours, households can avoid higher energy costs associated with grid usage at those times. This practice leads to efficient energy consumption, ensuring families only pay for the energy they need during high-cost periods, resulting in substantial savings.
Additionally, energy storage systems allow households to maximize the use of renewable energy sources by capturing surplus energy produced during their peak generation times. This capability results in reduced reliance on fossil fuels, which are often more expensive and subject to price swings. Over time, as households move toward energy independence and efficient management of their consumption patterns, their overall energy expenses significantly decline.
WHAT ARE THE CHALLENGES ASSOCIATED WITH ENERGY STORAGE IN NIGERIA?
Several obstacles hinder the widespread adoption of energy storage in Nigeria. Initial capital costs associated with purchasing and installing energy storage systems can be prohibitive for many households, particularly in lower socioeconomic brackets. Additionally, the limited availability of financing options can exacerbate these challenges, making it difficult for families to invest in energy solutions.
Moreover, the current regulatory environment may not provide adequate support or incentives for energy storage implementation. The lack of relevant policies may dissuade potential users from pursuing energy storage options despite their clear benefits. Lastly, there may be issues related to public awareness, with many households yet to comprehend the advantages and workings of energy storage technologies available to them.
6. CONCLUSION
Embracing energy storage systems holds profound potential for Nigerian households, transforming their energy economics and overall quality of life. The spectrum of benefits such systems provide—reduced energy costs, enhanced reliability, and increased stability—makes a compelling case for adoption. As families navigate the uncertainties associated with energy availability and pricing, energy storage offers a lifeline, allowing them to manage usage more effectively while fortifying their financial resilience.
Challenges persist, particularly concerning affordability and accessibility of storage technologies. However, with proactive government interventions, innovative policy frameworks, and an evolving marketplace, households can experience a burgeoning energy landscape. Education and community engagement will be crucial to demystifying these systems, paving the way for widespread acceptance and incorporation into everyday practices.
Transitioning to an energy storage paradigm will not only benefit individual households but also catalyze a broader economic renaissance across Nigeria. A concerted effort embracing renewables and storage can lead to a significant reduction in dependence on non-renewable sources, nourishing the nation’s environment while promoting sustainable development. Ultimately, the successful integration of energy storage within Nigerian households heralds a promising future—one characterized by energy independence, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-energy-storage-can-reduce-energy-costs-for-nigerian-households-2/