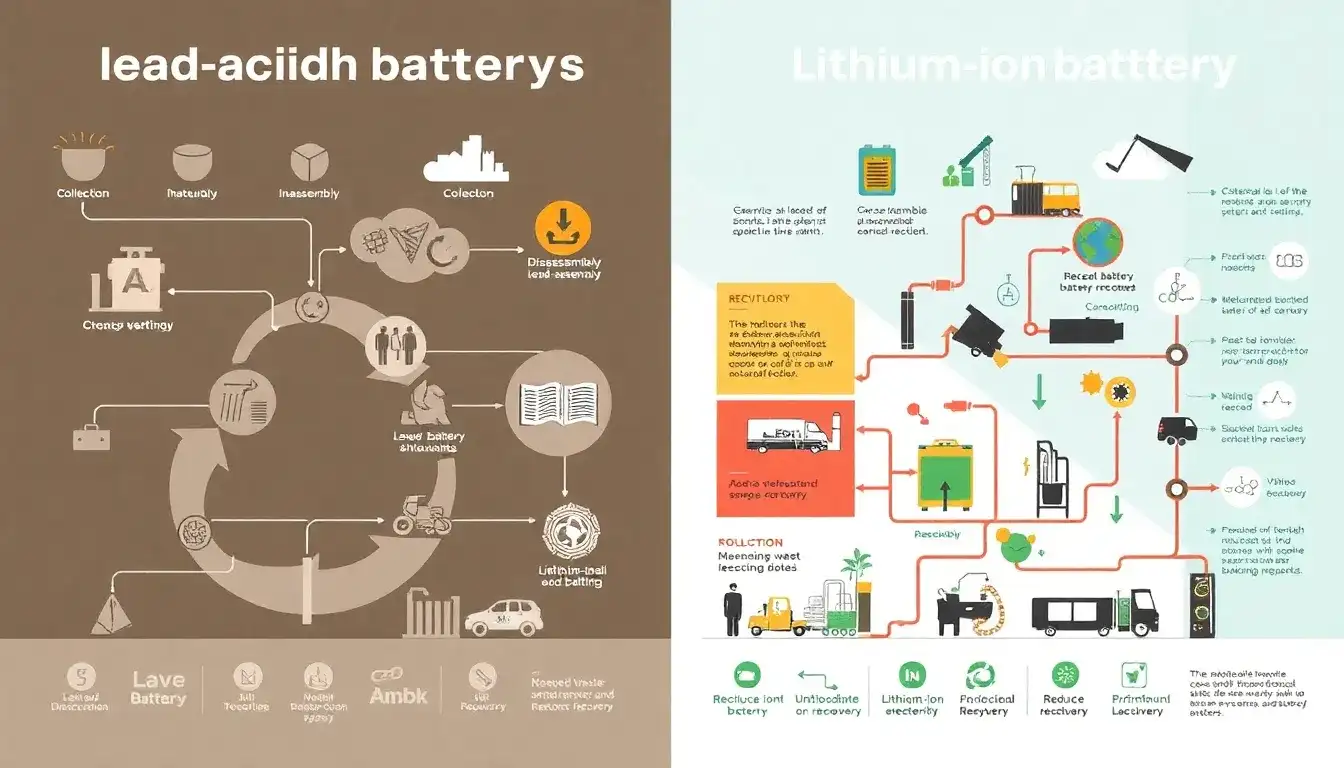
The recycling processes for lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries differ significantly due to their distinct chemistries and constructions. Here’s a comparison of their recycling processes:
Lead-Acid Battery Recycling
Process Steps:
- Collection and Disassembly: Used batteries are collected and transported to recycling facilities. The batteries are disassembled to separate lead from the plastic casing and other components.
- Acid Neutralization: Sulfuric acid is neutralized using a compound like baking soda to convert it into water.
- Crushing and Separation: Batteries are crushed to separate materials. The lead plates are separated from plastic, which is then recycled.
- Smelting: Lead components are melted in a furnace to purify the lead, allowing impurities to float to the surface.
- Reuse: The purified lead is used to manufacture new lead-acid batteries or other products.
Environmental Importance:
Lead-acid battery recycling is crucial for preventing toxic lead release into the environment, conserving resources, and reducing the need for primary lead production.
Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling
Process Steps:
- Collection and Sorting: Used lithium-ion batteries are collected and sorted based on their chemistry and design.
- Disassembly or Shredding: Batteries may be disassembled to extract cells or shredded to reduce size.
- Separation of Components: Cells are separated into their constituent materials, such as lithium, nickel, cobalt, graphite, and steel.
- Materials Extraction: Various methods, including hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical processes, are used to extract valuable metals like lithium and cobalt.
- Reuse: Extracted materials are used to produce new lithium-ion batteries or other products.
Environmental Importance:
Lithium-ion battery recycling is important for recovering valuable resources, reducing waste, and minimizing environmental risks associated with lithium and other heavy metals. However, lithium-ion recycling is still developing and faces challenges in efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to lead-acid recycling.
Differences
- Chemistry and Materials: Lead-acid batteries primarily contain lead, sulfuric acid, and plastic, while lithium-ion batteries contain a variety of metals like lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite.
- Recycling Complexity: Lithium-ion battery recycling is more complex due to the diversity of components and chemistries involved.
- Efficiency and Cost: Lead-acid battery recycling is highly efficient and well-established, whereas lithium-ion recycling is less mature but growing rapidly.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-the-recycling-processes-of-lead-acid-and-lithium-ion-batteries-differ/