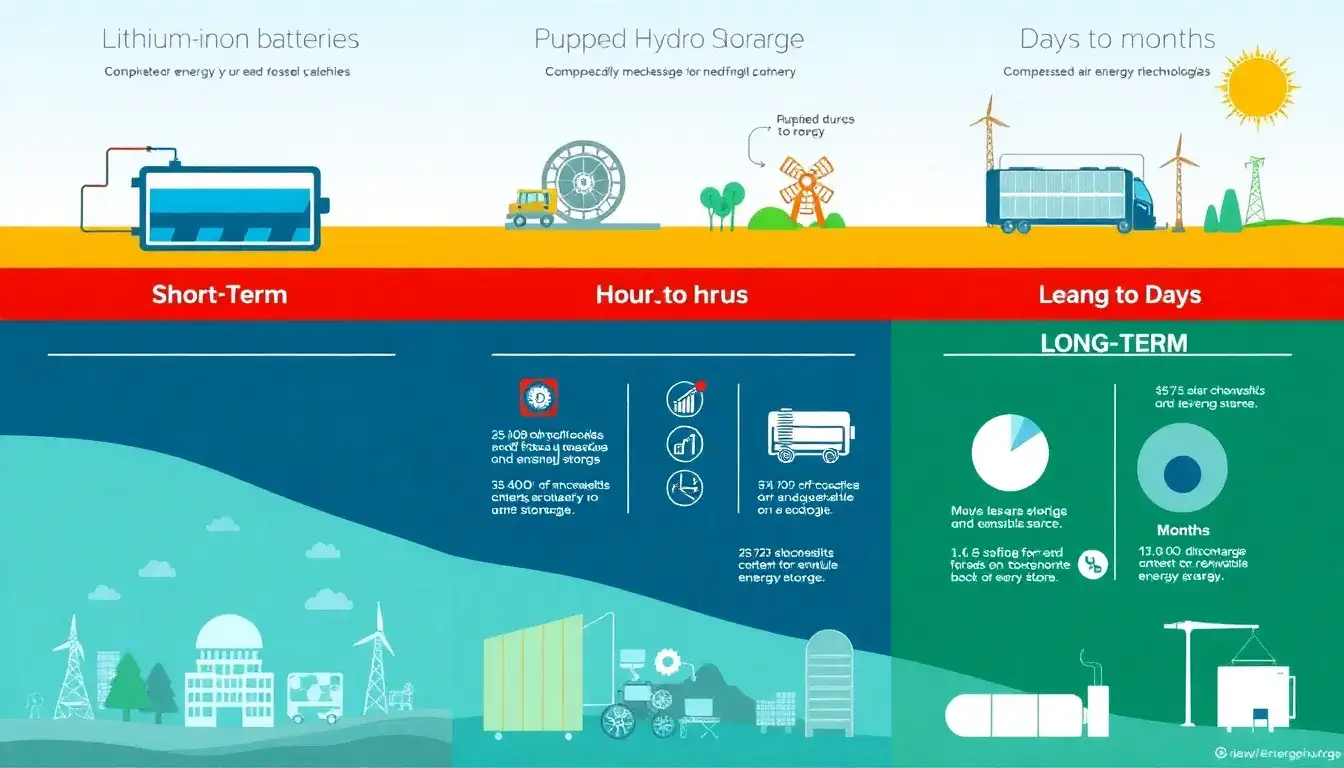
Energy storage technologies vary widely in their performance based on the duration of energy storage. Here’s a breakdown of different technologies and their typical duration capabilities:
Overview of Energy Storage Technologies by Duration
1. Short-Term Energy Storage (SDES)
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are the most prevalent technology for short-term storage, typically providing 1-6 hours of discharge time. They are highly efficient, scalable, and widely used in residential, commercial, and utility settings.
- Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs): While often used for long-term storage, VRFBs can also be effective for short-term energy needs due to their rapid response times and scalability.
- Supercapacitors: Known for their high power density and rapid response time, supercapacitors are useful for instantaneous power applications but have high self-discharge rates.
2. Long-Term Energy Storage (LDES)
- Mechanical Storage:
- Pumped Hydro Storage (PHS): Offers reliable long-duration storage with one of the highest storage capacities and efficiency rates (70-80%), but requires specific geographical conditions.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): Provides several hours of discharge time, suitable for bulk energy management with moderate efficiency (40-70%).
- Thermal Storage: Sensible heat storage can hold energy for extended periods (up to 200 hours), though often with lower efficiency (55-90%).
- Chemical Storage:
- Power-to-Gas (e.g., Hydrogen): Can store energy for days or even weeks, offering scalable solutions for renewable energy, though efficiency is generally lower (40-70%).
- Flow Batteries (e.g., Vanadium Redox): Can store and release energy over several days, with low degradation rates and long lifespans.
Performance Metrics by Duration
| Energy Storage Technology | Typical Duration | Round-Trip Efficiency (RTE) |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | 1-6 hours | High (>95%) |
| Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries | Several hours to days | Good (50-80%) |
| Supercapacitors | Instantaneous | Very High (>95%) but high self-discharge |
| Pumped Hydro Storage | Up to 24 hours | High (70-80%) |
| Compressed Air Storage | Several hours | Moderate (40-70%) |
| Thermal Storage | Up to 200 hours | Varies (55-90%) |
| Power-to-Gas | Days to weeks | Low to Moderate (40-70%) |
Choosing the right technology depends on the specific needs, such as storage duration, available resources, and cost constraints. For short-term applications, lithium-ion and VRFBs are often preferred, while PHS, CAES, and power-to-gas are more suitable for longer durations.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-different-energy-storage-technologies-perform-at-various-duration-levels/


