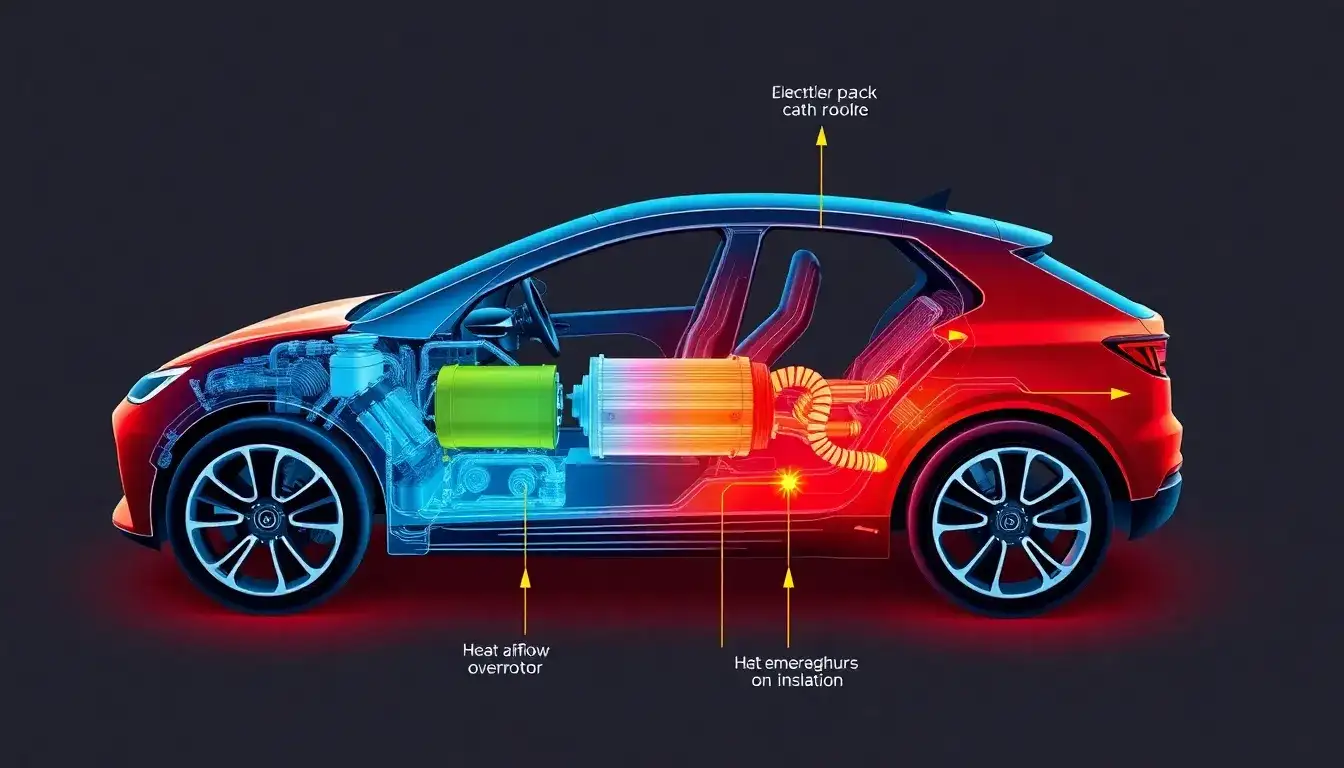
- Temperature Control: The system ensures that the electric motor operates within its optimal temperature range. High temperatures can lead to demagnetization of the motor’s magnets or degradation of insulation materials, which can cause inefficiency or even motor failure.
- Cooling Mechanisms: In hot conditions, the thermal management system uses cooling loops to prevent overheating. These loops can be configured in parallel or serial modes depending on environmental conditions. For example, in hot weather, the powertrain and batteries are cooled separately using a radiator for the powertrain and a chiller in the refrigerant loop for the batteries.
- Heat Management and Distribution: In colder conditions, the system can redirect heat generated by the motor to warm the batteries, ensuring efficient operation of both components. If necessary, additional heaters might be used to maintain optimal temperatures.
- Integration with Climate Control: The system also works in conjunction with the vehicle’s climate control to maintain a comfortable cabin temperature, which indirectly supports the overall thermal management by balancing heat flows within the vehicle.
By actively managing temperatures, the thermal management system helps prevent overheating, which is crucial for preventing motor burnout and maintaining overall vehicle efficiency.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-thermal-management-system-prevent-motor-burnout-in-evs/


