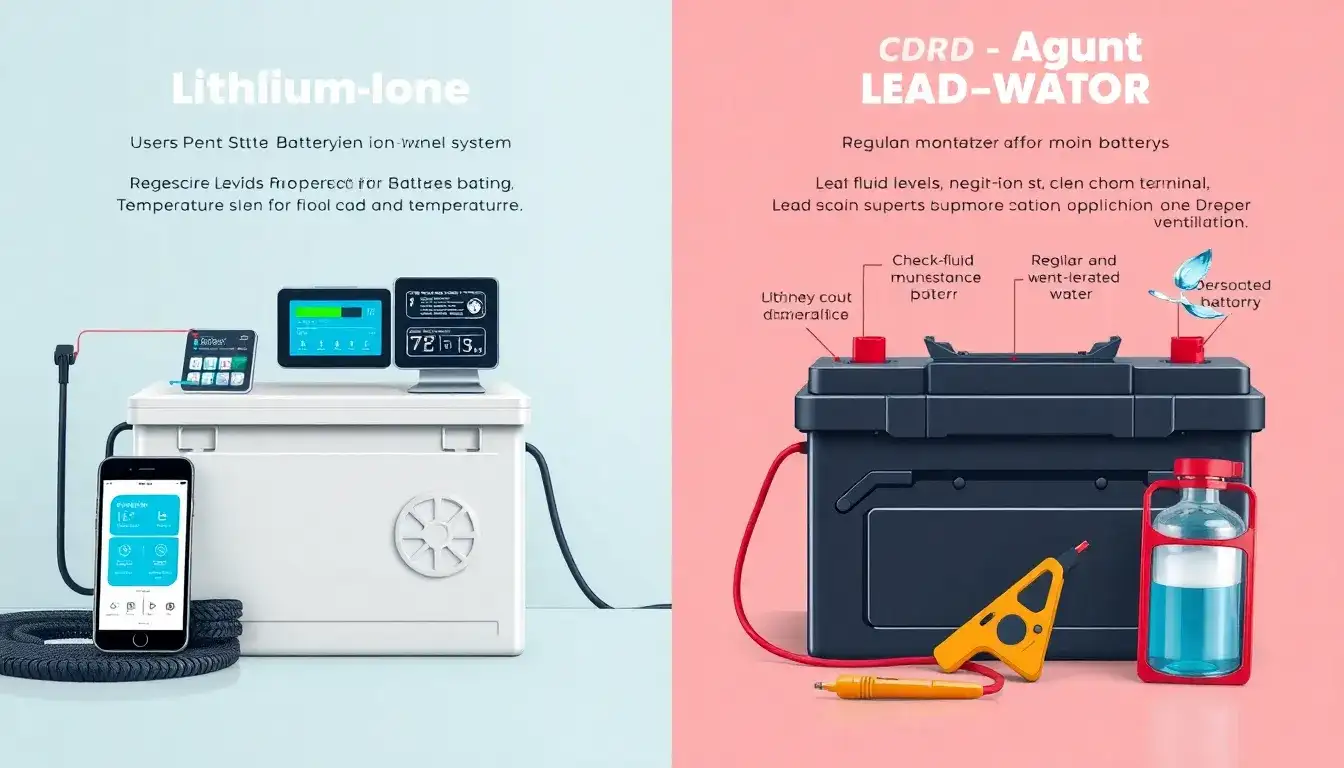
The maintenance requirements of lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries differ significantly in terms of complexity, cost, and operational flexibility. Here is a comparison of their maintenance needs:
Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Maintenance Level: Low maintenance requirements.
- Durability: They can handle high discharge levels (up to 90%) without significant performance degradation and have a longer cycle life (typically 300-500 cycles) compared to lead-acid batteries.
- Usage Conditions: Must be stored in a cool, dry environment and typically at a 40-60% charge level to maintain health.
- Safety Features: Often equipped with a Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging and overheating.
- Handling: Can be used in any orientation, reducing physical handling constraints.
Lead-Acid Batteries
- Maintenance Level: High maintenance requirements, including regular checks on electrolyte levels and physical cleaning of terminals to prevent corrosion.
- Durability: Have a shorter cycle life (typically 1500 cycles with proper maintenance) and can only be discharged to 50-30% without risk of damage.
- Usage Conditions: Must be stored upright to prevent electrolyte leakage and require more space for ventilation.
- Safety Features: No built-in safety features like BMS; can emit harmful fumes during charging.
- Handling: Require specific physical maintenance and handling precautions.
Overall, while lead-acid batteries are initially cheaper, their maintenance costs and environmental impact (e.g., toxic fumes) can make lithium-ion batteries a more cost-effective option over time.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-the-maintenance-requirements-of-lithium-ion-batteries-compare-to-those-of-lead-acid-batteries/


