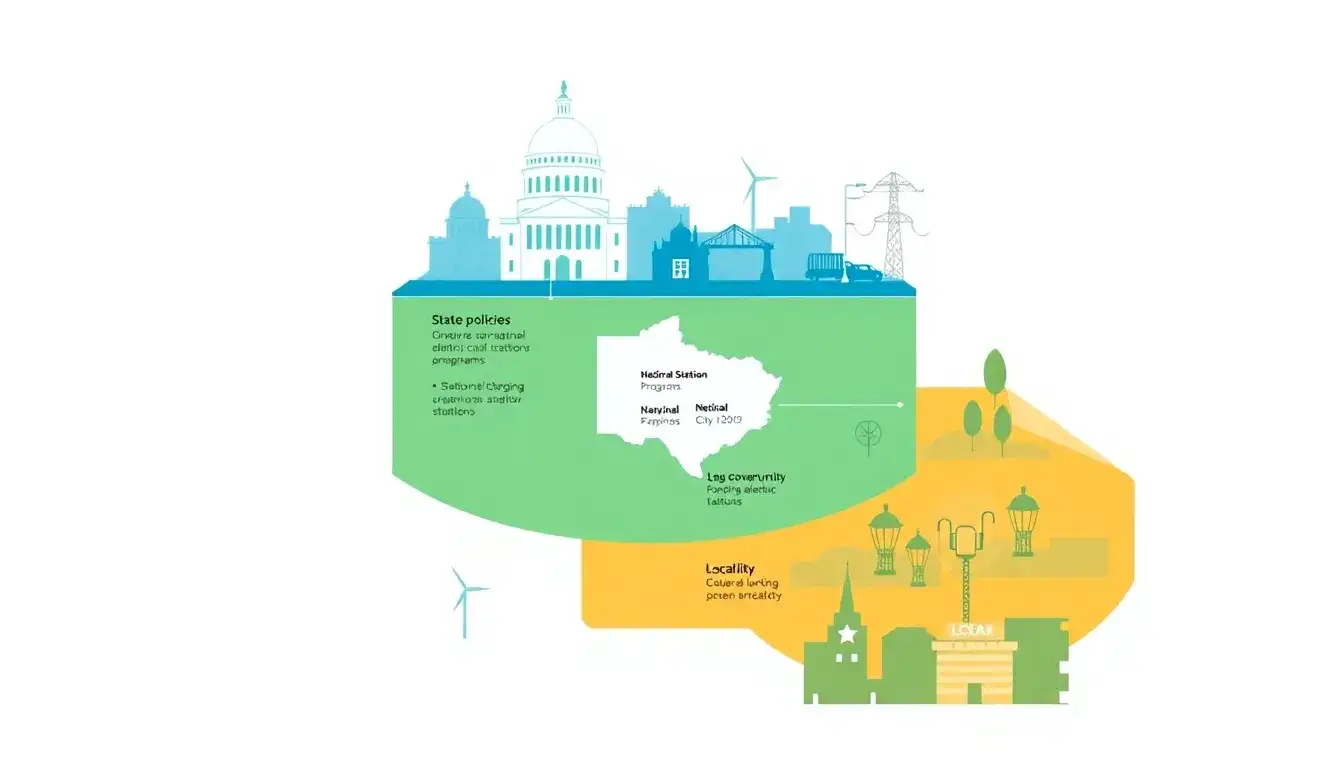
Federal policies on electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure significantly influence state and local initiatives. Here’s a comparison of these levels of policy:
Federal Policies
- National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Program: This program, part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, allocates $5 billion over five years to build a national network of EV charging stations along highways, specifically along Alternative Fuel Corridors (AFCs). It mandates that chargers be non-proprietary and offer open-access payment methods.
- Standards and Requirements: Federal standards require real-time pricing disclosure at charging stations and promote interoperability.
- Funding and Guidance: The federal government provides substantial funding and technical assistance to states through the Joint Office of Energy and Transportation, helping them develop strategic plans for EV infrastructure deployment.
State Policies
- Implementation of Federal Guidelines: States are responsible for implementing federal guidelines, such as ensuring that EV charging stations meet the federal minimum standards and submitting annual plans for the equitable use of NEVI funds.
- Additional State Incentives: Many states offer additional incentives for EV adoption, such as rebates for both EVs and charging infrastructure, and set their own goals for expanding EV charging networks.
- Equity and Public Engagement: States engage in public outreach, including Tribal Governments, to ensure that EV infrastructure development is equitable and meets local needs.
Local Policies
- Zoning and Land Use: Local governments often influence the placement of EV charging stations through zoning regulations and land-use policies, which can either support or hinder the expansion of charging infrastructure.
- Local Incentives: Some municipalities offer local incentives, such as reduced permitting fees or expedited review processes for EV charging installations.
- Community Engagement: Local policies may include community engagement initiatives to educate residents about EV benefits and involve them in the planning process for local EV infrastructure.
In summary, federal policies provide a broad framework and funding for EV charging infrastructure, while state and local policies focus on implementation, equity, and community engagement. Federal guidelines set standards for infrastructure quality and accessibility, while state and local policies can adapt these guidelines to fit regional needs and promote additional local incentives.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-federal-policies-compare-to-state-and-local-policies-in-addressing-ev-charging-infrastructure/


