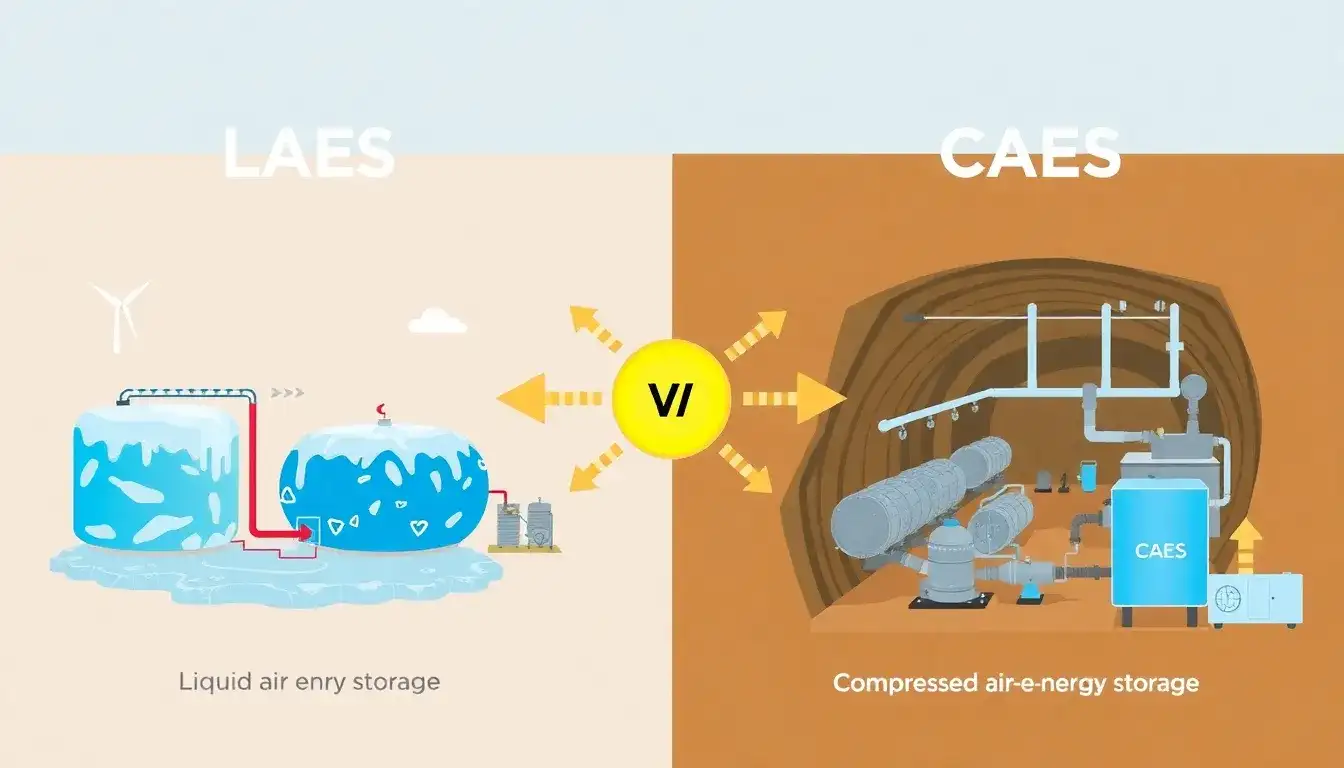
When comparing the efficiency of liquid air energy storage (LAES) to compressed air energy storage (CAES), several factors come into play:
Key Features and Efficiency of Each Technology
Liquid Air Energy Storage (LAES)
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a standalone LAES system can reach up to 57%. However, with innovations like using waste heat and oxy-fuel combustion, round-trip efficiencies can be significantly improved, even though exergy efficiency may slightly decrease.
- Mechanism: LAES works by liquefying air, which can be expanded to generate electricity. It can utilize waste heat to enhance thermal efficiency.
- Cost and Scalability: The Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) for LAES is relatively low, making it a promising option for grid-scale energy storage, especially when compared to lithium-ion batteries and pumped hydro storage.
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
- Efficiency: CAES typically has an efficiency between 40% and 52%. It involves compressing air into underground caverns and expanding it to generate electricity when needed.
- Mechanism: CAES requires substantial geological formations to store compressed air, limiting its geographical applicability.
- Cost and Scalability: While CAES can be more expensive than some alternatives due to site-specific requirements, it is still considered for large-scale energy storage due to its scalability.
Comparison
- Efficiency: LAES can achieve higher efficiencies than CAES, especially with advanced designs incorporating waste heat utilization and oxy-fuel combustion.
- Geographical Flexibility: LAES has an advantage over CAES in terms of geographical flexibility, as it doesn’t require specific underground formations.
- Cost and Scalability: Both technologies are scalable for large-scale energy storage, but LAES might offer more cost-effective solutions in the future, particularly for grid-scale applications.
In summary, LAES generally offers higher efficiency and greater geographical flexibility compared to CAES, though both technologies are suited for large-scale energy storage applications.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-efficiency-of-liquid-air-energy-storage-compare-to-compressed-air-energy-storage/


