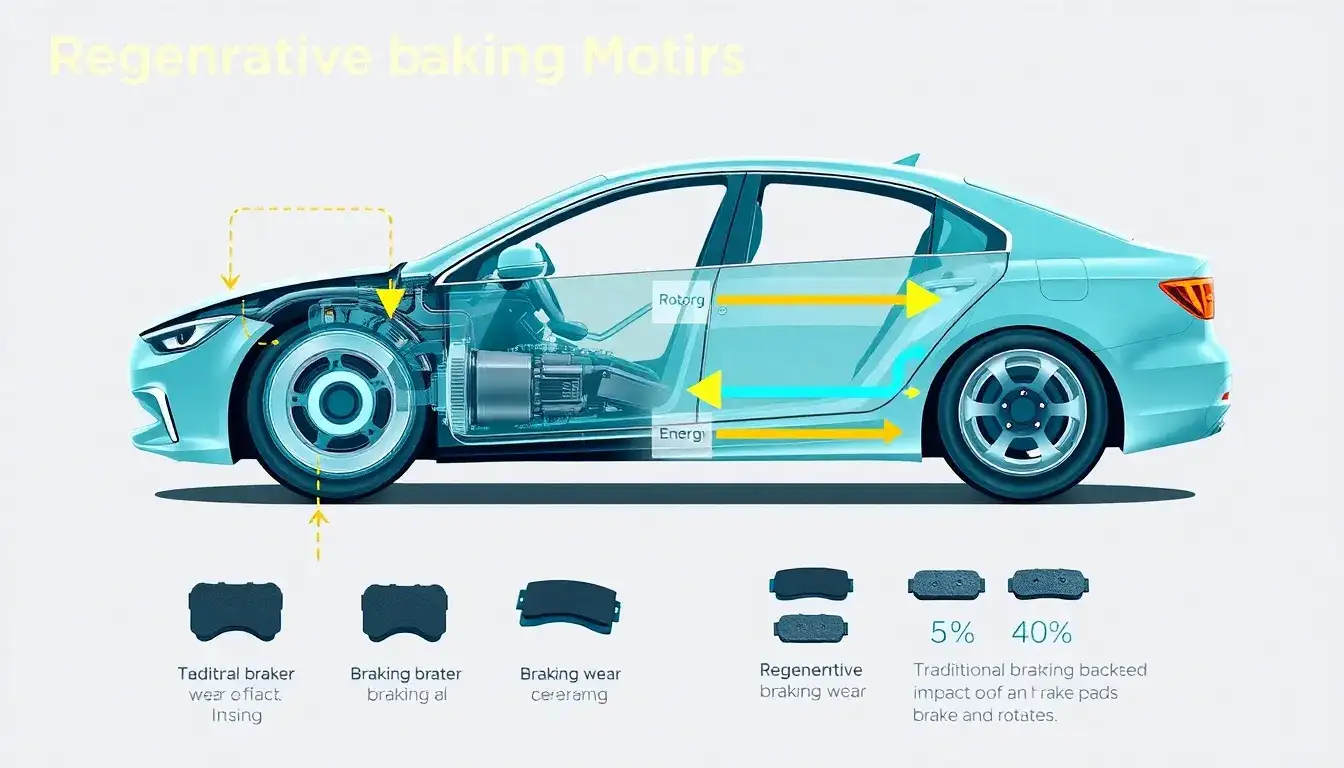
Regenerative braking can have both positive and negative effects on the lifespan of brake pads and rotors.
Positive Effects
- Extended Lifespan: Regenerative braking reduces the wear and tear on traditional brake components like pads and rotors by minimizing the use of friction-based braking. This can significantly extend their lifespan compared to vehicles that rely solely on conventional braking systems.
Negative Effects
- Corrosion and Rust: In vehicles that frequently use regenerative braking, the reduced friction between brake pads and rotors can lead to corrosion and rust buildup. This is particularly common in humid or high precipitation areas. If not addressed, it can cause uneven braking performance and potentially damage the rotors.
- Glazing of Brake Pads: The lack of regular friction can cause brake pads to glaze over, making them less effective when mechanical braking is needed. Glazed pads can increase stopping distances and pose a safety risk.
- Uneven Wear: When drivers primarily use regenerative braking but occasionally apply mechanical brakes under heavy loads, it can lead to uneven wear patterns on the brake pads. This inconsistent use can reduce braking efficiency.
Overall, while regenerative braking generally reduces wear on brake pads and rotors by minimizing their use, it also introduces potential issues if not properly managed.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-does-regenerative-braking-impact-the-lifespan-of-brake-pads-and-rotors/


