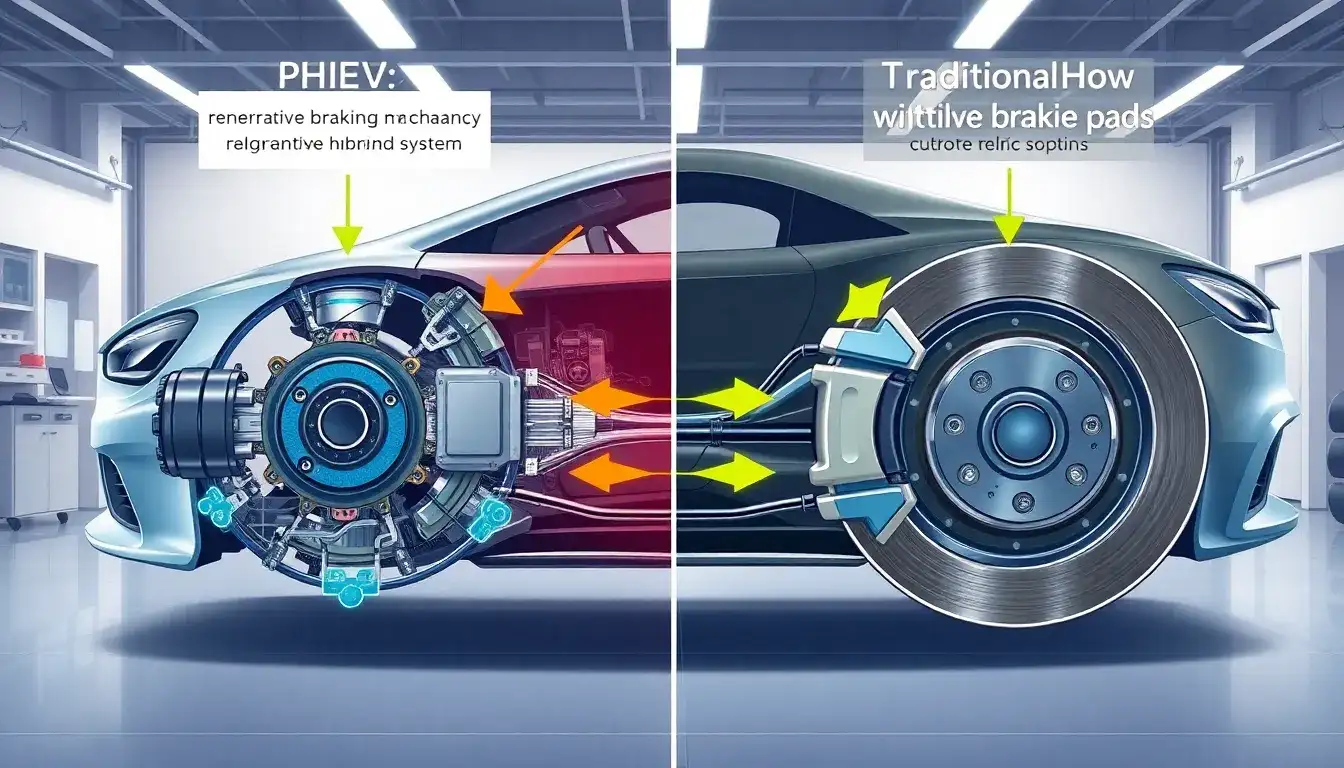
PHEVs (Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles) share similar brake pad requirements to traditional vehicles in terms of material composition (semi-metallic, low-metallic, ceramic), but face unique performance demands due to their design:
- Same pad types: Most PHEVs use conventional brake pads, avoiding the need for specialized replacements.
- Reduced wear: Regenerative braking systems recover kinetic energy, significantly reducing friction-based braking usage. This can extend pad lifespan up to ~70,000 miles in some cases.
- Increased stress factors:
- Weight: Battery packs add 300-1,000+ lbs compared to non-hybrids, requiring pads with higher heat resistance.
- Corrosion risk: Less frequent friction braking in urban driving may lead to rust buildup on rotors, emphasizing the need for durable pad compounds.
- Specialized options: Some manufacturers (e.g., Jurid) now offer EV/Hybrid-optimized pads with enhanced corrosion resistance, reduced noise, and faster stopping performance despite infrequent use.
Key difference: While not requiring distinct pad types, higher-quality pads engineered for electric/hybrid vehicle loads and usage patterns often improve performance and longevity. Mechanics recommend inspecting PHEV brake systems annually due to atypical wear patterns.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/do-phevs-require-different-brake-pads-compared-to-traditional-vehicles/