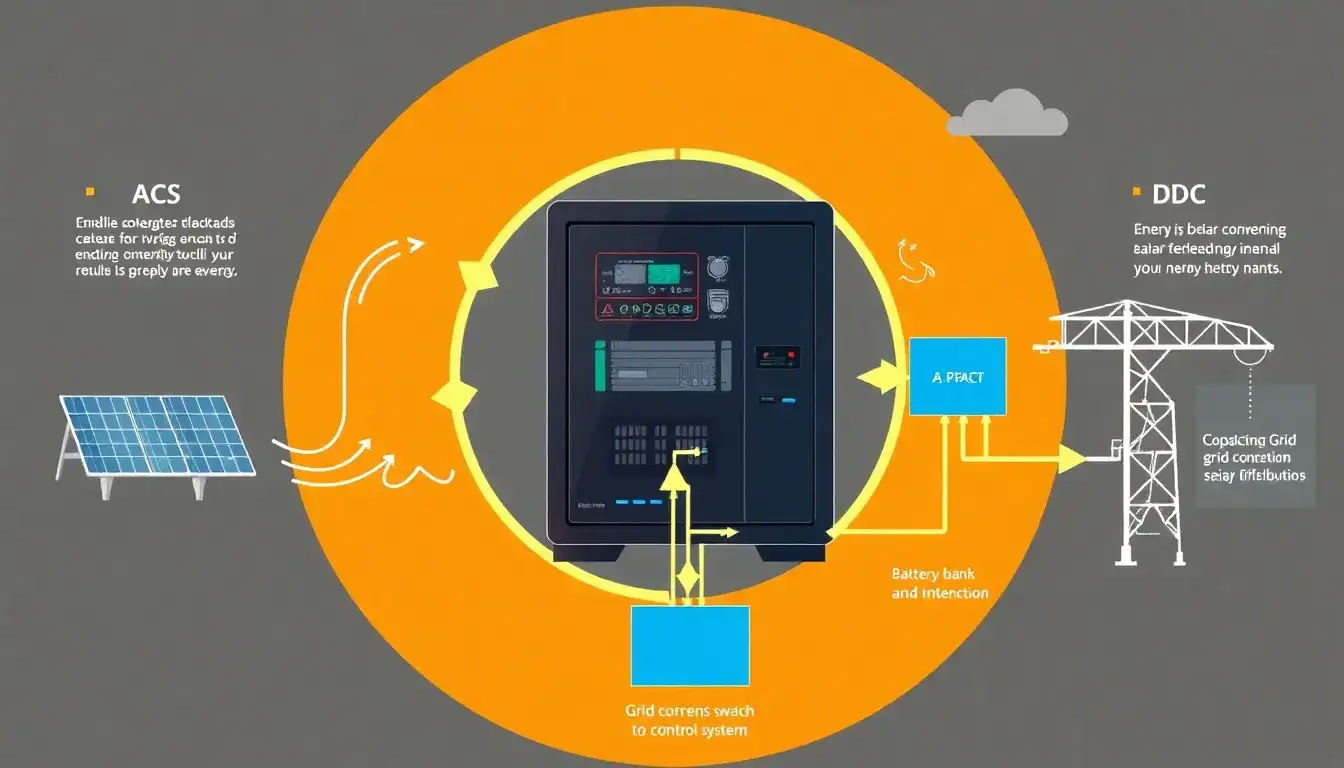
A Power Conversion System (PCS), often called a hybrid inverter in a Battery Energy Storage System (BESS), is a key component that manages the flow of electrical energy between the battery storage and the electric grid or load. It functions primarily as a bidirectional converter that can convert energy from DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current) and vice versa, enabling seamless integration of battery storage with the AC grid or AC loads.
Core Functions of PCS in a BESS
- Bidirectional power conversion:
- Inverter mode (DC to AC): When the battery discharges, PCS converts the stored DC electrical energy into AC power suitable for the grid or local AC loads.
- Rectifier/charger mode (AC to DC): During charging, PCS converts AC power from the grid or renewable sources into DC power to store in the battery.
- Power regulation and control:
PCS controls the voltage, frequency, and power factor of the output AC to comply with grid requirements and optimize the power quality. It regulates both active and reactive power flow to assist grid stability and efficient energy use. - Safety and protection:
Includes fault detection, isolation mechanisms, and shutdown procedures to ensure the safety of the battery system and connected electrical networks. - Communication and monitoring:
Integrates with the Battery Management System (BMS) and grid control systems via various communication protocols (e.g., RS-485, CAN) to monitor battery state, manage charge/discharge cycles, and enable remote control.
Additional Capabilities
- Grid support functions:
Modern PCS can participate in advanced grid services such as frequency regulation, voltage support, load leveling, peak shaving, black start capability, and island mode operation (off-grid). - Flexibility and integration:
PCS units can be modular and scalable, designed for various system sizes from small commercial to utility-scale applications. Some PCS designs support integration with renewable energy sources like solar PV and wind turbines, either on the DC side or AC side, offering hybrid energy management. - Efficiency and robustness:
Advanced semiconductor technologies including IGBT, MOSFET, and Silicon Carbide (SiC) devices enable high conversion efficiency, reducing losses and improving reliability, including operation in harsh environments.
Summary Table of PCS Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| DC to AC conversion | Converts stored battery DC power to AC for grid/load supply |
| AC to DC conversion | Converts grid or renewable AC power to DC to charge batteries |
| Voltage & frequency control | Ensures output matches grid/load electrical characteristics |
| Power factor correction | Aligns voltage and current phases to maximize real power transfer |
| Safety & protection | Fault detection, isolation, shutdown to protect system and connected infrastructure |
| Data monitoring & control | Real-time diagnostics, communication with BMS and grid controls |
| Grid services support | Load leveling, frequency regulation, peak shaving, black start, island mode |
| Renewable integration | Supports connection with solar/wind, enabling hybrid power flow management |
| Efficient & robust operation | High efficiency semiconductor technology, modular design, and operation in harsh conditions |
In essence, the PCS or hybrid inverter in a BESS is the intelligent bridge that facilitates two-way electrical energy flow, ensures safe and efficient operation of the battery storage, supports grid stability and power quality, and enables smooth integration of renewable energy sources and variable loads.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-power-conversion-system-pcs-or-hybrid-inverter-function-in-a-bess/


