The introduction of an artificial intelligence welding robot is set to take place at the Philadelphia shipyard, a symbol of the initiative to “Make American Shipbuilding Great Again.” This development was reported on February 19, 2026, following a recent visit to the Hanwha Ocean Gyeongju plant in South Korea.
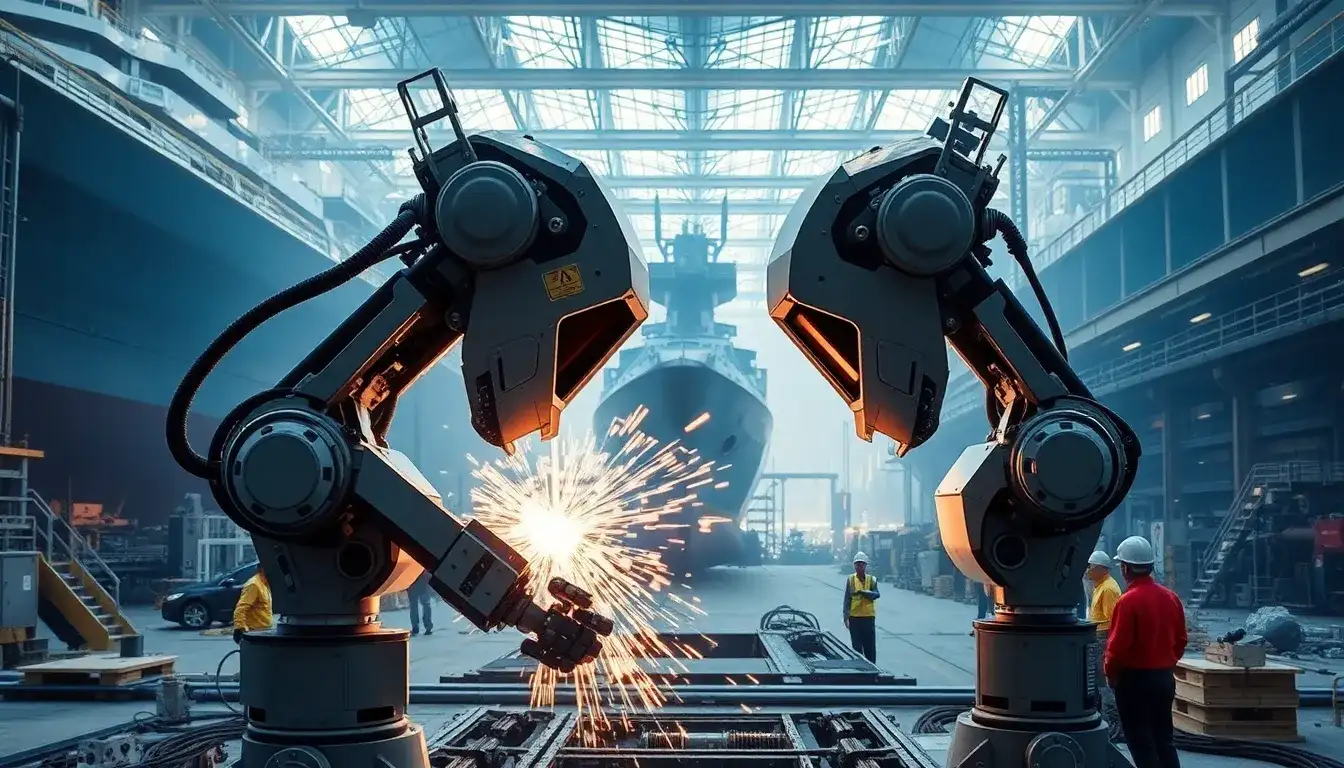
Inside the ship assembly facility, a 17-kilogram mobile welding robot named “Londi” was seen emitting electric sparks. The temperature of these sparks reaches an impressive 5,000 degrees Celsius, comparable to the surface of the sun, allowing it to seamlessly join thick steel plates.
While the welding robot continues its operation amidst the sparks, human workers are primarily tasked with supervising the robot. Kim Tae-keun, the head of the Smart Production Promotion Team at Hanwha Ocean, stated, “In shipyards, the role of workers is shifting from direct spark welding to that of ‘operators’ who manage and instruct the robots. By allowing robots to handle repetitive and hazardous tasks, we are improving the working conditions for our employees, and the robots can operate 24/7, increasing productivity by more than double.”
Hanwha Ocean is advancing automation in shipbuilding centered around the Gyeongju shipyard, aiming to address challenges posed by an aging skilled workforce and to prevent potential musculoskeletal disorders among workers. Currently, the indoor welding automation rate at Hanwha Ocean stands at approximately 67%, with a goal of achieving 100% automation in welding by 2030. The automation rate for pre-treatment painting will increase to 50%, while cable installation will rise to 60%.
The robot being utilized at the Gyeongju plant is expected to be introduced to the U.S. shipbuilding collaboration project, which aims to symbolize the revitalization of American shipbuilding at the Philadelphia shipyard by the end of 2027. This robot is capable of welding steel plates in tight spaces that are difficult for humans to access. It is rated to have the proficiency of a skilled welder with three years of experience.
Hanwha Ocean plans to gradually introduce smart robots in line with the expansion and modernization schedule of the Philadelphia shipyard. Notably, tasks that previously required workers to take risks, such as measuring a ship’s draft (the depth to which a ship is submerged), have been fully automated. Previously, three to four workers would navigate small boats in rough seas to measure the draft, posing significant safety risks. Now, drones capture images of the ship, and visual AI measures the draft, reducing the time required for this task from two hours to less than 30 minutes, eliminating the need for workers to climb onto hazardous waves.
Hanwha Ocean’s ultimate objective is to integrate artificial intelligence and robotics to address labor shortages and create a safer “smart shipyard.” This approach will not only replace hazardous tasks with physical AI but also maintain a certain level of operational quality even when less skilled workers are introduced to the site, thus tackling the issue of an aging skilled workforce. Representatives from Hanwha Ocean anticipate that by enhancing the intelligence of robots in the workplace and digitizing the work patterns and standards of skilled workers, AI will be able to assist in evaluating engineering, quality, and safety.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/ai-welding-robots-set-to-transform-philadelphia-shipyard-and-reinforce-u-s-shipbuilding-industry/


