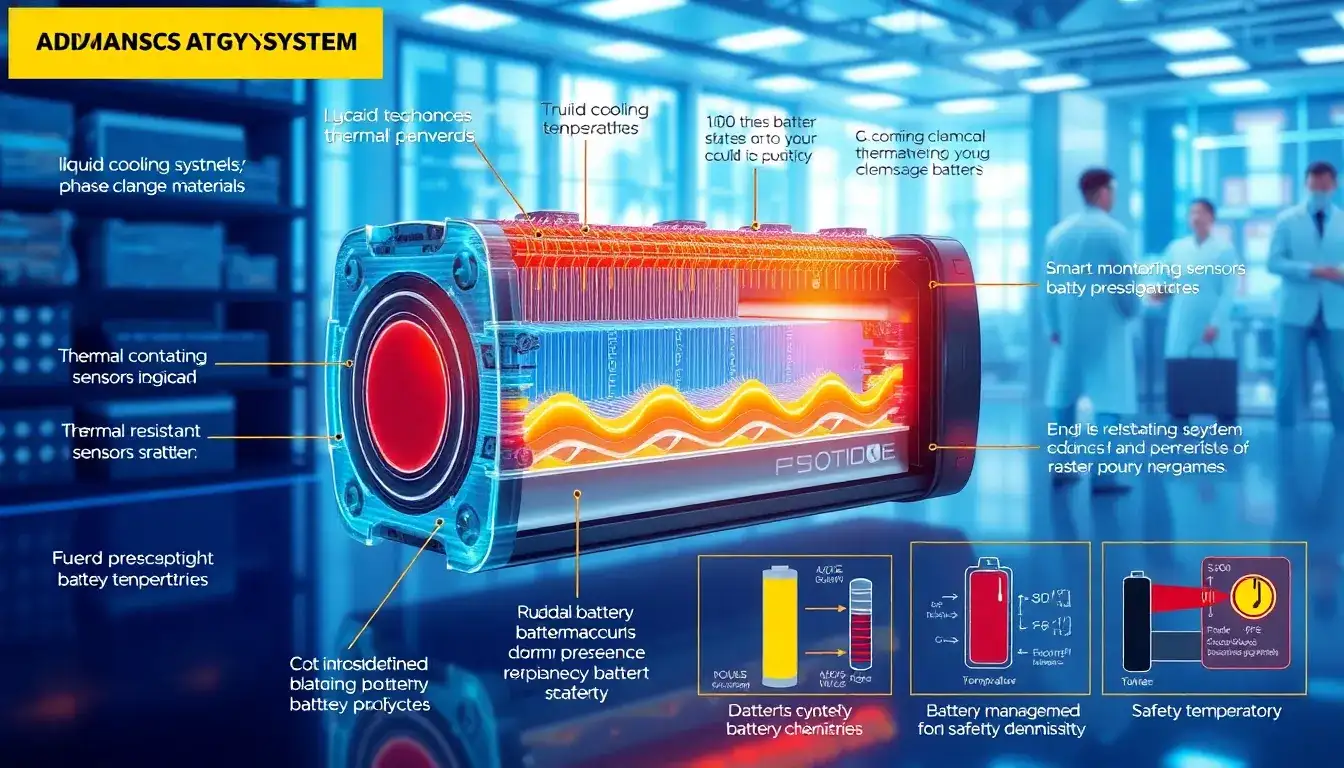
Thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries can be mitigated through a combination of design, monitoring, and containment strategies aimed at preventing the initiation of thermal runaway and stopping its propagation within a battery pack or system.
Key Mitigation Strategies
1. Battery Management Systems (BMS):
A sophisticated BMS is essential for thermal runaway prevention. It continuously monitors critical parameters such as cell-level voltage, current, temperature, and impedance. By detecting abnormal changes—like rapid temperature rises or voltage deviations—it can trigger protective actions such as disconnecting the battery from the load or charger to remove current flow and stop heat generation. This early intervention reduces the chance of thermal runaway initiation and spread.
2. Thermal Barriers and Physical Separation:
Incorporating thermal barriers between individual cells or groups of cells helps contain heat if one cell enters thermal runaway, preventing it from propagating to adjacent cells. These barriers should be made from materials that have high thermal resistance, are non-flammable, and can absorb or dissipate heat effectively. Additionally, designing battery packs with adequate physical spacing or isolation features between cells allows better heat dissipation and reduces the risk of cascading failures.
3. Fire Suppression Systems:
Advanced fire suppression technologies such as NOVEC dry-type gases or fine aerosol fire suppressants can be integrated into battery systems to quickly control and extinguish fires that may result from thermal runaway events, minimizing damage and enhancing safety.
4. Cell Screening and Quality Control:
Rigorous screening and testing of cells before assembly help ensure only cells with stable, defect-free internal components are used. This reduces the probability of initiating thermal runaway due to internal cell failures. Such screening combined with design features that interrupt energy transfer between cells lowers the risk and severity of thermal runaway propagation.
5. Circuit Protection and Current Removal:
Designs that incorporate breakers or fuses to rapidly open the electrical circuit during fault conditions are crucial. When a thermal runaway event is detected or suspected, quickly removing current flow reduces additional heating and helps contain the event.
6. Regular Preventative Maintenance:
For systems like VRLA batteries and by extension applicable in lithium-ion systems, regular inspections and maintenance are recommended to check battery health and ensure protective systems are functional.
Summary Table
| Mitigation Technique | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Battery Management System (BMS) | Real-time monitoring at cell level, automatic disconnection | Early detection and prevention |
| Thermal Barriers | Heat-resistant, non-flammable materials between cells | Contain heat, prevent propagation |
| Physical Separation | Spacing/isolation of cells within pack | Reduce heat transfer between cells |
| Fire Suppression Systems | Use of specialized fire suppressants (e.g., NOVEC gas) | Extinguish fires from thermal events |
| Cell Screening and Quality Control | Testing cells for defects before assembly | Prevent initial cell failures |
| Circuit Protection Devices | Breakers/fuses to open circuits on fault | Stop current flow, limit damage |
| Preventative Maintenance | Regular inspection and system checks | Ensure ongoing system reliability |
These combined approaches address both the prevention of thermal runaway initiation and the containment of its effects to improve safety and reliability of lithium-ion batteries.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-can-thermal-runaway-in-lithium-ion-batteries-be-mitigated/


