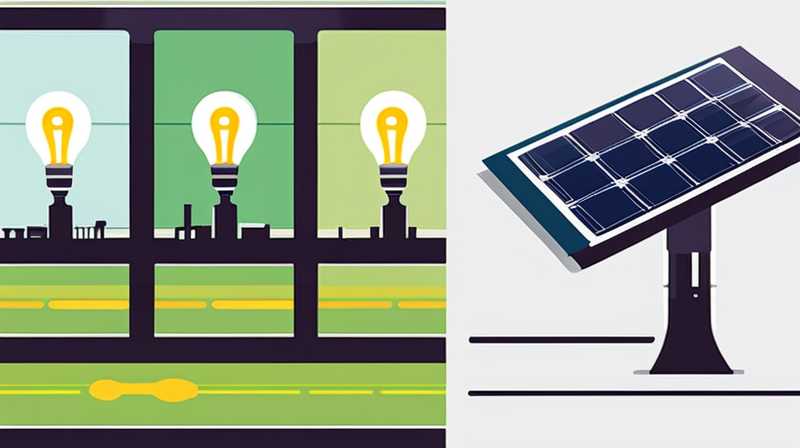
Solar panels function by converting sunlight into electrical energy, which can then be utilized to power various electrical devices, including light bulbs. 1. Solar panels harness the sun’s energy, 2. They convert sunlight into usable electricity, 3. This electricity powers light bulbs through a consistent energy supply, 4. The entire process requires minimal environmental impact. The detailed conversion process involves several steps, beginning with the absorption of sunlight by photovoltaic (PV) cells within the solar panels. These cells contain semiconductor materials, most commonly silicon, that facilitate the flow of electric current once light is absorbed. This current is then transmitted through wiring to light fixtures, illuminating bulbs with efficiency.
1. UNDERSTANDING SOLAR PANELS
Solar panels are sophisticated devices designed for the purpose of collecting sunlight and converting it into electrical energy. The technology relies on the principles of the photovoltaic effect, where certain materials can generate an electric charge when exposed to light. At their core, solar panels consist of multiple solar cells arranged in a grid-like structure, usually encased in protective glass to shield them from environmental elements. The primary material employed in solar cells is silicon, which works efficiently due to its ability to absorb photons and release electrons.
The effectiveness of solar panels can greatly depend on their design and placement. Factors such as the angle of inclination, orientation towards the sun, and geographic location can influence their performance. To optimize energy capture, systems often incorporate tracking devices that adjust the panel position in relation to the sun’s movement across the sky. This optimization not only increases efficiency but also maximizes the energy output, ensuring a consistent supply.
2. HOW SOLAR ENERGY IS CONVERTED TO ELECTRICITY
Once sunlight is captured, the next phase involves its conversion into electricity. This process begins within the solar cells, where photons knock electrons loose from their atomic bonds. This creates an electrical current that can flow due to the semiconductor’s unique properties. Within each solar cell, a built-in electric field directs these free electrons towards conductive metal plates, facilitating their movement out of the solar cell and into an external circuit.
The electricity generated is typically in direct current (DC) form. However, most household appliances, including light bulbs, operate on alternating current (AC). To convert DC to AC, an inverter is employed. This essential component transforms the direct current to an alternating current compatible with home electrical systems. The inverter plays a dual role: it ensures the produced electricity is usable and monitors the system’s performance, optimizing energy output.
3. THE ROLE OF ELECTRICITY IN POWERING LIGHT BULBS
Once electrical energy has been converted to the proper form, it can be channeled to power light bulbs. Light bulbs operate through different mechanisms, yet they all require a continuous flow of electricity to produce light. Traditional incandescent bulbs generate light by passing an electric current through a filament, which in turn heats up and produces light. Alternatively, compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) employ different methods to generate light but still depend on a reliable source of electrical power.
The integration of solar panels into a household’s energy system offers several benefits. With a self-sustaining power source, homeowners can significantly reduce their reliance on the grid. Not only does this lower electricity bills, but it also contributes to their overall energy independence. Moreover, utilizing solar energy for lighting enables users to decrease their carbon footprint, as this renewable energy source emits no greenhouse gases during operation.
4. ADVANTAGES OF USING SOLAR ENERGY FOR LIGHTING
Opting for solar energy to power light bulbs provides myriad advantages. Cost-effectiveness is one significant factor. After the initial investment in solar panels and related equipment, homeowners can enjoy reduced or eliminated electricity bills. Additionally, solar energy systems may lead to increased property value, as homes equipped with renewable energy sources are often more desirable in today’s eco-conscious market.
Environmental benefits are another crucial consideration. By shifting to solar energy, users contribute to reducing fossil fuel reliance, thus decreasing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The transition promotes sustainable practices that are pivotal in combating climate change and preserving natural ecosystems. Through the adoption of solar power for lighting, individuals not only fulfill their own energy needs but also partake in a larger movement towards environmental sustainability.
FAQS
HOW LONG DO SOLAR PANELS LAST?
Solar panels are designed with longevity in mind, with most manufacturers providing warranties ranging from 20 to 25 years. However, with proper maintenance and care, these systems can often perform efficiently for 30 years or more. The degradation rate – which is the gradual loss of energy efficiency over time – is relatively low, typically around 0.5% to 1% per year. After 20-25 years, solar panels can still produce a substantial portion of their original output. Regular inspections and cleaning can greatly extend their life and efficiency, ensuring maximum energy production over the years.
WHAT MAINTENANCE DO SOLAR PANELS REQUIRE?
Maintaining solar panels is crucial for preserving their efficiency and longevity. Routine maintenance is relatively minimal compared to traditional energy systems. Basic care involves regular cleaning to remove dust, debris, and snow from the surface, as dirty panels can significantly decrease energy production. In addition, an annual inspection by a professional can identify and address any potential issues, such as wiring problems or component failures, before they lead to significant power loss or costly repairs. Monitoring the output through an inverter can aid users in detecting problems early, allowing proactive maintenance.
HOW DO WEATHER CONDITIONS AFFECT SOLAR ENERGY PRODUCTION?
Weather conditions can greatly influence solar energy production, with factors such as cloud cover, rain, and snow impacting the system’s output. While solar panels can still generate electricity on cloudy days, production may decrease by 10-25%. Additionally, seasonal changes can affect sunlight availability; winters may result in reduced output while summers can yield higher energy generation. However, advancements in solar technology, such as bifacial panels that capture sunlight from all angles, and the use of batteries for energy storage, mitigate these challenges, ensuring a consistent supply of energy throughout the year.
Leveraging solar energy to illuminate light bulbs showcases the transformative potential of renewable energy sources. The process begins with harnessing sunlight through solar panels, which convert it into a usable electrical form. This electricity is then utilized to power various lighting solutions in residential and commercial spaces. Not only does this approach offer substantial savings on energy costs, but it also promotes sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Moreover, the long lifespan of solar panels, combined with minimal maintenance needs, makes them an attractive option for homeowners and businesses alike. Embracing solar power for lighting fundamentally shifts how we think about energy consumption, paving the way for a greener future. By understanding how solar panels function to light up our world, we empower ourselves with the knowledge necessary to engage with sustainable energy practices, fostering a holistic approach to environmental stewardship.
Original article by NenPower, If reposted, please credit the source: https://nenpower.com/blog/how-do-solar-panels-make-light-bulbs-light-up/


