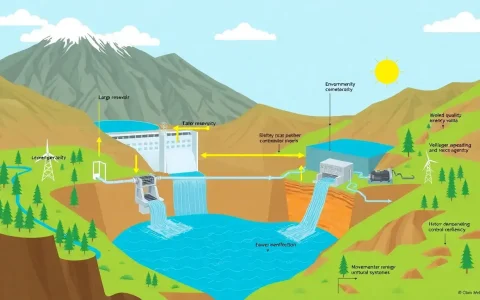
The lifespan of lead-acid batteries, particularly deep cycle lead-acid batteries, is generally shorter compared to other battery types like lithium-ion. Here’s a comparison of their lifespan and key characteristics:
Lead-Acid Batteries vs. Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Lifespan:
- Lead-Acid: Typically last between 300 and 1,000 charge cycles, with an average lifespan of 2 to 6 years. In optimal conditions, they can last 3 to 10 years.
- Lithium-Ion: Can last for 2,000 to 5,000 charge cycles, with an average lifespan of 5 to 15 years.
- Lifespan Factors:
- Lead-acid batteries are affected by depth of discharge; they should not be discharged beyond 50% to prolong their lifespan.
- Lithium-ion batteries can safely be discharged deeper without significant degradation.
- Environmental Impact:
- Lead-Acid: More environmentally hazardous due to lead content and frequent replacements.
- Lithium-Ion: Generally more environmentally friendly in terms of longevity and efficiency, though lithium mining has environmental concerns.
- Maintenance:
- Lead-Acid: Requires regular maintenance, such as checking electrolyte levels and ensuring ventilation.
- Lithium-Ion: Minimal maintenance requirements.
Other Considerations
- Energy Density and Charging Time:
- Lithium-ion batteries have a higher energy density and charge more quickly than lead-acid batteries.
- Operating Conditions:
- Lithium-ion batteries perform better in extreme temperatures compared to lead-acid, which can see reduced lifespan in hot conditions.
Overall, while lead-acid batteries are still widely used due to their cost-effectiveness upfront, lithium-ion batteries offer a longer lifespan and higher efficiency, making them a more cost-effective choice over time despite a higher initial cost.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-lifespan-of-lead-batteries-compare-to-other-battery-types/