Comparing the Cost of Pumped Hydro Storage to Other Energy Storage Technologies
Comparing the cost of pumped hydro storage (PHS) to other energy storage technologies can be done by examining both capital costs and cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Here’s a breakdown of how PHS compares to some prominent energy storage technologies:
Overview of Costs
-
Pumped Hydro Storage (PHS):
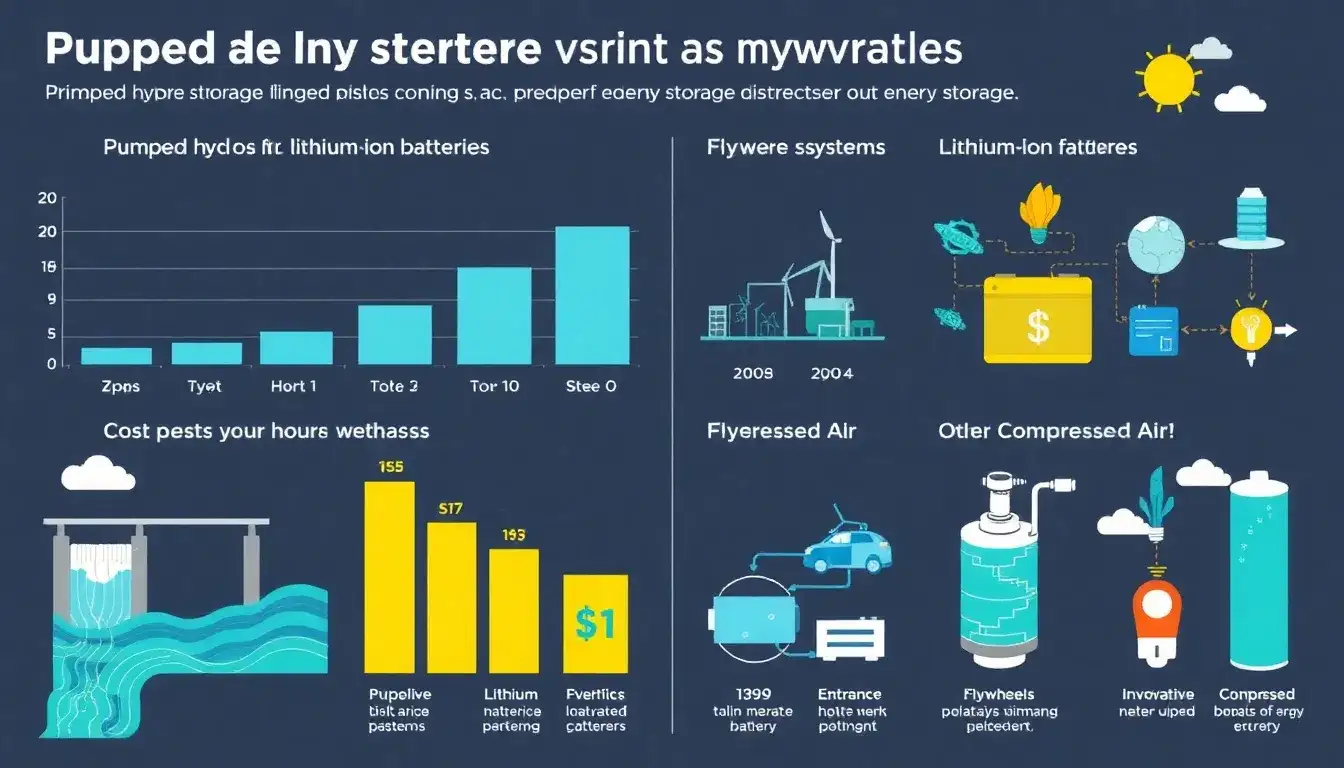
- Capital Costs: The cost of PHS typically ranges from about $1,800/kW to $3,200/kW, depending on the project specifics such as location, size, and design. For example, a 0.5 GW facility with 12 hours of storage might cost around $2,250/kW.
- Cost per kWh: When considering the energy storage aspect, PHS costs around $165/kWh for large-scale operations with an E/P ratio of 16, which includes construction and balance of plant costs.
-
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES):
- Cost per kWh: CAES has a cost of approximately $105/kWh for similar conditions, making it slightly more cost-effective per kWh than PHS.
-
Lithium-ion Batteries:
- Cost per kWh: Lithium-ion batteries vary significantly in cost, but for comparability, in a scenario with an E/P ratio of around 4, Li-ion batteries offer competitive pricing and potentially better overall value in terms of cycle life and cost reduction over time. The cost per kWh for Li-ion has been decreasing and now often ranges from about $150 to over $200 per kWh, depending on the specific application and scale.
Key Comparison Points
- Cost Basis: PHS is generally more favorable in large-scale, long-duration applications due to its high round-trip efficiency and ability to store energy for extended periods (like 8-16 hours).
- Scalability and Location: PHS requires specific geography (e.g., sufficient elevation difference), which limits its deployment sites compared to other technologies like Li-ion batteries, which can be installed virtually anywhere.
- Technology Maturity: PHS is a mature technology with established infrastructure and operational experience, whereas Li-ion batteries are undergoing rapid cost reduction and technological advancements.
Conclusion
Pumped hydro storage offers a cost-effective option for large-scale energy storage over long durations, especially when site-specific conditions are favorable. However, its suitability is highly dependent on geography, which limits widespread adoption compared to more versatile technologies like lithium-ion batteries.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-cost-of-pumped-hydro-storage-compare-to-other-energy-storage-technologies/


