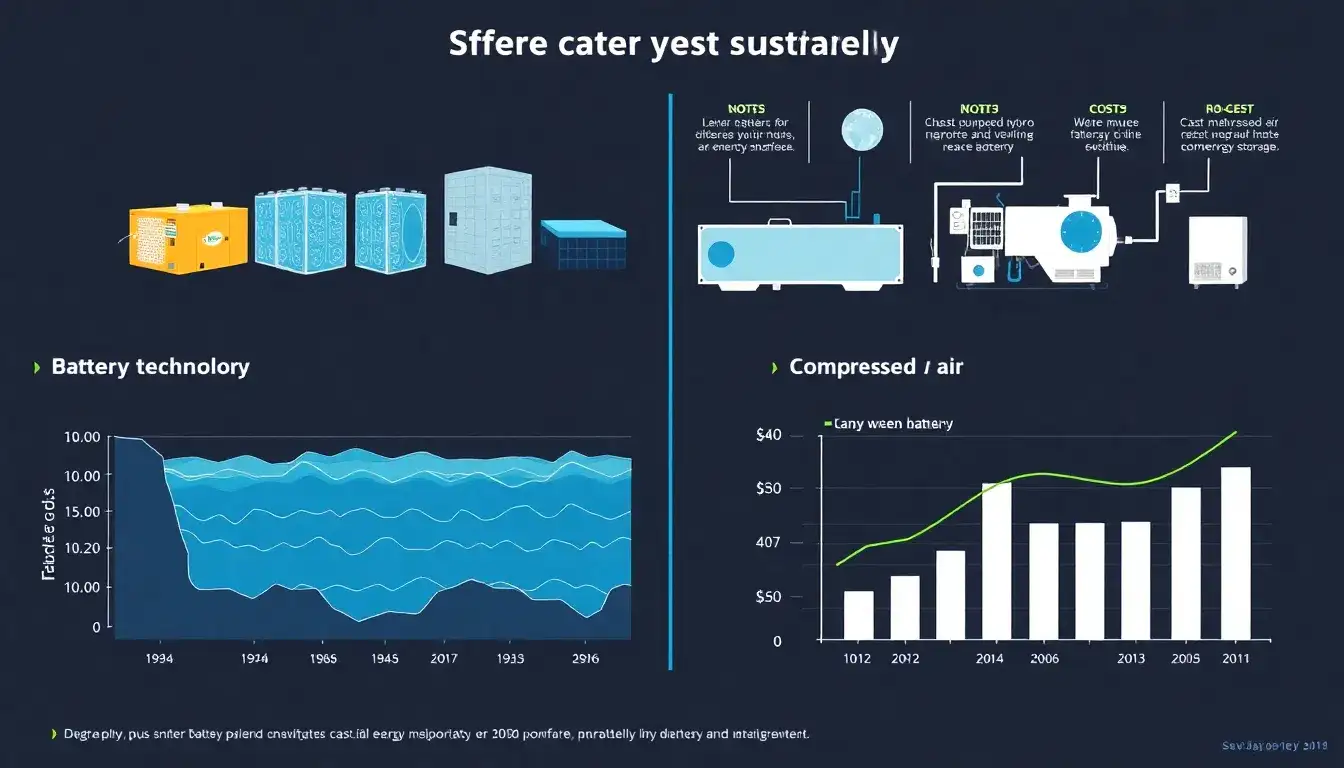
The cost of battery energy storage, particularly utility-scale lithium-ion battery systems, has seen significant reductions over the past decade but remains generally higher compared to some other long-duration energy storage (LDES) technologies.
Battery Energy Storage Costs
- For 4-hour lithium-ion battery storage systems, costs were about $482/kWh in 2022 and are projected to decline to a range of approximately $159 to $403/kWh by 2050 depending on cost scenarios (low, mid, high) according to NREL’s recent analysis.
- Commercial and industrial battery systems currently range broadly from about $400 to $750 per kWh, depending on technology and scale considerations.
- Battery pack costs drive most future cost reductions, driven by manufacturing scale and technological improvements, especially tied to electric vehicle battery demand growth.
Comparison to Other Energy Storage Technologies
- According to a BloombergNEF 2024 report, several LDES technologies with durations longer than 8 hours have capital costs lower than 4-hour lithium-ion batteries. For example:
- Thermal energy storage averaged $232/kWh
- Compressed air energy storage averaged $293/kWh
- Lithium-ion batteries for 4-hour storage averaged $304/kWh globally.
- In China, the cost advantage of certain LDES technologies like compressed air and thermal storage is more pronounced due to larger scale deployment and favorable policies, whereas lithium-ion batteries remain cheaper in that region versus other countries.
- Gravity storage had the highest average global capex cost at $643/kWh, showing significant variability among technologies.
- Non-lithium technologies generally have higher costs outside China and are unlikely to decline as rapidly as lithium-ion battery costs due to the latter benefiting from mass electric vehicle scale.
- Other technologies like pumped hydro and flow batteries also exist but tend to have different cost profiles and deployment scales.
Summary Comparison Table
| Technology | Approximate Capital Cost Range (USD/kWh) | Typical Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion Batteries (4 hr) | $304 – $482 (2022 data), projected down to $159-$403 by 2050 | 2-10 hours | Rapidly decreasing costs, EV-driven scale |
| Thermal Energy Storage | ~$232 (global average) | >8 hours | Cheaper for long duration, especially in China |
| Compressed Air Storage | ~$293 (global average) | >8 hours | Competitive for long duration, mature in China |
| Gravity Storage | ~$643 (global average) | Long duration | Highest CAPEX, less deployed |
| Flow Batteries | Higher than lithium-ion outside China | Long duration | Developing technology, variable costs |
| Pumped Hydro | Typically lower capital costs but site-dependent | Hours to days | Well-established but geographically limited |
Conclusion
While lithium-ion battery storage costs have fallen dramatically and are expected to continue decreasing, they remain relatively more expensive for long-duration storage compared to some alternatives like thermal and compressed air storage, especially for discharge durations beyond 8 hours. However, lithium-ion batteries benefit from strong manufacturing scale economies driven by the electric vehicle market, making them likely the fastest to see cost declines in the near term. Other technologies may be more economical for long-duration applications, particularly in regions like China where scale and policy support have matured their deployment.
This cost dynamic shapes the evolving energy storage landscape, with lithium-ion batteries dominant for short to medium durations and a growing role for alternative technologies in longer duration applications critical to deep decarbonization and grid reliability.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-the-cost-of-battery-energy-storage-compare-to-other-energy-storage-technologies/


