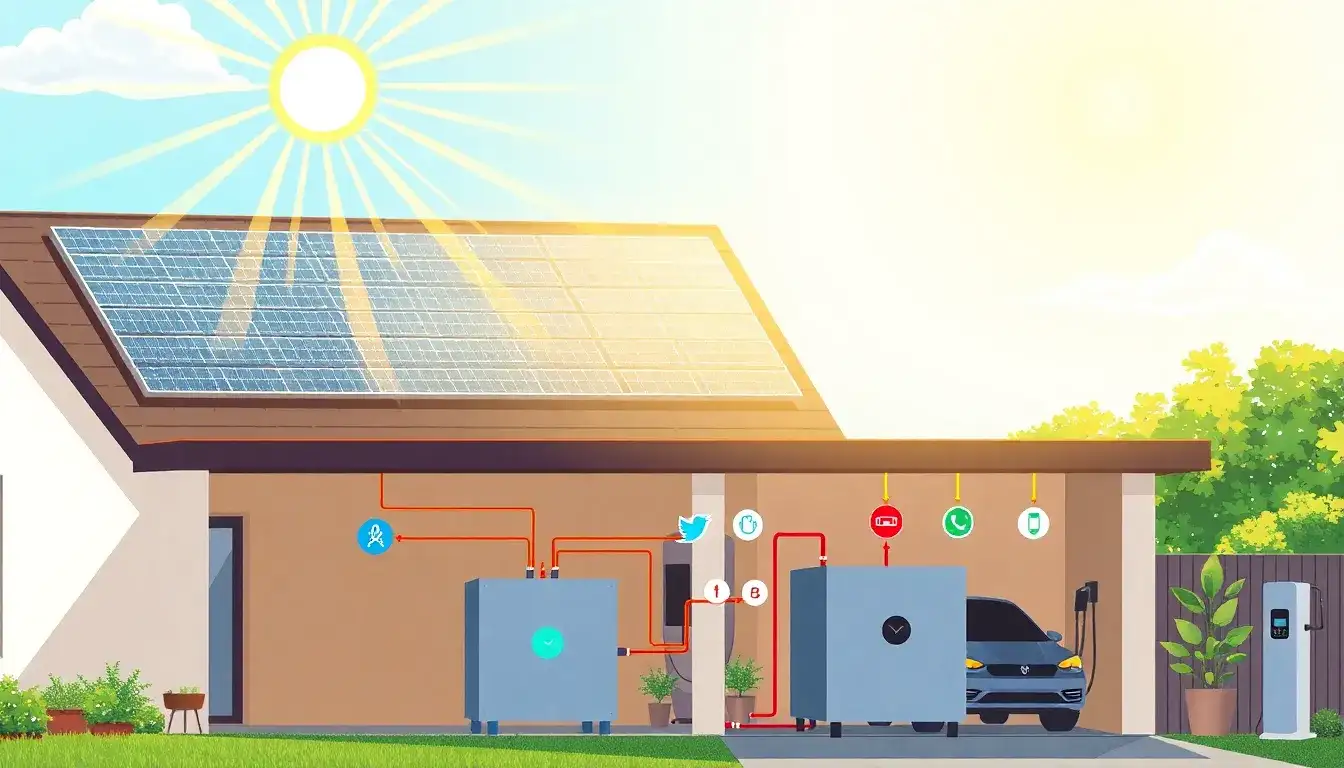
Residential Energy Storage Systems
Residential energy storage systems work in conjunction with solar panels to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during power outages. Here’s how they operate:
Key Components
- Solar Panels: Generate electricity from sunlight during daylight hours.
- Batteries: Typically lithium-ion, these store excess energy for later use.
- Inverter: Converts the direct current (DC) energy stored in batteries into alternating current (AC) power that home appliances can use.
- Control System: Monitors energy production, storage, and consumption, making decisions on when to store or use energy.
Energy Flow Process
- Energy Generation: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity during daylight hours.
- Energy Distribution: This electricity is used to meet immediate home energy needs or is sent to the battery storage system for excess energy.
- Energy Storage: Excess energy is stored in batteries, similar to filling a tank for future use.
- Energy Discharge: At night or during cloudy days, the stored energy is released from batteries to power the home.
Benefits
- Continuous Power Supply: Provides electricity around the clock, regardless of weather conditions.
- Energy Independence: Reduces reliance on the grid and offers backup power during outages.
- Cost Savings: Uses stored energy during peak demand periods, reducing electricity bills.
- Environmental Benefits: Supports greater use of renewable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
By integrating with solar panels, residential energy storage systems enhance the efficiency and reliability of solar energy, making homes more self-sufficient and grid-independent.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-residential-energy-storage-systems-work-with-solar-panels/


