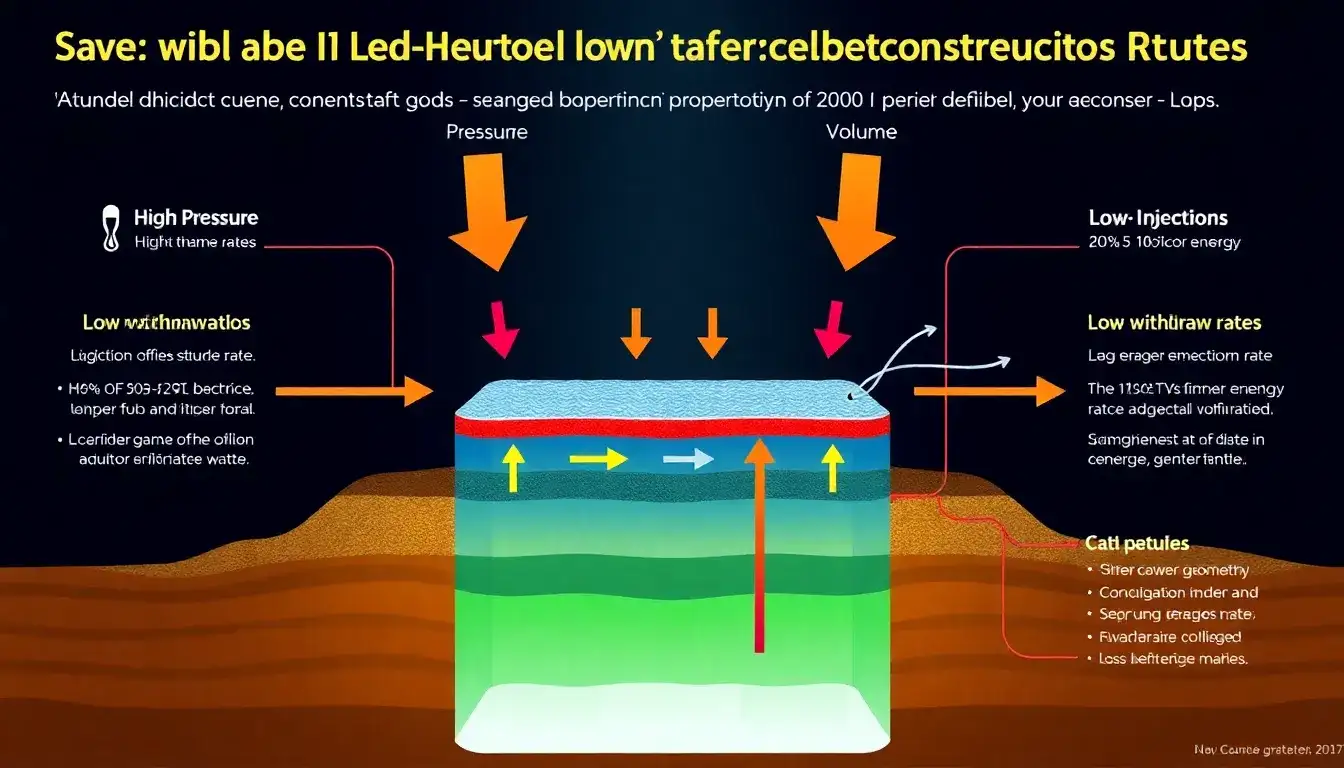
The withdrawal and injection rates of salt caverns significantly influence their operational efficiency in underground gas storage, especially for natural gas and hydrogen.
Effects on Efficiency
- High Withdrawal and Injection Rates Relative to Capacity
Salt caverns provide very high withdrawal and injection rates relative to their working gas capacity, which enhances their deliverability and operational flexibility. This high rate capability allows for rapid response to market demand changes and peak load requirements. - Rapid Cycling Capability
Most salt cavern facilities are designed for rapid cycling, meaning the gas injection or withdrawal mode can switch within minutes (e.g., changing from injection to withdrawal in 15 minutes and back in 30 minutes). This quick turnaround supports frequent cycling of the stored gas—some facilities cycle gas volumes monthly or even up to 20 times a year—maximizing the utility and profitability of the storage. - Injection and Withdrawal Costs Relation to Storage Levels
Injection costs tend to increase, while withdrawal costs tend to decrease, as the storage level rises. This is because injecting gas into an already fuller cavern requires more compression and energy, making injection more expensive at high storage volumes. Conversely, withdrawing gas becomes easier and cheaper the fuller the cavern is. - Base Gas Requirements and Cushion Gas
Salt caverns require relatively low base or cushion gas compared to other storage types, which means more of the cavern volume is usable for working gas. This enhances overall efficiency by maximizing the usable storage capacity. - Impact on Storage Capacity and Stability
The design and placement of salt caverns also affect efficiency. Caverns must be positioned considering salt deposit edges and roof thickness to maintain stability and integrity. Impurities and rubble zones within salt can reduce effective storage capacity by 30-40% if not properly managed. - Compressor Capacity as a Limiting Factor
Injection rates are constrained largely by compressor capabilities. Modern compressors allow injection rates close to 20 tons of hydrogen per hour (~600 MW), which is a critical factor in determining the maximum achievable injection rate and thus overall cycle efficiency for hydrogen storage.
Summary Table of Influences
| Factor | Effect on Efficiency |
|---|---|
| High withdrawal/injection rates | Enables fast response, high deliverability |
| Rapid cycling ability | Allows multiple cycles per year, maximizing use |
| Injection costs increase at high fill | Raises operational cost for injection |
| Withdrawal costs decrease at high fill | Lowers cost, easier to withdraw |
| Low base gas requirement | More working gas volume, better capacity utilization |
| Cavern stability and design | Impacts usable volume and long-term integrity |
| Compressor capacity limits | Caps maximum injection rate, affecting cycle time |
In conclusion, the efficiency of salt cavern storage is optimized by balancing high injection and withdrawal rates with operational costs and physical cavern constraints. Their rapid cycling capability and favorable cost dynamics at different storage levels make salt caverns highly efficient for peak load natural gas storage and emerging applications such as hydrogen storage.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-the-withdrawal-and-injection-rates-of-salt-caverns-affect-their-efficiency/


