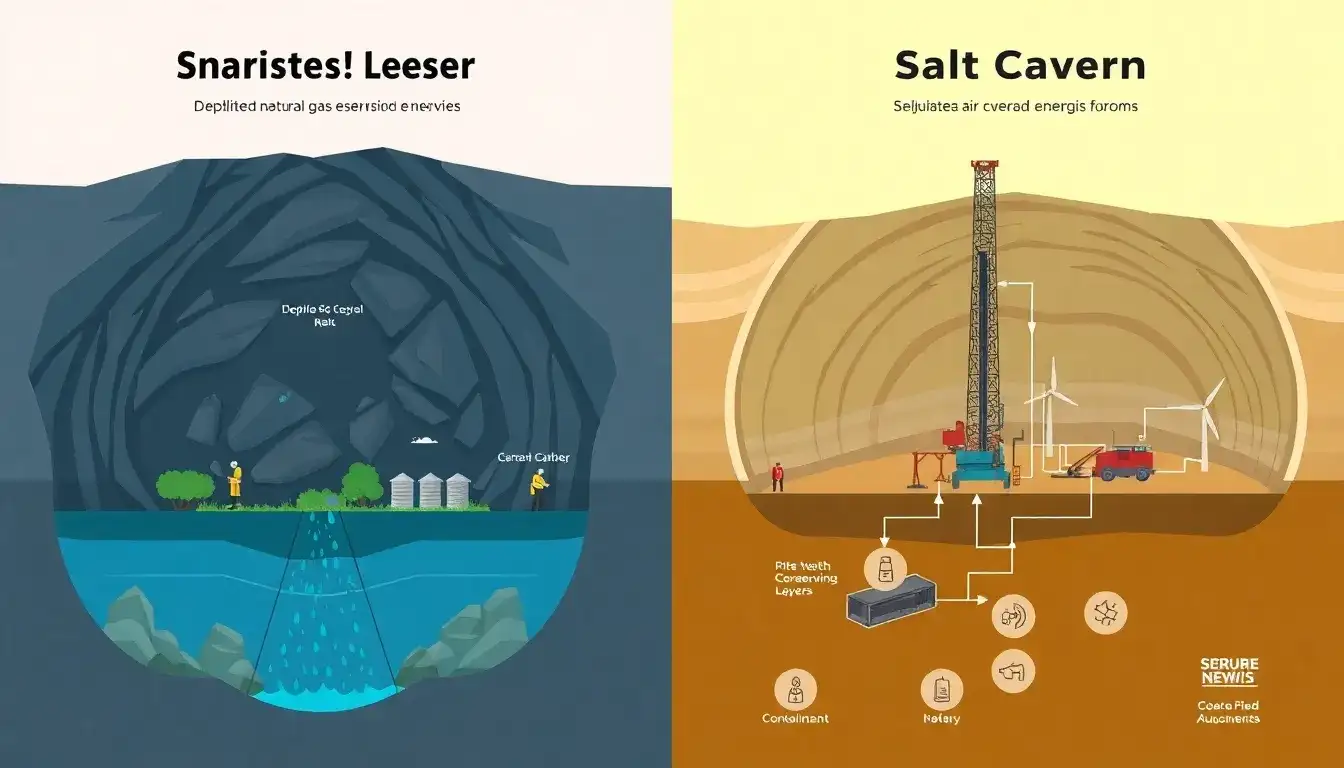
1. Flammability Risks
- Depleted gas reservoirs: Residual natural gas poses flammability concerns when mixed with injected air. Ignition risks exist both within the reservoir (from residual hydrocarbons) and in surface equipment (if gas-contaminated air enters turbines).
- Salt caverns: No residual hydrocarbons, eliminating intrinsic flammability risks during air cycling. Proven operational safety in existing CAES facilities (e.g., Huntorf, McIntosh).
2. Chemical Reactions
- Depleted reservoirs: Stored air reacts with residual methane, connate water, and rock minerals, risking oxygen depletion, corrosion, or spontaneous combustion.
- Salt caverns: Chemically inert salt minimizes reactions with air. Potential brine seepage can be managed through monitoring and well design.
3. Proven Operational History
- Depleted reservoirs: No operational CAES facilities exist yet in such formations. Safety measures (e.g., gas purging, in-situ monitoring) remain theoretical and require site-specific validation.
- Salt caverns: Two commercial CAES plants have operated safely for decades, demonstrating negligible air/rock interaction and stable mechanical behavior.
4. Mitigation Requirements
- Depleted reservoirs require:
- Pre-storage gas purging and air cycling to dilute hydrocarbons below flammability limits.
- Continuous downhole and surface gas monitoring.
- Rigorous combustion controls in turbines to handle variable air-fuel ratios.
- Salt caverns primarily need:
- Routine structural integrity checks.
- Brine management systems.
Key Safety Comparison
| Factor | Depleted Gas Reservoirs | Salt Caverns |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability | High (residual gas) | Low |
| Reactants | Methane, water, rock minerals | Limited (brine interaction) |
| Operational Data | None | Extensive (since 1978) |
| Mitigation Complexity | High (gas monitoring, purging) | Moderate (structural checks) |
While depleted reservoirs offer large-scale storage potential, their unproven safety profile contrasts sharply with the established safety record of salt caverns in CAES applications.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-depleted-natural-gas-reservoirs-compare-to-salt-caverns-in-terms-of-safety-for-caes/


