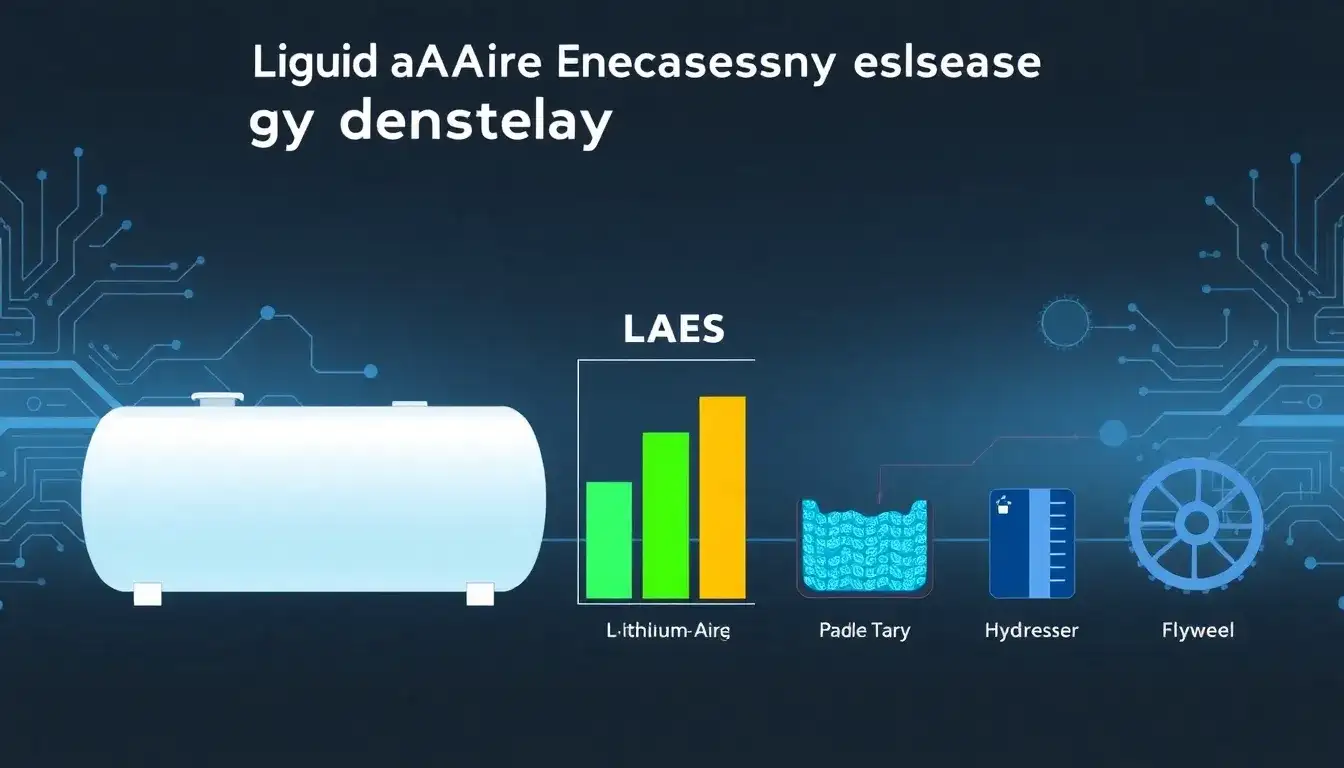
The energy density of Liquid Air Energy Storage (LAES) is notably higher than many other large-scale energy storage technologies, making it an attractive option for certain applications.
Energy Density Comparison:
- LAES has a high volumetric energy density, generally ranging from about 50 to 200 Wh/L, which surpasses that of Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES), typically in the range of 5 to about 40 Wh/L. This means LAES can store more energy per unit volume than CAES by approximately 5 times or more.
- Compared to pumped hydro storage (PHS), which is limited by geographical constraints and generally exhibits lower energy density, LAES offers much higher energy density and does not require specific topographical features like reservoirs at different elevations.
- The energy density of LAES is comparable to that of chemical energy storage systems, including some types of batteries, although typical lithium-ion batteries have higher round-trip efficiency. LAES energy density can be on the order of 40–100 kWh per cubic meter, which puts it in a competitive range with batteries in terms of storage capacity per volume, but with different cost and scalability profiles.
Other Considerations:
- While LAES boasts higher energy density than CAES and pumped hydro and is comparable to batteries, its round-trip efficiency is typically lower—often below 50% unless waste heat and cold recovery systems are employed, which can push efficiency above 60%.
- LAES benefits from using ambient air as an energy carrier (no fuel cost and no toxic materials) and from compact storage requirements because of its high energy density.
Summary Table:
| Storage Technology | Typical Energy Density | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Air Energy Storage | ~50–200 Wh/L (40–100 kWh/m³) | High volumetric density, compact, scalable |
| Compressed Air Energy Storage | ~5–40 Wh/L | Much lower energy density than LAES |
| Pumped Hydro Storage | Lower than LAES, geographically constrained | Large scale but requires specific terrain |
| Batteries (Li-ion) | Comparable or higher volumetric energy density | Higher efficiency but more costly and less scalable |
In conclusion, LAES offers a high volumetric energy density that surpasses traditional large-scale mechanical storage systems like CAES and pumped hydro while being comparable to chemical storage in terms of energy density, but its efficiency tends to be lower unless integrated with heat recovery systems.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-energy-density-of-laes-compare-to-other-energy-storage-systems/


