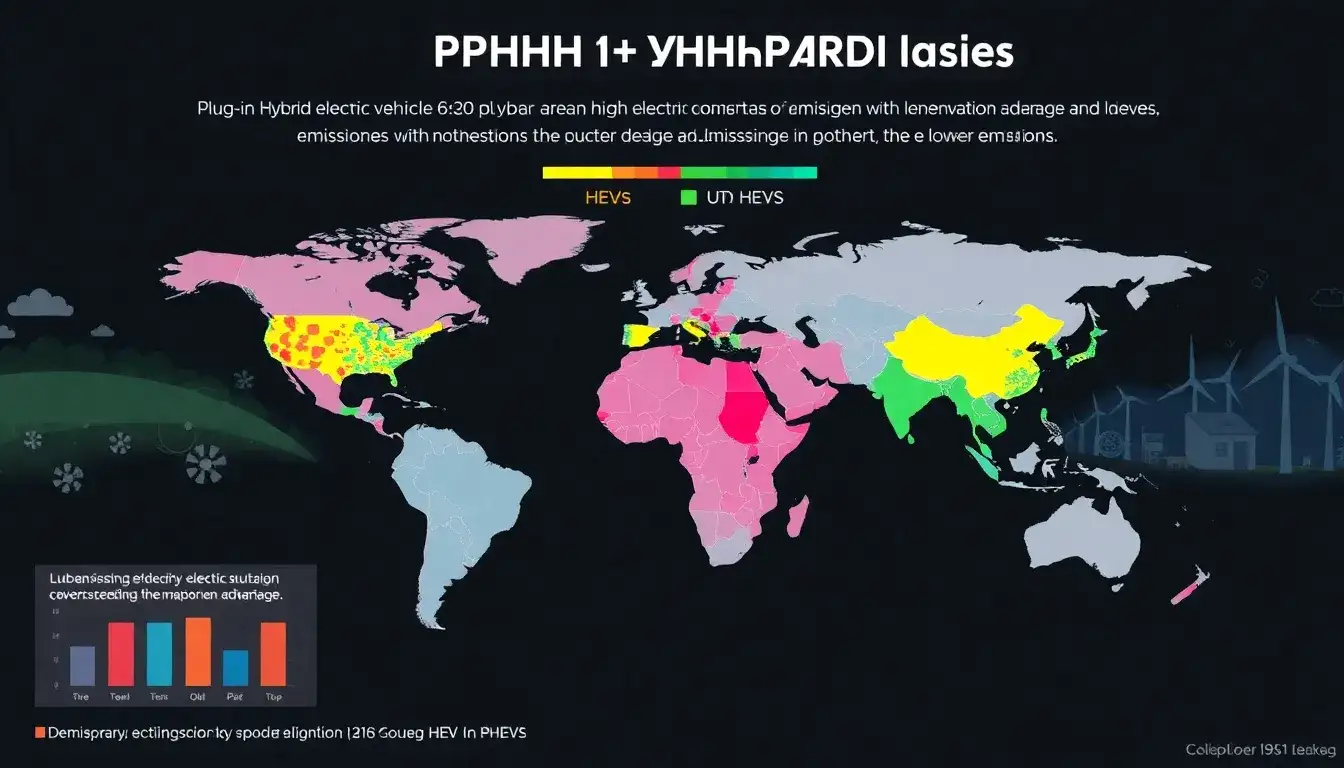
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) vs. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Emissions Advantage
PHEVs can offer a significant emissions advantage over HEVs in certain regions, depending on several factors:
- Grid Emissions: The advantage of PHEVs over HEVs is more pronounced in regions with cleaner electricity grids. In areas with high renewable energy sources like hydro or solar, PHEVs can provide substantial emissions reductions due to their ability to use grid electricity for a significant portion of their operation.
- Utility Factor: The emissions advantage of PHEVs is also contingent on their utility factor, which is the proportion of miles driven using electricity. If the utility factor is high, PHEVs can achieve greater emissions savings compared to HEVs.
- Battery Size and Resource Use: PHEVs generally have smaller batteries than full electric vehicles (BEVs), which can reduce emissions associated with battery production. This smaller size can contribute to an emissions advantage when compared to HEVs in terms of lifecycle emissions.
- Regional Considerations: In regions like the Midwest where the grid is predominantly powered by coal, PHEVs may not always have an emissions advantage. However, in cleaner energy regions, the PHEV’s ability to utilize grid power can significantly reduce emissions compared to HEVs.
Overall, PHEVs tend to offer a better emissions profile than HEVs in regions where the grid is transitioning to cleaner energy sources and where the utility factor of PHEVs is optimized. However, the exact advantage can vary based on local energy mix and usage patterns.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/are-there-specific-regions-where-phevs-have-a-significant-emissions-advantage-over-hevs/


