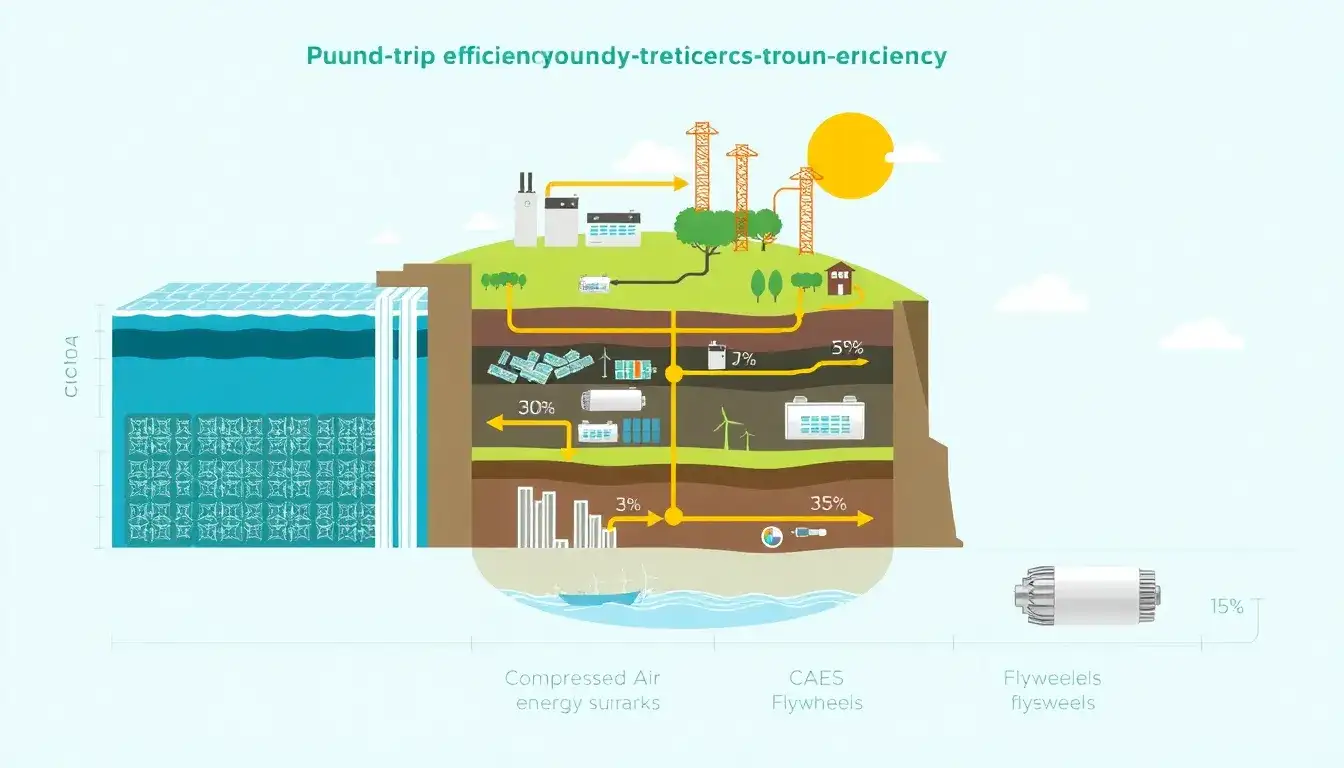
The round-trip efficiency of pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES) typically ranges between 70% and 80%, with some sources citing efficiencies slightly over 80% through a full cycle. This means that about 70-80% of the electrical energy used to pump water to a higher elevation can be recovered when the water is released to generate electricity.
Comparison with Other Energy Storage Technologies
| Technology | Round-Trip Efficiency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Pumped Hydroelectric Storage | ~70% to 80% (some >80%) | Largest-capacity grid storage; long duration (up to ~10 hours); economically beneficial for large-scale storage |
| Lithium-ion Batteries | Typically 85% to 95% | Higher efficiency but generally shorter duration (~4-6 hours); higher costs for very long-duration storage |
| Other Battery Technologies | Varies widely (~60% to 90%) | Examples: flow batteries, sodium-sulfur batteries with varying efficiencies and lifetimes |
| Compressed Air Energy Storage | Around 40% to 70% | Lower efficiency than pumped hydro; suitable for large scale but less common |
Key Points
- Pumped hydro storage is by far the largest-scale and most widely used form of grid energy storage worldwide, accounting for over 90% of utility-scale storage capacity.
- While its efficiency is somewhat lower than that of lithium-ion batteries, its ability to provide long-duration storage (typically around 10 hours) and cost-effectiveness makes it a crucial technology for grid stability and integrating renewable energy sources.
- The lower round-trip efficiency of pumped hydro (compared to certain batteries) is offset by the ability to store very large amounts of energy economically and release it over extended periods, which lithium-ion batteries cannot yet do at similar scales or costs.
In summary, pumped hydroelectric energy storage has a slightly lower round-trip efficiency (around 70%-80%) compared to lithium-ion batteries (85%-95%), but it excels in capacity, duration, and cost-effectiveness for large-scale grid storage, making it the cornerstone of current utility-scale energy storage systems worldwide.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-round-trip-efficiency-of-pumped-hydroelectric-energy-storage-compare-to-other-energy-storage-technologies/


