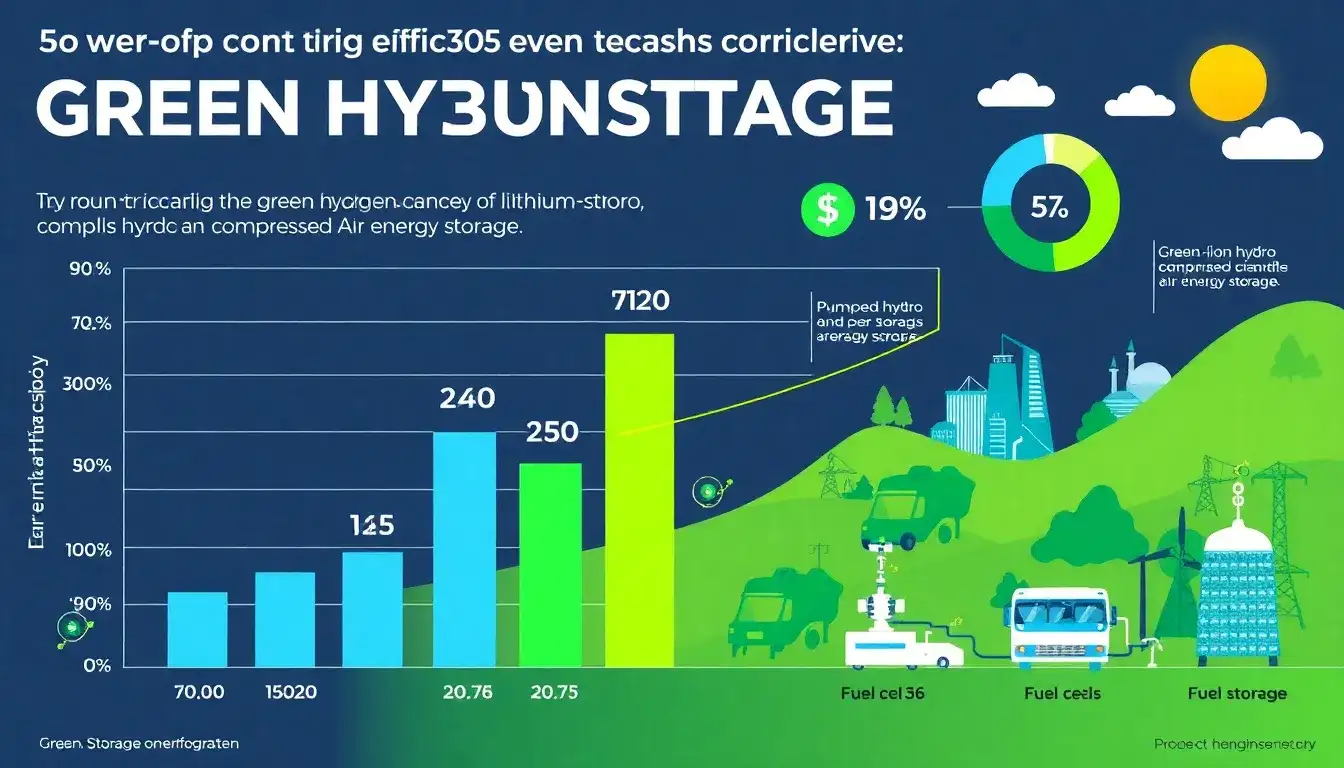
Hydrogen energy storage’s round-trip efficiency varies significantly based on technology and application:
- Green hydrogen storage (electrolysis + fuel cells) achieves 18–46% efficiency, with renewable-powered systems typically 30–32% and advanced systems potentially >80% under experimental conditions.
- Gasoline (for comparison): 28.5–31.4%, similar to renewable hydrogen but inferior to batteries.
- Batteries: 75–90% for lithium-ion, offering vastly superior efficiency.
- Pumped hydro: 70–85%, the most efficient large-scale storage.
- Compressed air: 42–67%, constrained by fossil fuel use in conventional systems.
- Flow batteries: 60–80%, emerging as a middle-ground solution.
Tradeoffs: Hydrogen’s lower efficiency is offset by long-duration storage capabilities and energy density advantages, making it viable for seasonal storage or heavy industries despite efficiency losses. Recent advancements aim to improve electrolysis and fuel cell efficiency, potentially closing the gap with other technologies.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-round-trip-efficiency-of-green-hydrogen-storage-compare-to-other-energy-storage-technologies/


