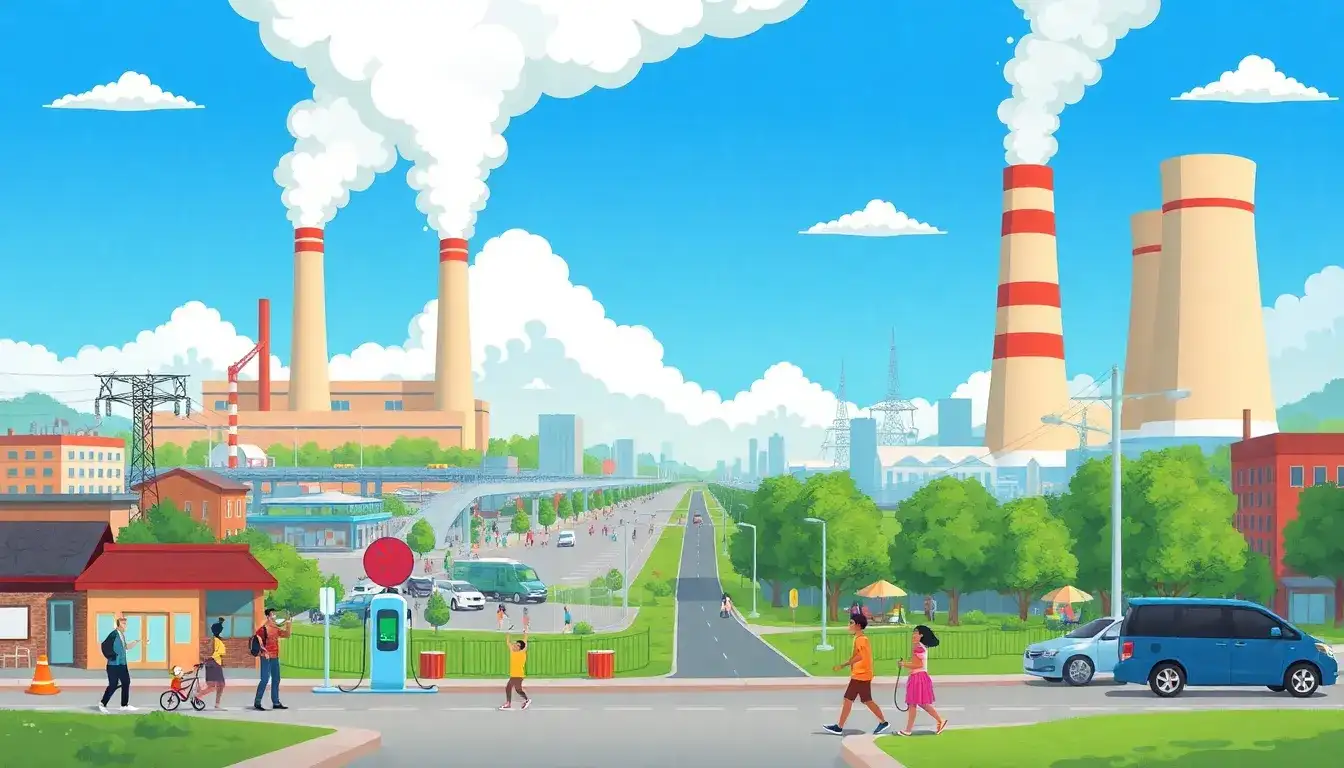
Electric vehicles (EVs) can positively affect health outcomes in states with high coal-fired power plant emissions, but the extent of these benefits depends on the energy mix used to generate their electricity.
Health Impacts of EVs in High Coal Emission States
1. Reduction in Tailpipe Pollution and Air Quality Improvement
EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not emit pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds that are directly harmful to human health. This leads to improved air quality, which is critical in areas with high baseline pollution from coal-fired power plants and conventional vehicles. Improved air quality is associated with fewer respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma, COPD), cardiovascular conditions, and premature deaths.
2. Pollution Shift from Tailpipe to Power Plants (“Long Tailpipe” Effect)
Because EVs rely on electricity, their environmental and health impacts partly depend on how that electricity is generated. In states heavily reliant on coal-fired power plants, the pollution from vehicle emissions is shifted to the power plants generating the electricity used for EV charging. Coal plants emit pollutants that contribute to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases and premature mortality. Hence, in coal-heavy states, while direct tailpipe emissions drop, overall emissions are not eliminated but are relocated to power plants.
3. Net Health Benefit Despite Coal Dependence
Studies show that even when electricity generation is coal-heavy, the overall emissions and associated health impacts from EVs tend to be lower than those from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This is because large power plants usually operate more efficiently than many individual car engines, and electric grids are becoming progressively cleaner with more renewables and less coal use over time. By 2050, widespread EV adoption could save thousands of lives annually and yield billions in health benefits in metropolitan areas.
4. Additional Health Considerations
– EVs are generally heavier than gasoline cars, potentially generating more tire and road dust, which contributes to particulate pollution, though regenerative braking can reduce this effect.
– Some individuals report sensitivity to electromagnetic fields from EVs, but this affects only a small fraction of the population and is mitigated by vehicle shielding.
Summary
In states with high coal-fired power plant emissions, EVs reduce direct vehicle emissions and improve local air quality, benefiting respiratory and cardiovascular health. However, coal-based electricity generation shifts pollutant emissions to power plants, partially offsetting benefits. Nonetheless, the overall health impact of EVs remains favorable because centralized electricity generation is more efficient and is gradually shifting toward cleaner sources. As coal plants are phased out and renewable energy grows, health benefits from EVs in these states will substantially increase.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-evs-affect-health-outcomes-in-states-with-high-coal-fired-power-plant-emissions/